
Introduction to HD and FHD Resolutions
High Definition (HD) and Full High Definition (FHD) are fundamental resolutions in modern display technology, widely used in video streaming, gaming, and television broadcasting. These resolutions play a pivotal role in determining the clarity and detail of images and videos on screens. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between HD and FHD, their applications, and how to choose the right resolution for your needs.
What Is HD? Key Features Explained
- Resolution: Typically 1280×720 pixels (720p) or 1920×1080 pixels (1080i/p)
- Pixel Density: Approximately 0.9 megapixels per frame (720p) or 2.1 megapixels per frame (1080p)
- Aspect Ratio: 16:9
- Frame Rate: 24, 30, or 60 frames per second
HD, or High Definition, features video resolutions starting at 1280×720 pixels (720p) and going up to 1920×1080 pixels (1080p). It offers sharper and more detailed visuals compared to standard definition, which has only 480 lines in North America. In Europe, standard definition includes 576 lines, making HD a significant improvement in visual clarity. HD uses a widescreen 16:9 aspect ratio, providing a broader field of view. This aspect ratio enhances modern displays and creates a more immersive viewing experience. HD supports both progressive (p) and interlaced (i) scanning methods for different visual effects. Progressive scanning redraws the entire frame, delivering smoother visuals during motion. Interlaced scanning alternates lines, offering sharper images for static visuals. Common frame rates in HD include 60 fps in North America and 50 fps in Europe. These frame rates ensure smoother motion, making HD ideal for sports and gaming. However, HD requires more storage space due to its higher resolution and quality. For example, HD-DVDs can hold up to 15 GB compared to 4.5 GB for standard-definition DVDs. This increase highlights the need for larger and more advanced storage solutions.
What Is FHD? Exploring Full High Definition
- Resolution: 1920×1080 pixels
- Pixel Density: Approximately 2.1 megapixels per frame
- Aspect Ratio: 16:9
- Frame Rate: 24, 30, or 60 frames per second
FHD, or Full High Definition, refers to a display resolution of 1920×1080 pixels, commonly known as 1080p. This resolution delivers sharp, detailed visuals and is a standard for high-definition video content, making it ideal for modern televisions, computer monitors, and streaming platforms. With a widescreen 16:9 aspect ratio, FHD provides an immersive viewing experience suited for various applications, from entertainment to professional use. Supporting both progressive (1080p) and interlaced (1080i) scanning methods, FHD ensures smooth motion and minimal visual artifacts. Its high resolution and clarity make FHD a significant improvement over standard-definition formats, offering exceptional picture quality for a wide range of devices and content.

Key Differences Between HD and FHD
Resolution:
HD typically offers a resolution of 1280×720 pixels, delivering better detail than standard definition (SD) with its 480 visible scanlines. In comparison, FHD (Full HD) boasts a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels, offering four times the clarity and significantly sharper visuals.
Number of Pixels:
HD contains approximately 921,600 pixels (1280×720), while FHD has about 2,073,600 pixels (1920×1080). This makes FHD roughly twice as detailed, resulting in more vibrant and defined images.
Aspect Ratio:
Both HD and FHD share a widescreen-friendly 16:9 aspect ratio, making them ideal for modern TVs, monitors, and video streaming platforms.
Scanning Methods:
HD supports both progressive scanning (p) and interlaced scanning (i). Progressive scanning redraws the entire image for each frame, offering smoother visuals. Similarly, FHD supports both scanning methods, providing versatility for different content formats.
Frame Rates:
Frame rates vary between HD and FHD, with common rates of 50/60 Hz for interlaced formats and 30/60 Hz for progressive formats. These ensure smooth playback, especially in high-motion content.
Image Quality:
FHD significantly outperforms HD in image quality due to its higher resolution and pixel count. The result is sharper, more detailed visuals that enhance the viewing experience for movies, games, and more.
Usage and Display:
While HD is suitable for various devices like HD televisions and online video, FHD is often the preferred choice for high-quality content. Its superior resolution and image clarity make it ideal for premium viewing experiences.
Applications of HD vs. FHD in TVs, Monitors, and Laptops
TVs
- Picture Quality: HD TVs deliver sharper and more detailed images than standard-definition TVs, making fine details like text or facial expressions much clearer. FHD TVs take this further, offering higher resolution and pixel density for an even more immersive viewing experience.
- Content Availability: HD content is widely available on cable TV, satellite TV, and streaming platforms. FHD content is also becoming more common, especially on services that support 1080p resolution.
- Display Technology: Both HD and FHD TVs use display technologies like LCD, Plasma, and DLP. However, advanced options like OLED provide exceptional performance for both resolutions, enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Monitors
- Professional Use: FHD monitors are the go-to choice for graphic design, video editing, and gaming. Their high resolution supports detailed work and improves performance in demanding tasks.
- General Use: For basic tasks like office work, browsing, or multimedia consumption, HD monitors offer an excellent balance of resolution and performance.
- Gaming: Gamers often prefer FHD monitors for their crisp visuals and fast refresh rates, enhancing gameplay and reducing lag.
Laptops
- Portability vs. Performance: HD displays are common in laptops due to their lower power consumption and lighter weight, improving battery life. FHD displays, while slightly heavier, provide better performance and an enhanced viewing experience.
- Content Creation: For detailed work such as video editing, graphic design, or programming, FHD laptops are preferred for their superior resolution and color accuracy.
- General Use: For everyday tasks like streaming, browsing, and office applications, HD laptops strike a practical balance between performance and battery efficiency.
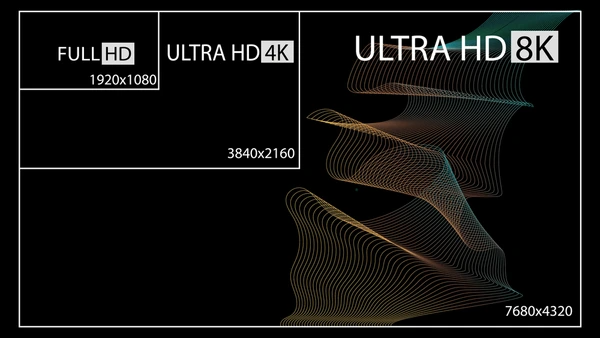
Which Resolution Is Better for Gaming, Streaming, and Work?
Gaming Requirements
For most casual gaming and everyday office work, a 1080P (Full HD) resolution is generally sufficient. However, if you enjoy playing graphics-intensive AAA games, you’ll benefit from higher resolutions like 2K (QHD) or 4K. For smooth 2K gaming, a GPU like the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3070 or higher is typically required. For 4K gaming, even high-performance GPUs like the RTX 3090 Ti may struggle to maintain maximum settings in some games, especially newer titles.
Streaming Needs
Streaming requires a high resolution to deliver clear, sharp video quality to viewers. While 1080P is the minimum standard for most platforms, opting for 2K or 4K provides noticeably better detail and image quality. Higher resolutions are particularly beneficial when streaming high-quality content, as they capture and present finer details more effectively.
Work Requirements
For general office tasks like spreadsheets, browsing, or presentations, 1080P offers more than enough clarity. However, for specialized work like graphic design, video editing, or other visually demanding tasks, higher resolutions such as 2K or 4K are advantageous. They provide increased screen real estate and sharper visuals, which can enhance precision and productivity in detail-oriented tasks.
Conclusion: Choosing Between HD and FHD
Choosing between HD and FHD depends on your specific needs and usage scenarios. HD is a great option for casual viewing, basic gaming, or general work, offering good picture quality and lower storage requirements. FHD, on the other hand, provides sharper visuals, better detail, and an enhanced viewing experience, making it ideal for gaming, professional tasks, and high-quality streaming. Ultimately, the choice comes down to balancing performance, cost, and the level of detail you require.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About HD vs. FHD
1. Can the human eye distinguish between HD and FHD on small screens?
On smaller screens, such as smartphones, the difference between HD and FHD may be less noticeable. However, on larger screens or when viewing up close, FHD’s higher resolution becomes more apparent.
2. Is there a significant price difference between HD and FHD devices?
As technology has advanced, the price gap between HD and FHD devices has narrowed. Nowadays, FHD devices are widely available at affordable prices, making them accessible to a broad range of consumers.
3. Does FHD consume more power than HD?
FHD displays may consume slightly more power due to the increased number of pixels. However, the difference is often minimal and depends on the specific device and display technology used.
4. How does FHD compare to 4K resolution?
FHD has a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels, while 4K (Ultra High Definition) boasts 3840×2160 pixels. This means 4K offers four times the resolution of FHD, resulting in even sharper and more detailed images.
To get detailed scientific explanations of HD vs. FHD, try Patsnap Eureka.

