
Technical Background and Objectives
Background
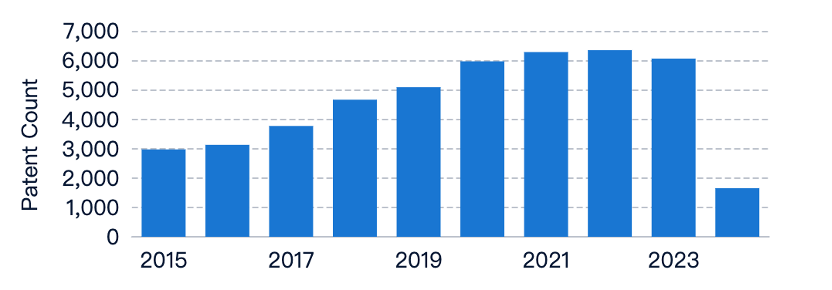
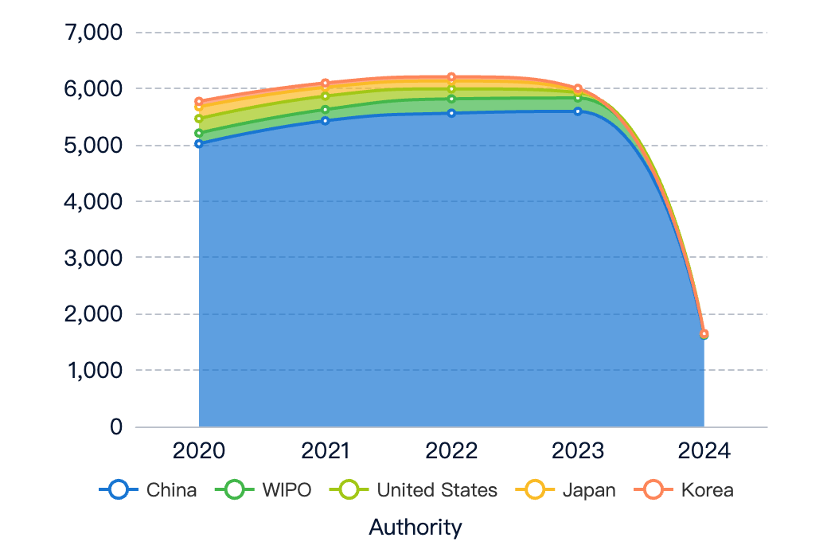
Research on enhancing efficiency in butt welding has seen a steady rise in patent applications over the years, indicating growing interest and research efforts in improving the efficiency of this welding technique. However, the number of related literature publications has remained relatively low and stable. This suggests that the research and development efforts in improving the efficiency of butt welding are primarily driven by industrial and commercial interests, rather than academic or theoretical pursuits. Companies and organizations are actively seeking to develop and patent new techniques or technologies to enhance its efficiency, motivated by the potential for commercial applications and competitive advantages.
Objectives
The primary objective is to develop innovative techniques and methodologies to significantly enhance the efficiency of butt welding processes. This involves addressing challenges in productivity, cost-effectiveness, and quality control, ultimately enabling faster, more precise, and economically viable welding operations.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of Butt Welding, try Eureka.
Technical Current Status Analysis
Butt Welding Overview
Butt welding is widely used in industries such as shipbuilding, construction, pipeline manufacturing, and automotive manufacturing. It involves fusing two metal components together by applying heat and pressure at their abutting edges. High efficiency is crucial for improving productivity, reducing costs, and ensuring the structural integrity of welded joints.
Applications and Impact:
- Shipbuilding: Assembling large steel structures like ship hulls and decks.
- Construction: Fabricating steel structures for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Pipeline Manufacturing: Joining long sections of pipes for oil, gas, and other fluid transportation.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Joining components like vehicle frames, body panels, and exhaust systems.
Technical Characteristics and Challenges:
- Heat Input and Control: Precise control of heat input is crucial for achieving consistent weld quality and minimizing defects.
- Joint Preparation and Fit-Up: Proper joint preparation and fit-up are essential for ensuring a tight fit between the components being welded.
- Welding Position and Accessibility: Welding in different positions and confined spaces can pose challenges.
- Material Properties: Chemical composition, physical properties, and thickness of the materials influence the welding process.
- Automation and Robotics: Implementing automation and robotic welding systems can improve efficiency.
- Weld Defects and Quality Control: Defects like porosity, lack of fusion, and cracking can compromise the welded joint’s integrity.
Technological Paths:
- Advanced Welding Processes: Implementing advanced processes like friction stir welding, laser beam welding, or hybrid welding.
- Process Monitoring and Control: Integrating real-time monitoring and control systems.
- Adaptive and Intelligent Systems: Developing systems that can automatically adjust parameters based on real-time feedback.
- Automation and Robotics: Implementing automated and robotic welding systems.
- Weld Simulation and Modeling: Using computational modeling and simulation tools.
- Advanced Materials and Consumables: Developing and utilizing advanced welding consumables.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Implementing advanced non-destructive testing techniques.
Research Content
Research Objectives
Develop innovative techniques and methodologies that can significantly enhance the efficiency of butt welding processes.
Research Direction and Focus
Advanced Welding Techniques
- Explore and develop advanced welding techniques to expedite the butt welding process without compromising quality.
- Investigate novel welding methods such as friction stir welding, laser beam welding, or hybrid welding processes.
- Optimize existing techniques through process parameter optimization, automation, and real-time monitoring.
Material Characterization and Selection
- Conduct comprehensive material characterization studies to identify and select suitable materials for efficient operations.
- Focus on understanding the metallurgical properties, thermal behavior, and weldability of various materials.
Process Modeling and Simulation
- Develop advanced computational models and simulations to predict and optimize the butt welding process.
- Use modeling techniques such as finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, and machine learning algorithms.
Technical Development Roadmap
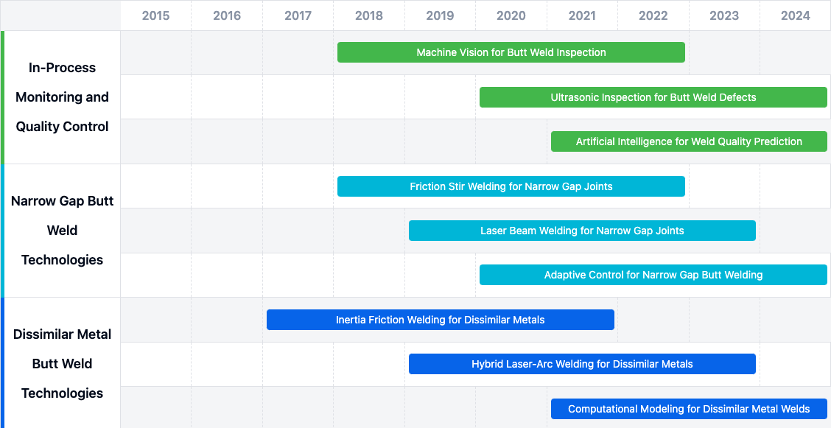
Key Areas of Advancement
- Narrow Gap Butt Weld Technologies: Developing innovative welding processes like friction stir welding and adaptive control systems.
- Dissimilar Metal Butt Weld Technologies: Exploring techniques such as inertia friction welding and hybrid laser-arc welding.
- In-Process Monitoring and Quality Control: Integrating technologies like machine vision, ultrasonic inspection, and artificial intelligence.
Main Player Analysis
Key Players and Focus
- Osaka University: Focus on mitigating hot cracking, joinability of dissimilar materials, and hybrid welding processes.
- Lappeenrannan-Lahden teknillinen yliopisto LUT: Improving the efficiency of laser beam welding for low-alloyed steels and thin sheet materials.
- Kobe Steel Ltd.: Extensive research on optimizing welding parameters and developing advanced welding techniques.
- NIPPON STEEL CORP.: Optimizing welding processes and developing new welding techniques.
- JFE Steel Corp.: Research on optimizing welding parameters and developing advanced welding techniques.
Current Technical Solution Overview
Butt Welding Methods for High-Strength Steel
- Flash Butt Welding Methods: Using electrical resistance to heat and force components together.
- Improved Heat Treatment: Applying specific heat treatment processes before or after welding.
- Improved Joint Design: Optimizing joint design or configuration.
- Hybrid Butt Welding Methods: Combining different welding processes.
- Improved Efficiency: Specialized equipment and techniques to optimize the welding process.
Butt Welding Techniques for Steel Pipes and Tubes
- Methods for Steel Pipes: Techniques for aligning and positioning pipe ends.
- Fixtures and Devices: Specialized tools for accurate and consistent welding.
- Techniques for Specific Materials: Methods tailored for specific types of steel pipes.
- Hybrid and Advanced Methods: Combining multiple welding processes.
Butt Welding Jigs and Fixtures
- Pipe Alignment and Positioning: Jigs and fixtures for proper alignment.
- Improving Weld Quality: Specific procedures and post-weld treatments.
- Efficient Welding: Techniques like laser butt welding and resistance butt welding.
- Joint Design and Finishing: Optimizing joint configurations.
- Specialized Techniques: Tailored for specific applications or materials.
Laser Butt Welding Techniques
- Metallic Strips or Plates: Techniques for improving weld quality and efficiency.
- Dissimilar or Composite Materials: Methods for strong and reliable welds.
- Thin-Walled or Lightweight Materials: Specialized methods to minimize distortion.
- Filler Materials or Wires: Improving weld quality and filling gaps.
- Fixtures, Jigs, and Support Systems: Ensuring proper alignment and support.
Post-Weld Heat Treatment for Butt Welds
- Processes for Welded Joints: Improving properties through controlled heating.
- Localized or Partial Treatment: Techniques for specific weld zones.
- Rail Welded Joints: Methods for improving rail joint properties.
- Equipment and Tooling: Specialized tools for efficient heat treatment.
- Improving Weld Properties: Enhancing toughness and strength through heat treatment.
Key Patent Interpretation
Patent Highlights
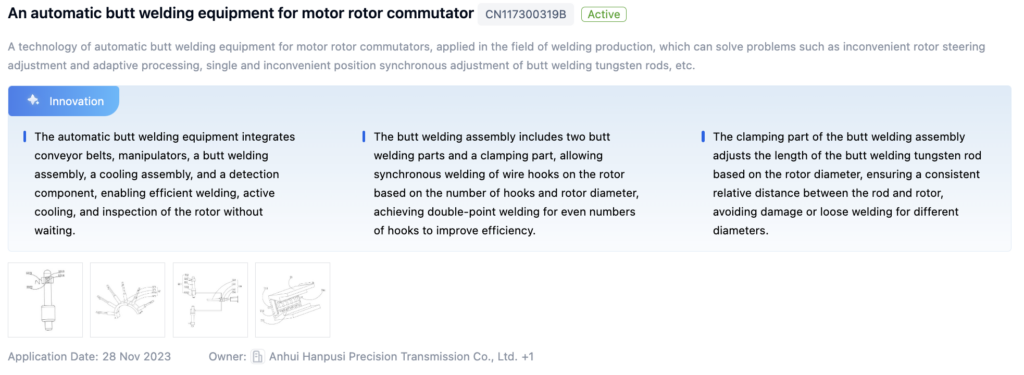
Patent 1: Automatic Butt Welding Equipment for Motor Rotor Commutator
- Core Invention Points:
- Integrated system with conveyor belts, manipulators, butt welding assembly, cooling assembly, and detection component for efficient welding.
- Synchronous welding for even numbers of hooks on the rotor to improve efficiency.
- Adjustable clamping part for consistent welding across different rotor diameters.
Patent 2: Electron Beam Welding Method for Locking Bottom Butt Joints of Large Size Thin-Walled Titanium Alloy Storage Tanks
- Core Invention Points:
- Optimized welding sequence to reduce deformation.
- Different welding methods based on structural characteristics to ensure cleanliness and strength.
- Segmental positioning welding to improve weld width and inspection pass rate.

Patent 3: Automatic Coating and Brazing Butt Welding Equipment for Aluminum Pot
- Core Invention Points:
- Fully automated process replacing manual operations, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Secondary automatic coating and powder dropping for higher product quality.
- Devices to prevent deviations during processing, ensuring consistent quality.

Possible Research Directions
- Butt Welding Methods for High-Strength Steel: Improving weld quality, toughness, and fatigue strength.
- Butt Welding Techniques for Steel Pipes and Tubes: Enhancing weld zone quality and pressure resistance.
- Laser Butt Welding Processes: Achieving high-quality, precise welds.
- Butt Welding Jigs, Fixtures, and Backup Systems: Ensuring proper alignment and joint configuration.
- Post-Weld Heat Treatment Methods for Butt Welds: Enhancing properties and performance of welded joints.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

