
Introduction to Carburetors in Combustion Engines
A carburetor is a vital component in internal combustion engines, responsible for mixing air and fuel in the right proportions for combustion. This process is essential for ensuring smooth engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reliable operation. While modern engines often use fuel injection systems, carburetors remain a cornerstone of classic and small-engine technology. In this article, we’ll explore how carburetors work, their advantages, and why they still matter in specific applications today.
Key Components of a Carburetor
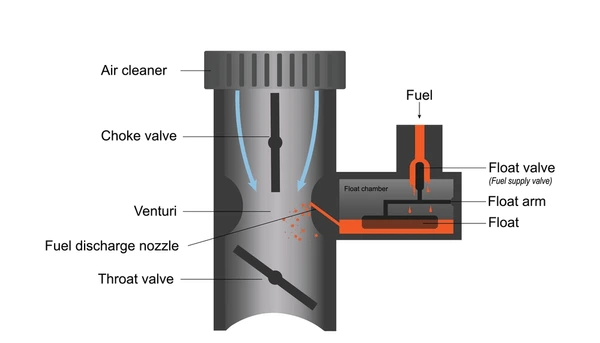
Venturi: Creating the Low-Pressure Zone
The venturi is a narrow section within the air passage of the carburetor. As air flows through this constricted area, its velocity increases, creating a low-pressure zone. This pressure drop draws fuel from the carburetor into the airstream, enabling efficient mixing with the incoming air.
Fuel Jet: Delivering the Fuel
The fuel jet is a nozzle responsible for delivering fuel into the venturi. As the low-pressure zone forms in the venturi, fuel is precisely metered and introduced into the airstream. This ensures the air-fuel mixture is consistent, supporting smooth combustion.
Float Chamber: Maintaining Fuel Levels
The float chamber acts as a reservoir, keeping the fuel level constant within the carburetor. A float mechanism regulates the fuel supply, ensuring a steady flow into the fuel jet. This consistency prevents engine sputtering and supports reliable operation.
Throttle Valve: Controlling Power and Speed
The throttle valve is a butterfly-style valve that manages the flow of the air-fuel mixture into the engine. By adjusting its position, the valve controls the engine’s speed and power output. Opening the throttle increases the mixture flow, boosting performance, while closing it reduces power.
Choke Valve: Assisting with Cold Starts
The choke valve is designed to restrict the air intake, enriching the air-fuel mixture during cold starts or high-load conditions. This richer mixture helps the engine start more easily and operate smoothly until it reaches optimal temperature.

How a Carburetor Works
The carburetor operates on Bernoulli’s principle, which states that as fluid speed increases, pressure decreases. As air flows through the venturi, its speed rises, causing a pressure drop that creates a vacuum. This vacuum draws fuel from the fuel jet, mixing it with the air. The throttle valve then regulates this air-fuel mixture, delivering it to the engine’s cylinders for combustion. This simple yet efficient process ensures the engine receives the right mixture for optimal performance.
Troubleshooting Carburetor Issues: A Step-by-Step Guide
A well-maintained carburetor is crucial for optimal engine performance. Follow these practical tips to keep your carburetor clean, efficient, and running smoothly.
1. Clean Clogged Passages
Debris, dirt, or varnish buildup can clog the carburetor’s passages, restricting air and fuel flow. Disassemble the carburetor and thoroughly clean all passages using carburetor cleaner or compressed air. Pay extra attention to critical areas like the main jet, idle jet, and venturi to ensure unobstructed flow.
2. Inspect and Replace Worn Parts
Check the carburetor for worn or damaged components such as gaskets, needles, seats, and floats. Replace any faulty parts to maintain proper fuel metering and a tight seal. Regular inspections can prevent performance issues caused by worn-out components.
3. Adjust the Fuel-Air Mixture
An incorrect fuel-air mixture can lead to poor engine performance. Use the manufacturer’s specifications to adjust the air and fuel screws for both idle and high-speed operation. Proper adjustments ensure efficient combustion and smoother engine operation.
4. Check for Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks in the carburetor or intake manifold can cause a lean fuel condition, affecting engine performance. Inspect all gaskets, seals, and connections for cracks or damage. Replace any defective parts to eliminate leaks and restore proper operation.

5. Synchronize Multiple Carburetors
For engines with multiple carburetors, synchronization is essential for even fuel distribution. Follow the manufacturer’s procedure to adjust the linkages and balance the carburetors. Proper synchronization ensures consistent performance and avoids uneven power delivery.
6. Verify Choke Functionality
A faulty choke can cause starting and idling issues, especially in cold conditions. Check the choke mechanism to ensure smooth operation and proper adjustment. Replace any worn or damaged components to maintain reliable performance.
7. Use Quality Fuel
Poor-quality or contaminated fuel can cause carburetor problems over time. Always use fresh, high-quality fuel and consider adding a fuel stabilizer or cleaner to the tank. This prevents deposits and extends the life of your carburetor.
Final Thoughts
By keeping your carburetor clean, adjusting it properly, and inspecting for wear, you can maintain peak engine performance. Regular maintenance not only ensures smoother operation but also extends the life of your engine.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Carburetors, try Patsnap Eureka.

