
Controlled variables are essential components of any scientific experiment. They ensure that the results of a study are accurate and attributable to the manipulation of the independent variable rather than to external factors. In a research landscape that demands precision, repeatability, and credibility, managing controlled variables effectively is critical. This article explores what controlled variables are, why they matter, how to manage them step-by-step, and how PatSnap Eureka can enhance every stage of the process.
What Is a Controlled Variable?
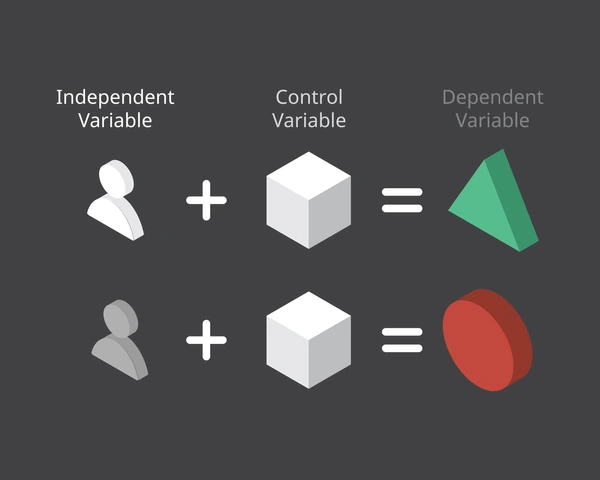
What is a controlled variable? Patsnap Eureka explains that it’s a constant factor in an experiment that ensures accurate results by isolating the effect of the independent variable.
A controlled variable—also called a constant—is any factor in an experiment that is intentionally kept unchanged throughout the process. Its role is to eliminate the influence of extraneous variables that could confound the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Examples of Controlled Variables
Controlled variables differ based on the experiment. Examples include:
- Temperature: Keeping temperature constant in chemical reactions to ensure rate consistency.
- Light Conditions: Regulating light exposure in plant experiments.
- Time: Applying the same time duration across test subjects or samples.
- Material Volume: Using identical quantities across experimental conditions.
In an experiment testing the effect of a drug on blood pressure, controlled variables may include the dosage time, patient diet, activity levels, and pre-existing conditions.
Why Controlled Variables Are Crucial
Enhancing Internal Validity
Researchers control external influences to ensure they can confidently attribute observed changes to the manipulated variable.
Preventing Confounding Variables
By keeping all other variables constant, researchers avoid misleading results caused by external influences.
Enabling Reproducibility
Controlled conditions allow other researchers to replicate experiments, strengthening the credibility and acceptance of findings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Controlled Variables
Step 1: Identify Potential Influential Variables
Begin by listing all factors that could affect the dependent variable. These can include environmental conditions, procedural inconsistencies, or human error.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Use Eureka’s advanced search capabilities to review prior studies and uncover how experts have identified and controlled similar variables. AI-powered literature exploration helps generate a comprehensive control checklist for your specific domain.
Step 2: Determine Which Variables to Control
Evaluate the list and isolate the most critical factors that must be controlled for the results to remain valid.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Benchmark protocols against peer-reviewed literature and global patents. Eureka enables side-by-side comparisons of how top researchers define and manage controlled variables in similar experimental frameworks.
Step 3: Develop Standardized Protocols
Once the key variables are chosen, define exact procedures to keep each one constant. This includes measurements, ranges, monitoring tools, and time schedules.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Access templates and historical protocol blueprints via Eureka’s database to build standardized procedures quickly. This ensures procedural accuracy and scientific alignment with industry norms.
Step 4: Implement Monitoring Systems
Establish checks to ensure variables remain controlled. This includes using logs, sensors, audits, or automated systems.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Leverage Eureka’s monitoring feature to track experimental trends, environmental shifts, and changes in technical inputs across time. This helps maintain consistency across long-term or collaborative projects.
Step 5: Document and Share Methodologies
Clearly document how controlled variables were maintained and any exceptions or anomalies.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Eureka allows seamless collaboration and recordkeeping, enabling research teams to document control strategies, version protocols, and share findings through visual dashboards or exportable reports.
Conclusion
Controlled variables are a foundation of valid and reproducible scientific research. Without them, findings become unreliable, and conclusions lose meaning. Properly identifying, defining, and managing controlled variables is key to producing high-quality, credible research.
With PatSnap Eureka, researchers gain a powerful edge in this process. From planning experiments and consulting global best practices to tracking consistency and sharing results, Eureka streamlines the complex task of variable control with AI, real-time data, and intuitive collaboration tools. In today’s competitive and evidence-driven research environment, the ability to control for precision has never been more essential—or more achievable.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Controlled Variable, try Patsnap Eureka.


