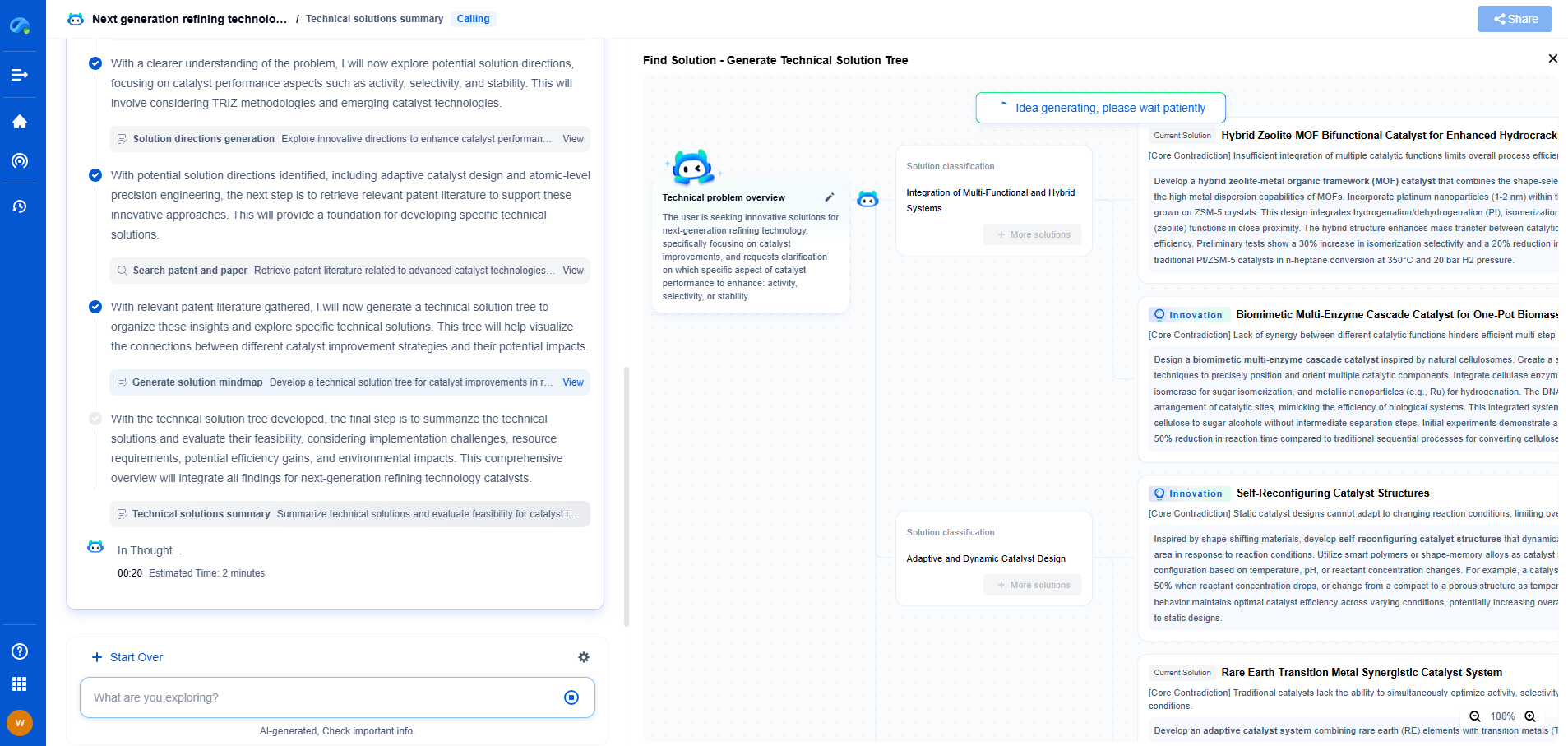
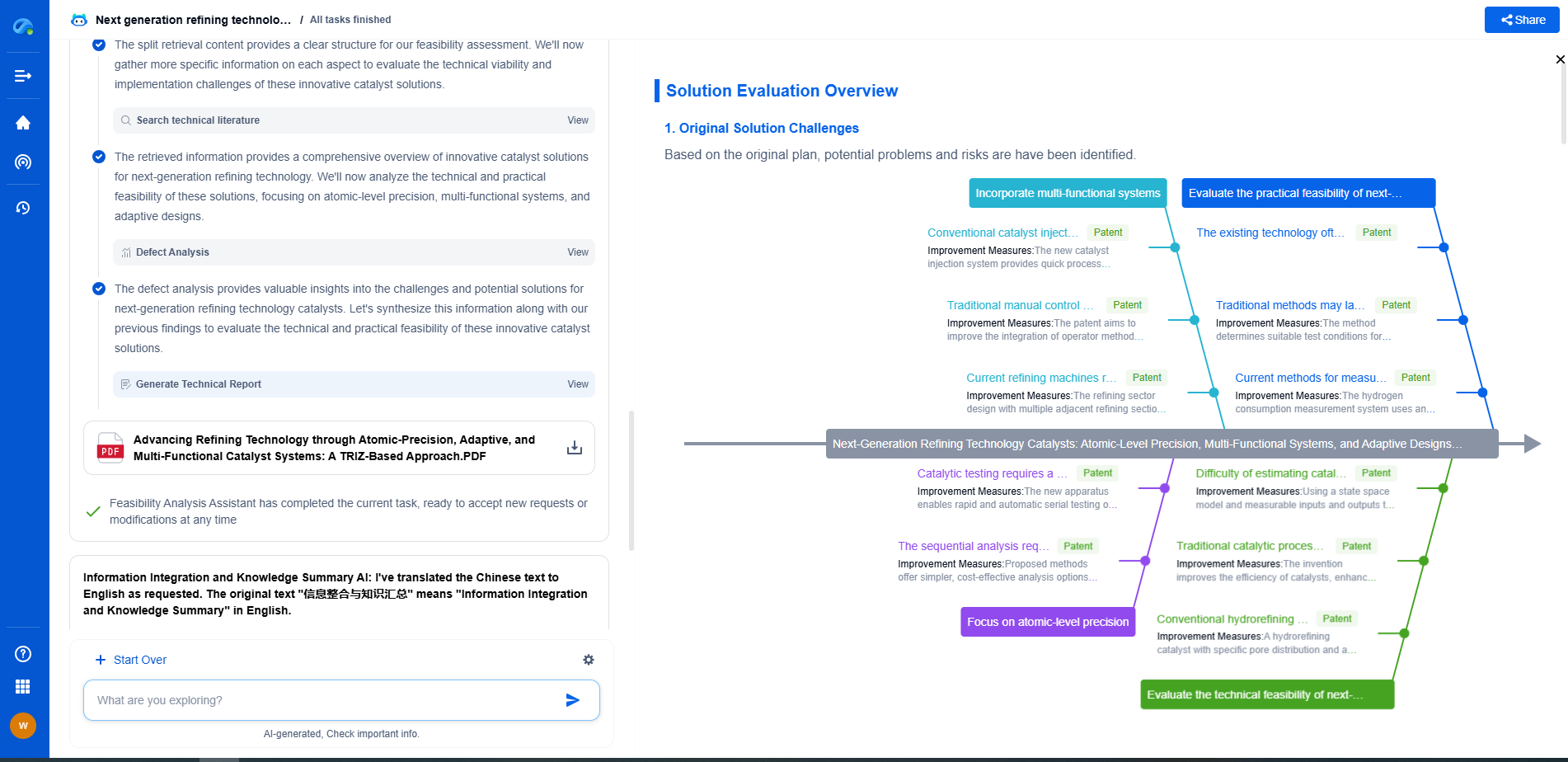
An Introduction to Face Recognition: Algorithms, Accuracy, and Ethics
JUL 10, 2025 |
Face recognition technology has rapidly evolved over the past few decades, becoming a pivotal part of various sectors such as security, social media, and customer service. At its core, face recognition is a biometric technology that identifies or verifies a person by analyzing and comparing patterns based on the facial features of an individual.
How Face Recognition Algorithms Work
The process of face recognition typically involves several stages, each utilizing sophisticated algorithms to ensure accuracy:
1. **Detection**: The first step is detecting a face within an image or video. This is usually achieved through algorithms that scan for human facial features like the eyes, nose, and mouth. Technologies such as the Viola-Jones object detection framework are commonly used for this task due to their speed and accuracy.
2. **Alignment**: Once a face is detected, the next step is to align it properly. This involves compensating for changes in pose, scale, or rotation that might affect the recognition process. Techniques such as facial landmark estimation help in aligning the face by identifying key points on the face.
3. **Feature Extraction**: In this stage, distinctive features from the aligned face are extracted. Deep learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), are extensively used to identify unique features that distinguish one face from another.
4. **Matching**: The extracted features are then compared against a database of known faces. If the features match a profile in the database, the identity of the face is verified or identified. This matching process often involves sophisticated algorithms that measure the similarity between feature vectors.
Assessing the Accuracy of Face Recognition Systems
The accuracy of face recognition systems is a critical aspect that determines their effectiveness. Several factors can influence accuracy, including:
- **Lighting Conditions**: Variations in lighting can significantly affect the accuracy of face recognition systems. Algorithms need to be robust enough to handle changes in illumination, shadows, and reflections.
- **Pose Variation**: Faces are three-dimensional and can appear very different when viewed from different angles. Advanced face recognition systems can account for these variations to improve accuracy.
- **Expression Changes**: Facial expressions can alter the appearance of a face. High-accuracy systems can recognize faces despite changes in expression.
- **Aging and Disguise**: Over time, a person’s appearance can change due to aging or intentional disguises. Robust systems use temporal changes and adapt their models to maintain accuracy.
The Role of Ethics in Face Recognition
As face recognition technology becomes more prevalent, ethical considerations have come to the forefront. The potential for misuse and privacy violations is a significant concern. Here are some key ethical issues:
- **Privacy Concerns**: The deployment of face recognition in public spaces raises questions about surveillance and the right to privacy. There is an ongoing debate about how much personal data should be collected and how it is used.
- **Bias and Fairness**: Studies have shown that some face recognition systems exhibit biases, particularly against certain racial and gender groups. Ensuring fairness and eliminating bias in algorithm training data is essential.
- **Consent and Transparency**: Individuals should have the right to know when and how their biometric data is being collected and used. Transparent policies are necessary to build trust and ensure consent.
- **Security Threats**: Face recognition systems can be vulnerable to spoofing attacks, where an image or video is used to impersonate someone. Developing robust security measures is crucial to prevent such threats.
Conclusion: Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
Face recognition technology offers incredible potential and convenience but also presents significant challenges in terms of accuracy and ethics. As this technology continues to develop, balancing innovation with responsibility is essential. Policymakers, developers, and society must work together to ensure that face recognition systems are accurate, fair, and ethical, protecting individuals’ rights while enabling technological progress.
Image processing technologies—from semantic segmentation to photorealistic rendering—are driving the next generation of intelligent systems. For IP analysts and innovation scouts, identifying novel ideas before they go mainstream is essential.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
🎯 Try Patsnap Eureka now to explore the next wave of breakthroughs in image processing, before anyone else does.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com