
When it comes to high-performance polymers and materials that offer exceptional resistance to heat and chemical degradation, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and Teflon are two terms that often come up. While they are frequently used interchangeably, there are important distinctions between them that are worth understanding. This article dives into the differences between PTFE vs. Teflon, exploring their unique properties, uses, and why it’s important to understand these differences.
What is PTFE?
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance plastic valued for its non-reactive properties. It offers strong resistance to heat, chemicals, and electrical conductivity. Industries like chemical processing, electronics, and pharmaceuticals use PTFE for its exceptional durability and low friction. Its unique qualities make PTFE a preferred material in demanding environments.
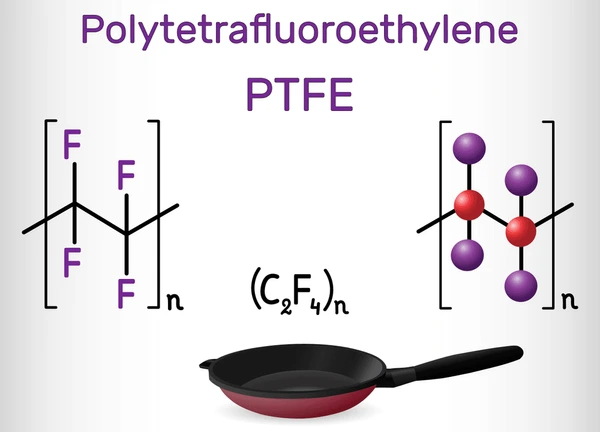
Key Characteristics of PTFE:
- Non-reactive: PTFE is highly resistant to most chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents.
- High-Temperature Resistance: It can withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without degrading.
- Low Friction: PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction among solid materials, making it ideal for lubricating parts.
- Electrical Insulation: It is a great electrical insulator, often used in cable coatings.
- Non-stick Properties: PTFE is known for its non-stick capabilities, especially in cookware and industrial applications.
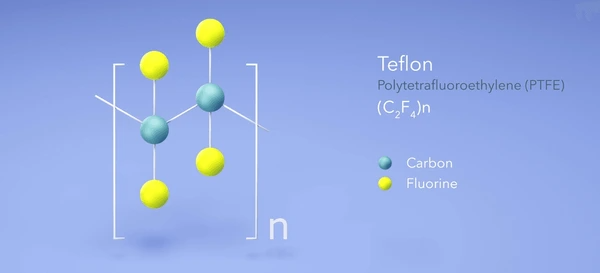
What is Teflon?
Teflon is the brand name for a specific formulation of PTFE, produced by the chemical company Chemours, which was once a part of DuPont. Teflon refers to the same polymer as PTFE but is often marketed for specific applications, particularly non-stick cookware, as well as coatings for various industrial products.
Key Characteristics of Teflon:
- Non-stick Coating: The most popular application of Teflon is in non-stick cookware, where it reduces the need for oils or fats.
- Durability: Teflon-coated products are resistant to scratches, high temperatures, and most chemicals, similar to PTFE.
- Easy to Clean: The non-stick surface allows for easy cleaning, making Teflon an attractive option for cookware.
Key Differences Between PTFE and Teflon
| Feature | PTFE | Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | A polymer of tetrafluoroethylene | A specific brand of PTFE |
| Trademark | PTFE is a general term for the polymer | Teflon is a trademarked brand |
| Common Applications | Wide range (industrial, electronics) | Primarily cookware, industrial coatings |
| Manufacturing | Generic production of PTFE polymers | Teflon involves proprietary formulations |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals | Excellent resistance to chemicals |
How PTFE and Teflon are Used in Different Industries
PTFE in Industrial Applications:
- Chemical Processing: PTFE is commonly used in the chemical industry for gaskets, seals, and tubing. Its resistance to corrosive substances makes it ideal for these applications.
- Aerospace: In aerospace, PTFE insulates electrical wiring and components. Its high dielectric strength and thermal stability make it perfect for demanding environments.
- Automotive: PTFE enhances engine components, such as seals, bearings, and gaskets. It offers excellent wear resistance and reduces friction.
Teflon in Commercial and Household Applications:
- Cookware: Teflon is best known for its non-stick properties in cookware, including frying pans, pots, and baking sheets.
- Industrial Coatings: Teflon coats industrial products to protect them from corrosion and friction. Examples include conveyor belts and valves.
- Medical Devices: Teflon coatings improve medical devices like catheters. Their biocompatibility and low friction make them suitable for medical applications.
💡When comparing PTFE vs. Teflon, Eureka Technical Q&A provides in-depth answers, helping you understand their unique properties, applications, and performance in various industries to make an informed choice for your specific needs.
Advantages of PTFE vs. Teflon
Advantages of PTFE:
- Versatility: PTFE can be used in a broader range of industries, from aerospace to electronics, due to its unique properties.
- Heat Resistance: PTFE’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures (up to 260°C) without breaking down makes it valuable in demanding industrial applications.
- Electrical Insulation: PTFE offers excellent electrical insulating properties, making it crucial for various electronic components.
Advantages of Teflon:
- Non-stick Surface: Teflon’s non-stick properties are highly valued in cooking, providing convenience and ease of cleaning.
- Durability: Teflon coatings are resistant to scratches, stains, and corrosion, ensuring long-term use.
- Smooth Surface: Teflon-coated surfaces reduce friction, which is beneficial in a range of industrial applications.
Common Misconceptions About PTFE and Teflon
Misconception 1: Teflon is Different from PTFE
While Teflon is a specific brand of PTFE, many people mistakenly believe that it is a different material entirely. However, Teflon is simply a proprietary form of PTFE produced by Chemours.
Misconception 2: PTFE is Toxic
PTFE itself is non-toxic. However, when PTFE-coated products are overheated (such as in cooking at very high temperatures), they can release fumes that can be harmful to humans and pets. This is why it’s important to follow proper temperature guidelines for Teflon-coated cookware.
Misconception 3: Teflon is Always Non-Stick
Not all Teflon coatings are the same. While they offer non-stick properties, the effectiveness can vary depending on the quality of the coating and the product it’s applied to.
Conclusion: PTFE vs. Teflon—Which is Better?
The decision between PTFE and Teflon largely depends on the application. PTFE is the material of choice for industrial applications due to its superior chemical resistance, electrical properties, and high-temperature stability. On the other hand, Teflon—which is a brand name for a specific form of PTFE—is most commonly used for non-stick cookware and other consumer products.
For industrial uses, PTFE’s versatility and robustness make it an essential material in a wide variety of fields, from chemical processing to aerospace. For consumer applications, Teflon offers the non-stick surfaces needed in cookware and is often found in household items where durability and ease of cleaning are important.
FAQs
- Is PTFE the same as Teflon?
Teflon is a brand name for a specific formulation of PTFE, but in essence, both refer to the same polymer. - Can PTFE be used for cooking?
Yes, PTFE, under the brand name Teflon, is widely used as a non-stick coating in cookware. - Is PTFE safe for cooking?
Yes, PTFE itself is safe for cooking; however, overheating Teflon cookware above 500°F can release harmful fumes, so it’s important to follow temperature guidelines. - Can PTFE be used in extreme environments?
Yes, PTFE is highly resistant to extreme temperatures (up to 260°C) and is used in industries like aerospace, chemical processing, and electronics.
To get detailed scientific explanations of PTFE vs. Teflon, try Patsnap Eureka.


