
When choosing a smartphone, tablet, or monitor, display quality plays a big role. Two of the most common screen technologies are AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching LCD). Both offer sharp visuals, but they differ in how they produce light and color, which can affect brightness, battery life, and overall visual experience. This article compares AMOLED vs. IPS displays across various factors to help you decide which is better for your needs.
AMOLED vs. IPS – Which display tech is better? Eureka Technical Q&A compares AMOLED’s deep blacks and vibrant colors with IPS’s accurate color reproduction and wide viewing angles, helping you choose the best screen for your device and preferences.
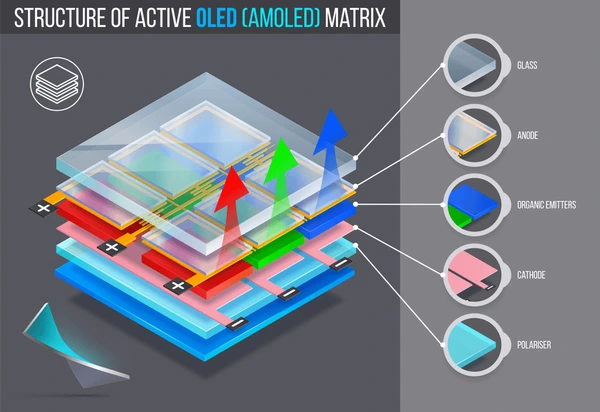
What Is AMOLED?
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. It’s a display technology where each pixel emits its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight.
Key Characteristics:
- Self-Illumination: Unlike LCDs that require a backlight, AMOLED displays emit light from each pixel independently. This allows for thinner and lighter designs.
- Fast Response Time: AMOLEDs have a faster response time, which is beneficial for displaying fast-moving images or video content without motion blur.
- Energy Efficiency: AMOLEDs are generally more energy-efficient than LCDs, especially in bright environments, because each pixel only consumes power when it is lit.
- Wide Color Gamut: AMOLEDs can display a broader range of colors, which is advantageous for applications requiring high color fidelity, such as photography and video editing.
- Flexibility: Some AMOLED technologies can be made flexible, allowing for innovative form factors such as curved or foldable displays.
What Is IPS?
IPS stands for In-Plane Switching, a type of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) that improves on older TN (Twisted Nematic) panels. It uses a backlight behind liquid crystals and offers improved color accuracy and viewing angles.
Key Characteristics:
- Real-time Monitoring and Blocking: IPS continuously monitors network traffic and can take real-time actions to block suspicious activities, such as dropping malicious packets or resetting connections.
- Integration with Other Security Measures: IPS can be integrated with other security tools, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS), to provide layered security defenses.
- Adaptive Capabilities: Some advanced IPS systems use machine learning and threat intelligence to adapt to new threats and improve their detection and prevention capabilities over time.

AMOLED vs. IPS: Feature-by-Feature Comparison
Viewing Angles:
- AMOLED: Offers a wider viewing angle and better color accuracy across different viewing positions. This is due to the technology’s ability to emit light independently at each pixel, which reduces color shifting and maintains color accuracy regardless of the angle at which the screen is viewed.
- IPS: Also provides wide viewing angles, but some users report slight color shifts at extreme angles. IPS technology relies on the rotation of liquid crystal molecules in a plane parallel to the substrate, which can lead to limitations in color accuracy at wider angles compared to AMOLED.
Power Consumption
- AMOLED: Generally consumes less power than IPS displays, especially in bright sunlight. This is because AMOLED screens can adjust the brightness of each pixel individually, leading to better energy efficiency.
- IPS: Tends to have higher power consumption, particularly in bright environments, as it requires a backlight to illuminate the liquid crystal layer. This can lead to faster battery drain on devices like smartphones and tablets.
Color Accuracy and Brightness
- AMOLED: Known for its high contrast ratios and deep blacks, which contribute to better color reproduction and overall image quality. AMOLEDs can produce more vibrant colors and have higher peak brightness levels.
- IPS: Often praised for its color accuracy and ability to display natural colors. IPS technology is commonly used in professional displays and cameras due to its ability to maintain color consistency across different viewing angles.
Response Time
- AMOLED: Offers faster response times compared to IPS displays, which is beneficial for applications that require quick pixel transitions, such as gaming and video playback.
- IPS: Generally has slower response times, which can lead to motion blur in fast-moving content. However, advancements in IPS technology, such as Super IPS, have improved response times to some extent.
Durability and Lifespan
- AMOLED: More susceptible to damage from physical impacts and environmental factors like moisture and oxygen, which can affect the lifespan of the organic materials used in the display.
- IPS: Typically has a longer lifespan and is more durable, as it uses liquid crystal technology that is less prone to degradation over time.
| Feature | AMOLED | IPS LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Contrast Ratio | Very high (true blacks) | Moderate (backlight always on) |
| Color Vibrancy | Rich, saturated colors | Natural, accurate colors |
| Brightness | Slightly lower peak brightness | Often brighter in daylight |
| Viewing Angles | Excellent | Excellent |
| Power Efficiency | More efficient with dark content | More efficient with bright content |
| Burn-in Risk | Possible with static content | No burn-in issues |
| Panel Thickness | Thinner and flexible | Thicker due to backlight |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally more affordable |
Which Display Is Better for Different Uses?
For Smartphones
AMOLED is preferred due to deeper blacks, always-on display features, and better contrast. It’s widely used in flagship phones from Samsung, Google, and OnePlus.
For Monitors and Laptops
IPS is better suited for long productivity sessions, photo editing, and gaming. It offers consistent color accuracy and no risk of burn-in.
For Outdoor Use
IPS generally offers better visibility under direct sunlight, although newer AMOLED panels are catching up in brightness.
For Battery Life
AMOLED tends to save battery when using dark themes, while IPS is more consistent with bright or white content.
Real-World Examples
- AMOLED Devices: Samsung Galaxy S23, Google Pixel 7 Pro, OnePlus 11
- IPS Devices: Apple iPad (non-Pro models), Dell Ultrasharp monitors, many budget Android phones
FAQs
Both are good, but AMOLED’s higher contrast may be easier on the eyes in dark environments. IPS displays are better for long-term viewing with consistent brightness.
They can suffer from burn-in or pixel aging, especially with static images. This is less of an issue with recent improvements in software and hardware.
IPS panels are generally more stable under constant use. AMOLEDs are thinner and more fragile but offer better design flexibility.
Yes. AMOLED tends to have more vibrant colors and deeper blacks, while IPS looks more natural with better daylight readability.
If you prioritize contrast, color depth, and modern features like always-on display, it’s worth it. Otherwise, IPS offers excellent value and color accuracy for everyday use.
Conclusion
AMOLED and IPS each have their strengths. AMOLED shines in contrast, color vibrancy, and slim design, making it ideal for modern smartphones and premium devices. IPS offers balanced brightness, color accuracy, and long-term reliability—great for monitors, laptops, and budget-friendly phones.
The best choice depends on how you use your device. For stunning visuals and deeper blacks, go with AMOLED. For consistent performance, lower cost, and bright viewing in all lighting conditions, IPS is a solid pick.
To get detailed scientific explanations of AMOLED vs IPS, try Patsnap Eureka.


