316L stainless steel is a low-carbon austenitic chromium-nickel-molybdenum alloy known for its outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in chloride and acidic environments. It is widely used in marine engineering, biomedical implants, and chemical processing, offering long-term reliability in harsh conditions.
This blog explores the composition, grades, performance, industry applications, and technological innovations of 316L stainless steel. It also highlights how the PatSnap Eureka AI Agent empowers material developers and manufacturers to stay ahead of innovation trends, sustainability standards, and intellectual property strategies.
What is 316L Stainless Steel?
316L stainless steel is a low-carbon version of standard 316 stainless steel. The “L” stands for “low carbon,” which improves weldability and reduces the risk of carbide precipitation—thus preserving corrosion resistance after welding or high-heat exposure.
316L contains 2–3% molybdenum, which significantly enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in saline or acidic environments. This makes it ideal for aggressive chemical, marine, or medical applications.

Composition & Properties / Performance
Chemical Composition (% by weight)
| Element | Content |
|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.0–18.0 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10.0–14.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.0–3.0 |
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.030 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 2.0 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 1.0 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.045 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.030 |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
Key Mechanical & Physical Properties
- Density: 7.99 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 1,370–1,400 °C
- Tensile Strength: ~485 MPa
- Yield Strength: ~170 MPa
- Elongation: ≥ 40%
- Modulus of Elasticity: 193 GPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 16.3 W/m·K
- Magnetic Behavior: Non-magnetic in annealed condition
- Weldability: Excellent, with minimal intergranular corrosion risk
Material Grades & Designations
Global Standards
| Standard | Grade Name |
|---|---|
| ASTM | A240, A276, A312 |
| UNS | S31603 |
| EN/DIN | 1.4404 / 1.4435 |
| JIS | SUS316L |
| ISO | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 |
Equivalent Grades
| Region | Grade |
|---|---|
| USA | ASTM A240 316L |
| Europe | EN 1.4404 |
| China | GB 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 |
| Japan | JIS SUS316L |
Application Landscape
316L is the preferred stainless grade for applications demanding superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Its low carbon content also enables superior weld integrity, especially for thick-section parts.
Key Application Sectors
- Medical & Surgical
- Orthopedic implants (hip/knee replacements)
- Dental implants, surgical tools, needles
- Bone fixation plates and pacemaker housings
- Marine Engineering
- Boat fittings, shafts, and fasteners
- Desalination equipment
- Subsea piping and fasteners
- Chemical Processing
- Acid storage tanks, heat exchangers
- Piping in pharmaceutical and biotech plants
- Reactor vessels in corrosive environments
- Architecture & Construction
- Coastal buildings and facades
- Bridges exposed to sea spray
- Long-span stainless tension rods
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- High-strength, corrosion-resistant parts for aerospace and defense
- Customized biomedical implants with porous lattice structures
Emerging Trends
- Bioactive coatings for improved bone integration
- Hybrid 316L-composite implants for lighter, stronger orthopedic solutions
- Green hydrogen electrolyzers leveraging 316L for internal corrosion-resistant tubing
- Automated orbital welding with 316L piping for high-purity fluid systems
316L Stainless Steel vs Other Similar Materials
| Feature | 316L SS | 316 SS | 304 SS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Content | 2–3% | 2–3% | 0% |
| Carbon Content | ≤ 0.030% | ≤ 0.08% | ≤ 0.08% |
| Chloride Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate |
| Weldability | Superior | Good | Excellent |
| Biocompatibility | Certified Grade | General Purpose | Limited |
Advantages of 316L Stainless Steel
- Outstanding resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion
- Superior performance in chloride-rich and acidic environments
- Excellent biocompatibility—suitable for human implantation
- Ideal for welding and thick-section forming
- Maintains strength and ductility at elevated temperatures
- Long lifecycle in harsh environments reduces maintenance costs
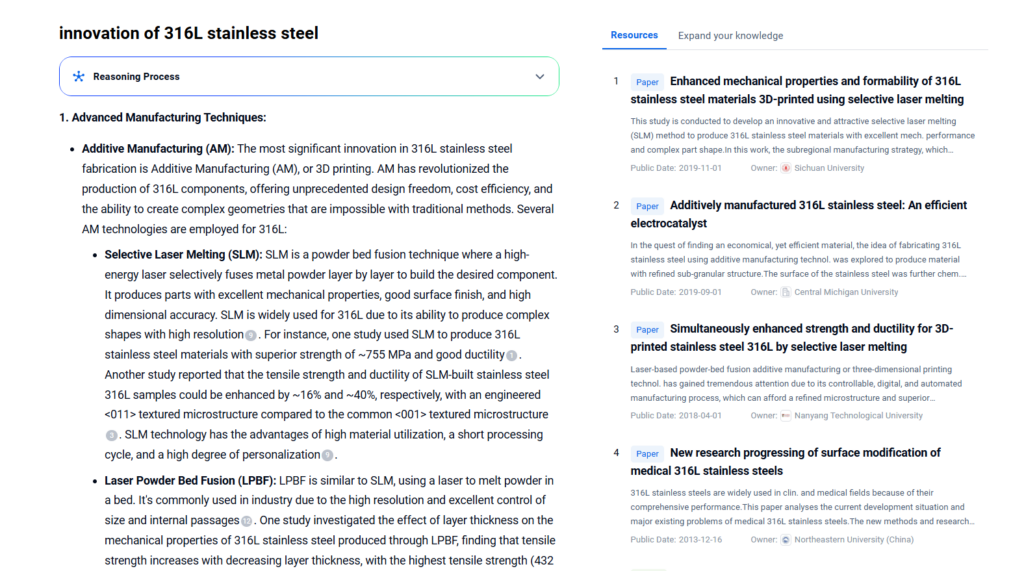
Innovations & Technology
Recent Technological Developments
- Metal Additive Manufacturing (MAM)
- Widespread use of 316L powders in laser sintering (SLM), binder jetting, and electron beam melting
- Microstructure control for improved fatigue life in aerospace and biomedical parts
- Biomedicine Integration
- Development of nanoporous 316L surfaces for enhanced osteointegration
- Smart implants with embedded sensors built from 316L substrates
- Anti-fouling & Anti-biofilm Coatings
- Thin-film plasma-deposited antimicrobial coatings on surgical-grade 316L
- Surface patterning to disrupt bacterial adhesion on medical and marine parts
Sustainability & Environmental Impact
- Fully recyclable in existing stainless steel loops
- High durability reduces lifecycle resource consumption
- Low-maintenance material in architecture and infrastructure
- Meets international compliance: RoHS, REACH, FDA, and ISO 10993
- Environmental footprint mainly associated with molybdenum and nickel mining, prompting research into low-impact alloying
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
With PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, material scientists and procurement teams can:
- Track patent filings in biomedical-grade and marine-grade stainless steel
- Identify market-ready coating and alloying innovations
- Discover startup activity and university collaborations in 316L development
- Explore data-driven insights for pricing trends and regulatory updates
- Locate substitute materials and predict performance with AI-powered simulation
Conclusion
316L stainless steel offers a unique combination of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, weldability, and biocompatibility, making it indispensable in industries from healthcare to shipbuilding. As demand for high-performance and sustainable materials grows, 316L continues to prove its value across critical applications.
By leveraging platforms like PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, engineers and strategists can explore next-gen applications, evaluate IP landscapes, and ensure their materials strategy remains future-proof.
FAQs
No. It is non-magnetic in the annealed condition, making it suitable for MRI-safe medical devices.
Yes. It performs exceptionally well in saline and marine environments due to its molybdenum content.
316L contains molybdenum for better corrosion resistance and has lower carbon, enhancing weldability.
Yes. It’s ISO 10993 and ASTM F138 compliant, widely used in permanent biomedical implants.
Absolutely. It is 100% recyclable and commonly remelted into new stainless steel products.
For more scientific explanations of 316L stainless steel , try PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.