
Technical Background and Objectives
TPE Materials (Thermoplastic Elastomer) combine the properties of thermoplastics and elastomers, offering flexibility, elasticity, and processability. TPE Materials have gained attention in electronics due to their potential for various applications. Research on the applications of TPE Materials in electronics is driven by the demand for lightweight, flexible, and durable components in wearables, flexible displays, and sensors.
Objectives
- Flexibility and Electrical Conductivity: Achieve a balance between flexibility and electrical conductivity using conductive fillers like carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metallic particles.
- Thermal and Chemical Resistance: Improve the thermal and chemical resistance of TPEs to withstand harsh environments and exposure to chemicals.
- Durability and Longevity: Enhance the durability and longevity of TPE-based electronic components.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of tpe, try Eureka.
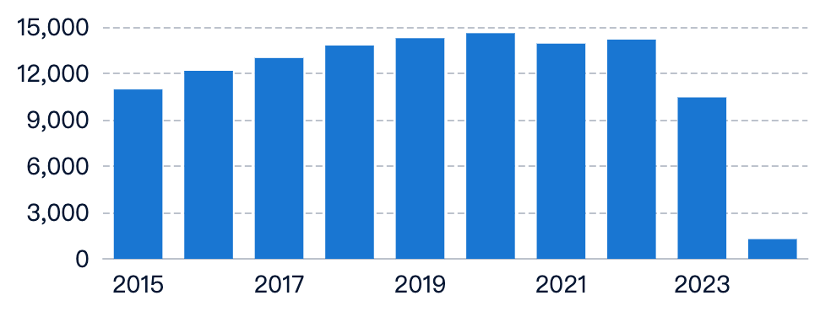
Market Demand Analysis
The demand for TPE materials in electronics is growing, driven by the need for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials.
Key Drivers
- Wearable Devices: TPEs offer flexibility, impact resistance, and durability for smartwatches, fitness trackers, and VR headsets.
- Cables and Wire Insulation: TPEs provide abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and environmental protection for cables and wire insulation.
- Miniaturization and Portability: TPEs enable the production of compact and lightweight components for smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
- Sustainability: Recyclable and renewable TPEs align with eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Applications
- Wearables and Flexible Electronics: High-performance materials for durable, flexible devices.
- Cable Insulation and Connectors: Long-lasting, moisture-resistant materials.
- Miniature Electronics: Stable, complex-shaped components.
- Eco-Friendly Devices: Sustainable and recyclable materials.
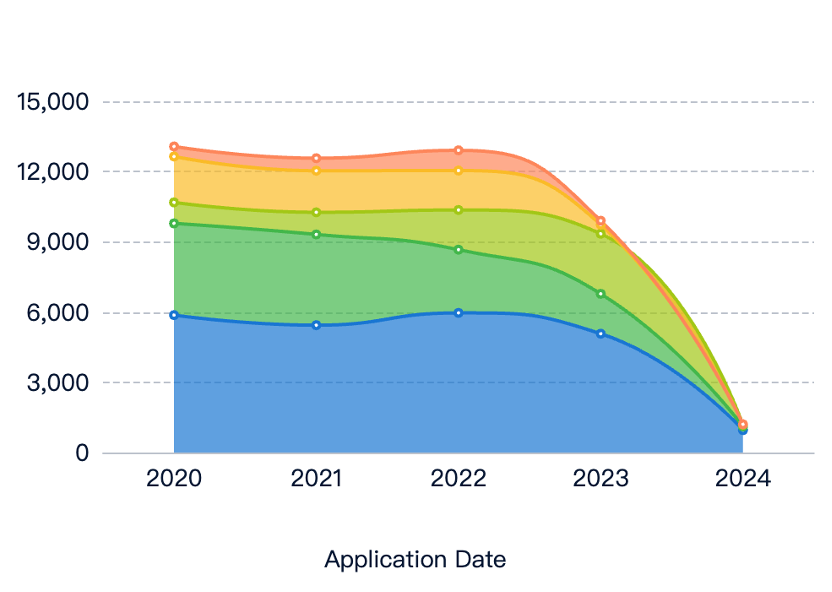
Current State and Challenges
Despite their potential, TPEs face challenges in electronics.
Challenges
- Thermal and Electrical Properties: Need for improved heat resistance and electrical insulation.
- Material Compatibility and Adhesion: Ensuring strong bonding with metals, ceramics, and rigid plastics.
- Processing Complexity: Specialized techniques required for processing and manufacturing.
- Geographical Distribution: Research and development are spread across regions like North America, Europe, and Asia.
Solutions
- Material Formulation: New TPE formulations to enhance properties.
- Advanced Processing Techniques: Innovative methods for better quality and consistency.
Technology Evolution Path
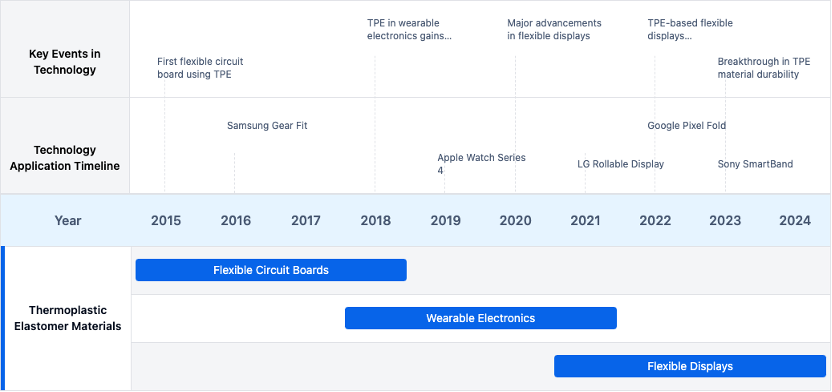
Current Technical Solutions
Thermoplastic elastomer compositions are blends of thermoplastic polymers and elastomers tailored to achieve desired properties such as flexibility, impact resistance, and vibration damping.
Types of TPE Compositions
- Dynamic Vulcanization: Improves mechanical properties and heat resistance.
- Fillers and Additives: Enhance specific properties like flame retardancy and color.
- Specific Applications: Tailored for soling materials, vibration damping, gaskets, hoses, and artificial leathers.
- Improved Processability: Formulated for better melt flow or foaming behavior.
Applications of TPE Materials
- Footwear, Tires, Gaskets, Vibration Damping: Designed to meet performance requirements.
- Additive Manufacturing: Optimized for 3D printing and selective deposition.
Key Players Analysis
The TPE market is competitive with major players like Mitsubishi Kasei Corp., Dai Nippon Printing Co. Ltd., Toray Industries Inc., Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, and Sichuan University leading research and development.
Key Players
- Mitsubishi Kasei Corp.: 2479 patents, focusing on biocompatibility and composite materials.
- Dai Nippon Printing Co. Ltd.: 2564 patents, specializing in carbon nanotubes and electrical conductivity.
- Toray Industries Inc.: 3009 patents, expertise in composite materials and flexible electronics.
- Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur: 160 publications, focusing on biocompatibility and conductive composites.
- Sichuan University: 126 publications, research in composite materials and piezoresistive materials.
Key Technology Insights
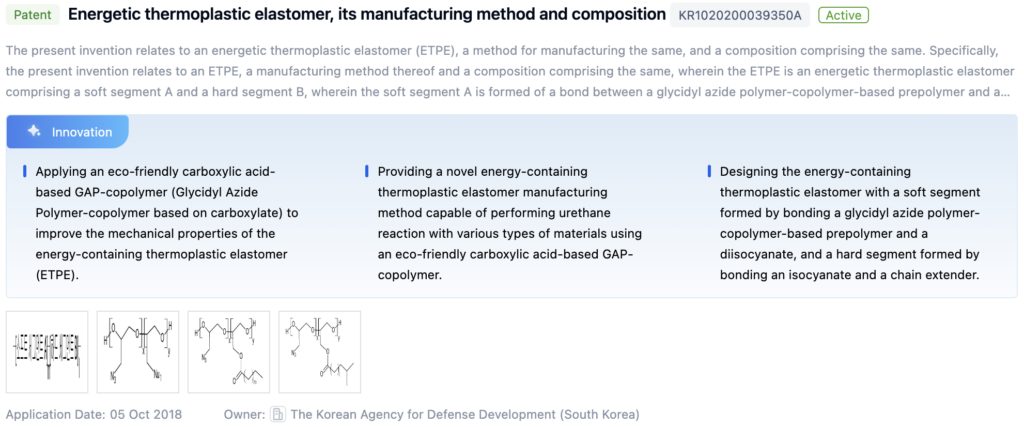
Patent 1: Energetic Thermoplastic Elastomer
- Core Invention Points:
- Eco-friendly carboxylic acid-based GAP-copolymer for improved mechanical properties.
- Urethane reaction with various materials using GAP-copolymer.
- Soft segment formed by bonding glycidyl azide polymer-copolymer and diisocyanate, hard segment formed by bonding isocyanate and chain extender.
Patent 2: Thermoplastic Elastomer with Hot Melt Adhesive
- Core Invention Points:
- SEBS and SEB mixture for better compatibility with PP and improved adhesion.
- Propylene-based olefin polymer as an adhesion modifier.
- Styrene elastomer, polypropylene, and olefin polymer blend for improved adhesion.

Paper 1: Progress in Research of Polypropylene Modified by TPE
- Core Invention Points:
- Classification and toughening mechanism of TPEs.
- Modification of polypropylene with TPEs like TPU, TPS, TPO.
- Predictions for further studies on PP modification by TPEs.

Potential Innovation Directions
Thermoplastic Elastomer Compositions
Various compositions are formulated to achieve desired properties like flexibility, toughness, and processability.
Materials for Specific Applications
Tailored for applications such as vibration-damping materials, footwear components, tire materials, and overmolded articles.
Preparation Methods and Processing
Techniques like compounding, extrusion, molding, and foaming to achieve desired properties, shapes, and forms.
Blends and Composites
Combining TPEs with other materials to create new materials with enhanced properties or functionalities.
Films and Coatings
Used in packaging, protective layers, or decorative surfaces for flexibility, durability, and barrier properties.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
Regulatory and environmental considerations are crucial for TPE adoption in electronics.
Regulations and Standards
- REACH and EPA: Guidelines on the use of chemicals in consumer products.
- Sustainability: Align with circular economy principles, promote resource efficiency, waste reduction, and recyclability.
Compliance
- Ensures safety and sustainability.
- Substitute hazardous substances with safer alternatives.
- Implement rigorous testing and certification processes.
Future Trends in Thermoplastic Elastomers
The future trends in TPEs are promising with potential for innovative applications and advancements.
Key Trends
- Conductive and Electromagnetic Shielding TPEs: For protection against EMI and ESD in electronic devices.
- Integration with Advanced Materials: Incorporation of nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes or graphene.
- Sustainability: Use of bio-based and biodegradable TPEs.
- Self-Healing and Self-Repairing TPEs: Extend the lifespan of electronic components.
- Flexible, Stretchable, and Conformable Electronics: For IoT and wearable technology.
Applications
- Flexible Circuits and Sensors: Conductive TPEs for compact and lightweight components.
- Additive Manufacturing: TPEs combined with 3D printing for complex geometries and customized designs.
- Eco-Friendly Devices: Bio-based TPEs for reduced environmental impact.
- Durable Components: Self-healing TPEs for harsh environments.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

