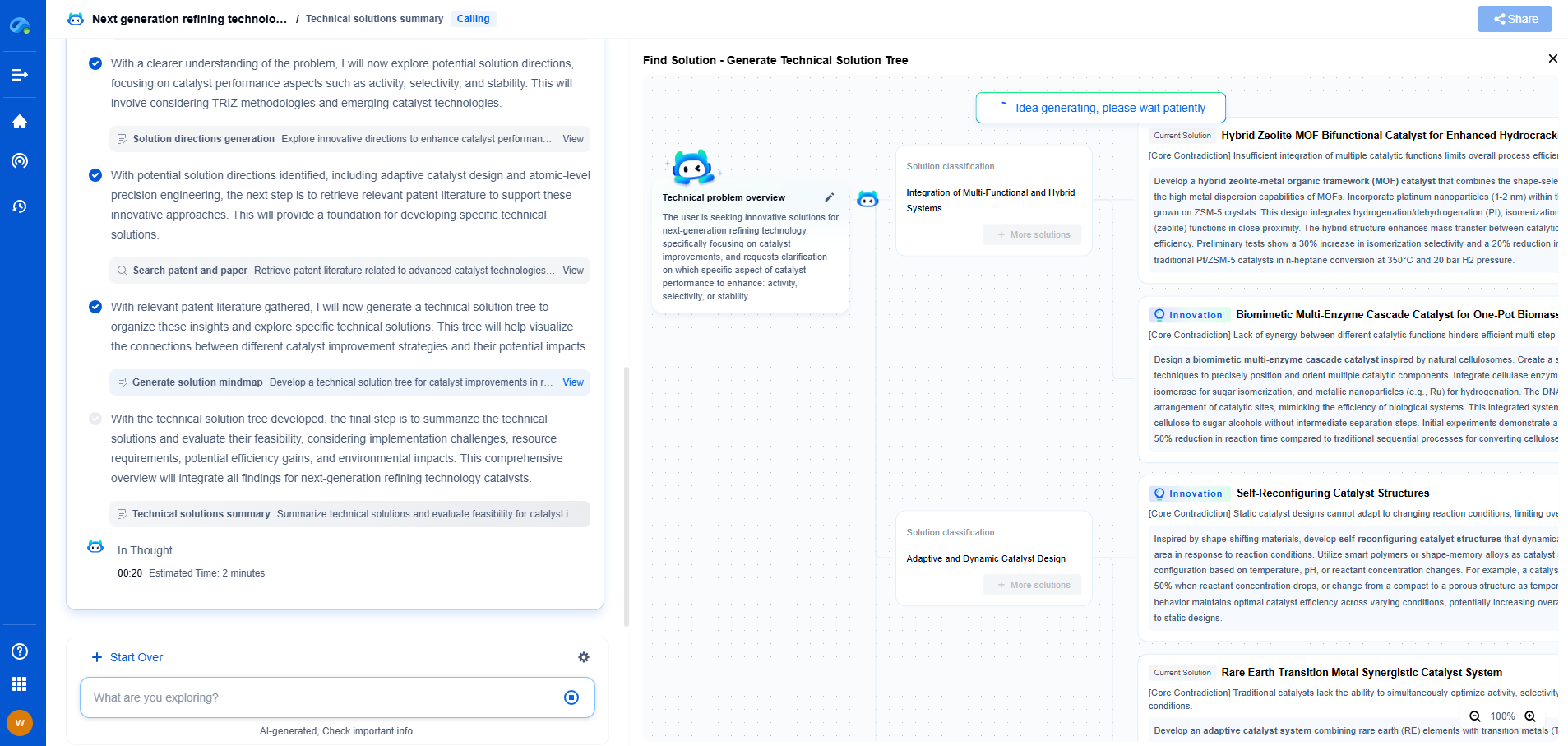
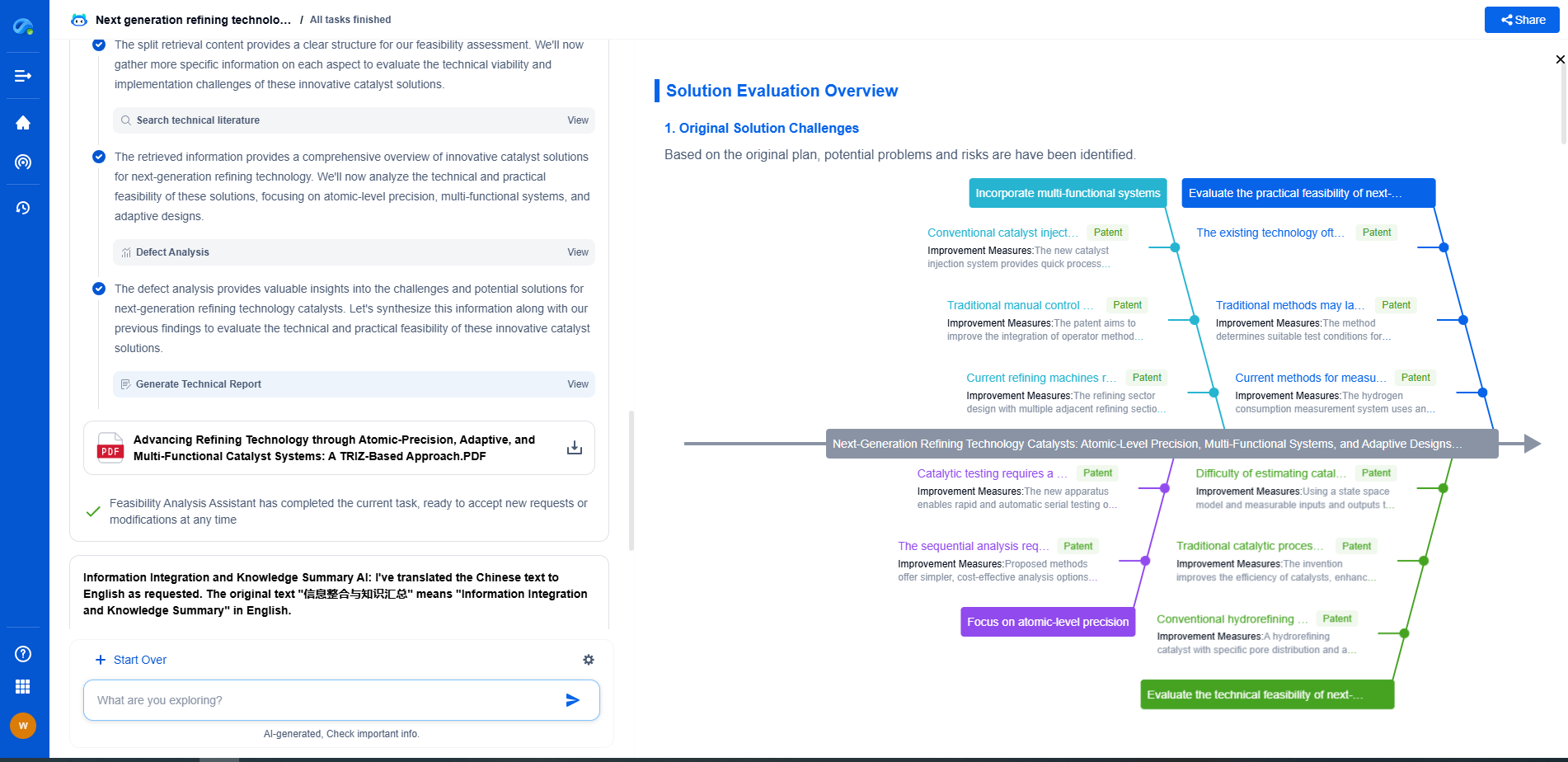
ESR vs. Dissipation Factor: What’s the Difference and Which One Matters More?
JUL 9, 2025 |
When it comes to electronic components, particularly capacitors, two terms often come up in discussions among engineers and hobbyists alike: Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and Dissipation Factor (DF). Understanding these concepts can significantly enhance your ability to select the right components for your projects. Let’s delve into what these terms mean and explore which one might matter more depending on your application.
What is Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)?
Equivalent Series Resistance, or ESR, is a measure of the resistive losses in a capacitor. In an ideal capacitor, you would expect zero resistance; however, real-world capacitors always have some level of resistance due to the construction and materials used. ESR is crucial because it affects the efficiency of a capacitor in filtering or storing energy. High ESR can lead to increased power loss, reduced performance in high-frequency applications, and potential overheating.
ESR is particularly important in applications like power supplies, audio equipment, and RF circuits, where capacitors are used for filtering and decoupling. Low ESR capacitors are preferred because they minimize energy loss, leading to improved performance and reliability.
What is Dissipation Factor (DF)?
Dissipation Factor, or DF, is another parameter that reflects the inefficiency of a capacitor. It is defined as the ratio of the resistive power loss to the reactive power stored in the capacitor. Essentially, it measures how much energy is dissipated as heat rather than being used effectively. A lower dissipation factor indicates a more efficient capacitor, with less energy wasted as heat.
DF is often used in conjunction with ESR but provides a broader picture of the capacitor's performance. While ESR gives a snapshot of resistive losses at a specific frequency, DF offers insight into how these losses vary with frequency, which is crucial in dynamic applications like signal processing.
Comparing ESR and Dissipation Factor
While both ESR and DF are measures of inefficiency in capacitors, they are not interchangeable. ESR is more focused on resistive losses, whereas DF encompasses a wider range of losses, including dielectric losses. In low-frequency applications, ESR might be the more critical parameter, as resistive losses can directly affect performance. On the other hand, DF becomes more important in high-frequency applications where dielectric losses can dominate.
Selecting Capacitors: Which Matters More?
The importance of ESR versus DF largely depends on your specific application. For power circuits and applications requiring high efficiency at low frequencies, ESR is often the key parameter to consider. Low ESR capacitors are ideal for applications such as DC-DC converters, where minimizing energy loss and heat generation is crucial.
In contrast, for high-frequency applications such as RF circuits and signal processing, the dissipation factor might play a more significant role. Here, a low DF is desirable to ensure minimal dielectric losses, maintaining signal integrity and efficient energy transfer.
Practical Considerations
When selecting capacitors, it’s essential to consider both ESR and DF, along with other parameters like capacitance, voltage rating, and temperature stability. Manufacturers often provide datasheets that detail both ESR and DF, making it easier to choose components suited to your needs.
For applications sensitive to energy loss and efficiency, prioritize low ESR capacitors. If your focus is on high-frequency performance, look for capacitors with a low dissipation factor. Ultimately, the right balance between ESR and DF, along with other characteristics, will ensure optimal performance in your electronic designs.
Conclusion
In summary, ESR and Dissipation Factor are vital parameters that help determine the efficiency and suitability of capacitors for various applications. Understanding the nuances of these terms enables better decision-making in component selection. Whether ESR or DF matters more depends on the specific needs of your project, but both should be carefully considered to optimize performance and reliability.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com