
Bromic acid is an important yet highly reactive compound used in chemical synthesis, industrial oxidation processes, and various research applications. As a strong acid with significant oxidizing properties, it plays a critical role in analytical chemistry, electrochemical processes, and environmental science. But what exactly makes Bromic Acid unique, and how is it utilized across different industries? This article explores the chemical properties, industrial applications, benefits, challenges, and future innovations related to bromic acid.
What is Bromic Acid?
Bromic acid (HBrO₃) is an unstable, strong acid that exists only in aqueous solution. It is known for its powerful oxidizing capabilities and is the conjugate acid of the bromate ion (BrO₃⁻).
Key Chemical Characteristics
- Molecular Formula: HBrO₃
- Molecular Weight: 128.91 g/mol
- Acidity: Strong acid, dissociates completely in water
- Oxidizing Properties: Acts as a potent oxidizing agent in chemical reactions
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water but unstable in pure form
💡 Did You Know?
HBrO₃ does not exist as a pure substance because it rapidly decomposes into bromates and bromine gas in solution.
How Bromic Acid Works in Chemical Reactions
HBrO₃ is an oxidizing agent that participates in redox reactions across multiple chemical and industrial processes.
- Strong Acidic Behavior: Fully dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bromate ions (BrO₃⁻).
- Oxidizing Function: Converts metals and nonmetals into their higher oxidation states.
- Formation of Bromates: Scientists often compare bromic acid to other strong acids for its oxidizing potential and reactivity.
Chemical Reaction Example:
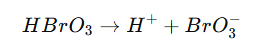
This dissociation shows how HBrO₃ forms bromate ions in aqueous solutions, which further contribute to oxidation reactions.
Industrial Applications of Bromic Acid
Curious about the industrial applications of bromic acid? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its role in chemical synthesis, oxidation processes, and industrial manufacturing, helping you understand its uses and safety considerations in various industries.
HBrO₃ plays a significant role in chemical manufacturing, environmental science, and industrial processing. Here are its primary applications:
Chemical Synthesis and Manufacturing 🏭
- Precursor for Bromates: Used in the production of potassium and sodium bromates, which are essential in chemical oxidation reactions.
- Oxidizing Agent: Utilized in organic and inorganic chemistry for controlled oxidation processes.
Water Treatment and Environmental Science 💧
- Disinfection Agent: Helps eliminate bacteria and contaminants in industrial water treatment.
- Removal of Organic Pollutants: Used in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) to degrade harmful organic compounds.
Electrochemical and Analytical Chemistry ⚡
- Electrode Cleaning: Acts as a reagent in electrochemical surface treatment and analytical testing.
- Indicator in Titrations: Used in redox titration methods for precise chemical analysis.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Research 💊
- Oxidation of Drug Precursors: Involved in the synthesis of certain pharmaceutical intermediates.
Bromic Acid vs. Other Strong Acids: Key Differences
Scientists often compare HBrO₃ to other strong acids for its oxidizing potential and reactivity. Here’s how it differs:
| Feature | Bromic Acid (HBrO₃) | Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) | Nitric Acid (HNO₃) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Properties | Strong oxidizer | Moderate oxidizer | Strong oxidizer |
| Stability | Highly unstable | Very stable | Moderately stable |
| Common Uses | Chemical oxidation, bromate production | Acid catalysts, dehydration reactions | Explosives, nitration reactions |
| Industrial Application | Water treatment, pharmaceuticals | Petroleum refining, batteries | Fertilizers, metal etching |
💡 Tip: If you need a highly reactive oxidizing agent, HBrO₃ is suitable, but for stable acid applications, sulfuric acid or nitric acid may be preferable.
Challenges and Safety Considerations
High Reactivity and Instability ❌
- Decomposes rapidly into bromates and bromine gas in solution.
- Cannot be stored as a pure liquid or solid due to its instability.
Hazardous Oxidizing Properties ❌
- Reacts violently with organic materials and reducing agents.
- Must be handled in controlled environments to prevent explosions.
Environmental Impact ❌
- Bromates formed from bromic acid can be toxic to aquatic life.
- Strict regulations govern its use in water treatment and industrial applications.
⚠️ Safety Tip: Always handle HBrO₃ under strict chemical safety protocols using protective gear and proper ventilation.
Future Trends in Bromic Acid Research and Innovation
Green Chemistry Applications 🔹
- Development of eco-friendly oxidation processes to replace hazardous oxidizing agents.
Advanced Electrochemical Research 🔹
- Exploring bromic acid’s role in next-generation battery technologies and electrode modifications.
Improved Industrial Handling Methods 🔹
- Innovations in stabilizing bromates for safer storage and controlled chemical use.
How Eureka by PatSnap Accelerates Bromic Acid Research
What is Eureka by PatSnap?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that assists researchers in discovering the latest advancements in HBrO₃ chemistry.
How It Benefits Bromic Acid R&D
- Patent Analysis: Identifies new patents and innovations related to HBrO₃ applications.
- Competitive Intelligence: Helps industries benchmark against leading chemical manufacturers.
- Technology Roadmapping: Provides insights into emerging trends in oxidation chemistry and industrial applications.
🚀 For professionals in chemical research, environmental science, and pharmaceuticals, Eureka by PatSnap accelerates discovery and innovation.
Conclusion
Bromic acid is a powerful but highly unstable acid with strong oxidizing properties used in chemical synthesis, water treatment, and analytical chemistry. While its instability and reactivity present challenges, ongoing research and innovations are expanding its applications in sustainable chemistry and electrochemical advancements.
By leveraging AI-driven tools like Eureka by PatSnap, researchers and manufacturers can stay ahead of industry trends and develop safer, more efficient applications for HBrO₃.
🚀 Want to explore the latest breakthroughs in HBrO₃ research? Sign up for Eureka by PatSnap today and accelerate your innovation journey!
FAQs
1️⃣ Can bromic acid be stored as a pure substance?
No, HBrO₃ is highly unstable and only exists in aqueous solutions.
2️⃣ What are the primary uses of HBrO₃?
Industries use it in chemical oxidation, water treatment, pharmaceutical research, and analytical chemistry.
3️⃣ Is bromic acid hazardous?
Yes, handle it carefully as a strong oxidizer to prevent violent reactions and decomposition.
4️⃣ Can bromic acid be used in electrochemical applications?
Yes, it plays a role in electrode cleaning, electrochemical oxidation, and battery research.
5️⃣ How can I stay updated on bromic acid research?
Using AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap helps track the latest patents, innovations, and industrial applications in HBrO₃ chemistry.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Bromic Acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


