
Technical Background and Objectives
Background
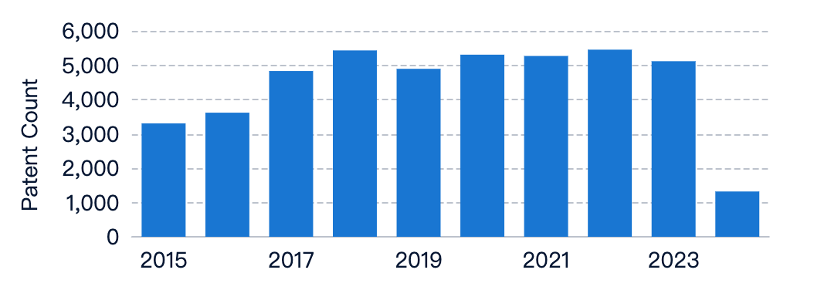
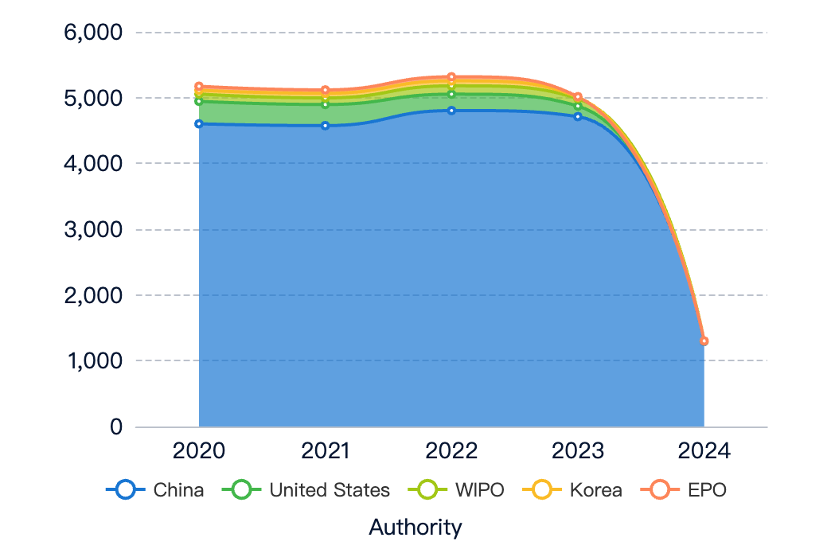
In the field of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools, the trend of patent applications related to ‘easy to use’ has shown a steady increase over the years. This indicates growing interest and investment in developing user-friendly CNC machine tools. However, the number of related literature publications has remained relatively low and fluctuated, suggesting less academic focus compared to industrial research and development efforts. This divergence may be due to the industry’s emphasis on proprietary research and development, driven by the need for automation and skilled operator efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Objectives
The primary objective is to develop innovative solutions that enhance the usability and accessibility of CNC machine tools. By focusing on user-friendly interfaces, intuitive operation, and streamlined workflows, the aim is to empower operators of varying skill levels to effectively utilize these advanced manufacturing systems. The goal is to bridge the gap between technological complexity and user experience, ultimately increasing productivity, reducing errors, and fostering a more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing environment.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of CNC Machine Tool Easy to Use, try Eureka.
Technical Current Status Analysis
CNC Machine Tools
CNC machine tools are widely used in various manufacturing industries such as automotive, aerospace, mold making, and general machining. Despite their advanced capabilities, many users find CNC machine tools challenging to operate, particularly those with limited technical expertise or experience.
Applications and Impact:
- Automotive Industry: Production of engine components, transmission parts, and body panels.
- Aerospace Industry: Manufacturing intricate and high-precision components for aircraft structures, engines, and avionics systems.
- Mold Making Industry: Creating complex mold cavities and cores for injection molding, die casting, and stamping.
- General Machining: Producing custom parts and components for various industries.
Technical Characteristics and Challenges:
- User Interface and Programming: Traditional CNC programming languages like G-code are complex and difficult to learn, especially for novice operators.
- Machine Control and Automation: Integrating advanced control systems and automation features to simplify operation and reduce manual intervention.
- Setup and Tooling: The setup process is time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Maintenance and Diagnostics: Effective systems are crucial for reliable operation and minimizing downtime.
- Integration and Connectivity: Seamless integration with other systems like CAD/CAM software, ERP systems, and IIoT platforms.
- Operator Training and Support: Comprehensive training programs and real-time support systems to enhance ease of use for operators.
Technological Paths:
- Intuitive and Intelligent User Interfaces: Develop user-friendly graphical programming interfaces with features like drag-and-drop programming, 3D simulations, and virtual reality environments.
- Advanced Control and Automation Systems: Implement advanced control algorithms and sensor technologies for real-time monitoring and process optimization.
- Intelligent Setup and Tooling Systems: Develop automated or semi-automated systems for workpiece positioning, tool changing, and fixture management.
- Predictive Maintenance and Remote Monitoring: Implement predictive maintenance strategies and remote monitoring systems for real-time fault detection and support.
- Seamless Integration and Connectivity: Adopt open standards and protocols for integration with other systems and secure data exchange mechanisms.
- Comprehensive Training and Support Systems: Develop interactive training programs leveraging technologies like augmented reality and virtual reality.
Research Content
Research Objectives
The primary objective is to develop innovative solutions that enhance the usability and accessibility of CNC machine tools.
Research Direction and Focus
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Design
- Extensive research on HMI design principles, leveraging human-computer interaction, ergonomics, and cognitive psychology.
- Develop intuitive and user-friendly interfaces to facilitate seamless communication between operators and CNC machines.
Workflow Optimization and Process Simplification
- Optimize CNC machine operation workflows to streamline processes and reduce complexity.
- Use process mapping, task analysis, and user experience research to identify areas for improvement.
Intelligent Assistance and Automation
- Incorporate AI and machine learning technologies for real-time guidance, error detection, and automated decision-making support.
- Implement adaptive learning systems to personalize the user experience based on individual preferences and skill levels.
User Training and Skill Development
- Develop interactive training modules, simulation environments, and augmented reality solutions for hands-on learning and skill acquisition.
- Integrate training solutions directly into the CNC machine tool interface for seamless on-the-job learning.
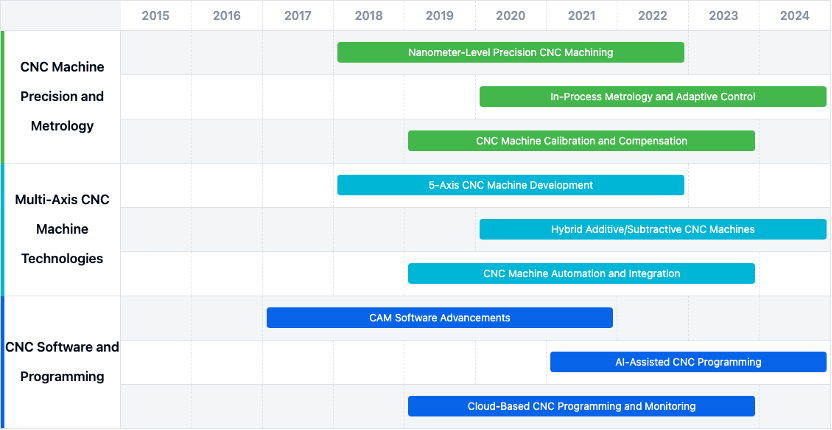
Technical Development Roadmap
Key Areas of Advancement
- Multi-Axis CNC Machine Technologies: Development of 5-axis CNC machines, hybrid additive/subtractive CNC machines, and CNC machine automation and integration.
- CNC Software and Programming: Advancements in CAM software, AI-assisted CNC programming, and cloud-based CNC programming and monitoring.
- CNC Machine Precision and Metrology: Research on nanometer-level precision CNC machining, in-process metrology, and adaptive control and CNC machine calibration and compensation.
Main Player Analysis
Key Players and Focus
- Huazhong University of Science & Technology: Focus on user-friendly interfaces and intuitive control systems to simplify CNC machine operation.
- FANUC Corp.: Renowned for advanced control systems and automation solutions with a focus on user-friendly control interfaces and intelligent monitoring systems.
- Chengdu Aircraft Industrial Group Co. Ltd.: Development of advanced CNC machine tools for aircraft manufacturing with user-friendly programming interfaces and real-time monitoring systems.
- Georgia Institute of Technology: Research on computer-aided manufacturing and CNC technologies, including freeform surface offsetting, cloud manufacturing, and motion accuracy measurement for CNC machine tools.
Current Technical Solution Overview
CNC Machine Tools with User-Friendly Controls
- Intuitive Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): Simplified operation and programming with intuitive icons and menus.
- Simplified Control Systems: Streamlined interfaces and automated functions for ease of use.
- Ergonomic Designs: Features like easy access to controls and adjustable workstations for operator comfort.
- Automated Tool Management: Systems that simplify tool changing and maintenance, reducing manual intervention.
CNC Machines with Automated Tool Handling
- Automated Tool Handling System: Efficient tool changes during machining with tool magazines and automated tool changers.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Simplified programming and monitoring with intuitive control panels.
- Easy Maintenance and Repair: Features that facilitate maintenance and repair, reducing downtime and costs.
- Integration with Robotic Systems: Automated tasks like loading/unloading workpieces and part handling for improved productivity.
CNC Machines with Integrated Safety Features
- Safety Mechanisms and Devices: Protective covers, emergency stop buttons, and sensors to prevent accidents.
- User-Friendly Operation: Intuitive control interfaces and ergonomic designs for efficient operation.
- Improved Maintainability: Modular components and easy access to critical parts for convenient maintenance.
- Fire Safety Protection: Fire suppression systems and fire-resistant materials for safe operation.
CNC Machines with Monitoring and Diagnostic Capabilities
- Monitoring Systems: Real-time tracking of performance parameters like tool wear and spindle condition.
- Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: Systems for remote data collection, diagnostics, and maintenance alerts.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Simplified operation and monitoring with intuitive control panels.
- Intelligent Monitoring and Analysis: AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance and performance optimization.
CNC Machines with Flexible and Adaptable Configurations
- Modular and Reconfigurable Architectures: Customizable setups for different applications.
- Automated or Semi-Automated Features: Tool changing, workpiece loading/unloading, and process completion recognition.
- Versatile or Multi-Functional Capabilities: Perform various machining operations like turning, milling, grinding, and wire cutting.
- Remote or Mobile Control Capabilities: Easy operation from a distance or different locations for user convenience.
Key Patent Interpretation
Patent Highlights
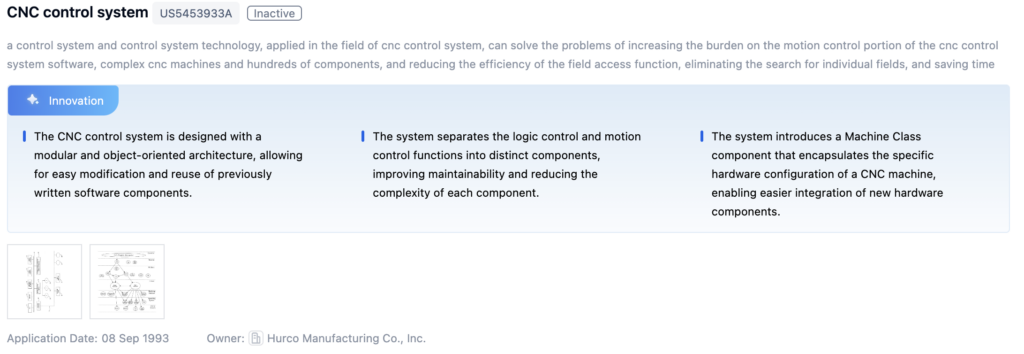
Patent 1: CNC Control System
- Core Invention Points:
- Modular and object-oriented architecture for easy software modification and reuse.
- Separation of logic control and motion control functions for improved maintainability.
- Machine Class component for easier hardware integration.
Patent 2: CNC Turning Machine
- Core Invention Points:
- Closed loop control system with feed forward signal processing for precise control.
- Tool head with preloaded bearing means for maintaining precise positioning.

Patent 3: Dialog-Oriented Programming System for CNC Machine Tool
- Core Invention Points:
- Interactive dialogs and graphical representations for program creation.
- Customizable functions and program structures based on user requirements.
- Direct changes and inputs in the machine program or NC record format.
Possible Research Directions
- CNC Machine Tools with User-Friendly Interfaces: Touchscreen displays and simplified control panels for enhanced user experience.
- CNC Machine Tools with Automatic or Semi-Automatic Features: Tool changing, workpiece loading/unloading, and process completion recognition to reduce manual intervention.
- CNC Machine Tools with Integrated Safety Features: Protective covers, tool release mechanisms, and monitoring systems for user safety.
- CNC Machine Tools with Versatile or Multi-Functional Capabilities: Perform various machining operations for increased flexibility.
- CNC Machine Tools with Remote or Mobile Control Capabilities: Easy operation from a distance or different locations for convenience.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

