
Polycarbonate Light Transmittance Goals
The primary goal of research on light transmittance properties of polycarbonate is to enhance the material’s optical transparency while maintaining its mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. This is essential for applications such as automotive headlights, protective visors, and optical components where clarity is critical.
- Enhancing Transparency: Focus on optimizing the molecular structure and minimizing impurities to reduce light scattering and absorption.
- Advanced Processing Methods: Develop compounding and processing techniques to minimize optical defects such as bubbles and haze.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Explore anti-reflective or scratch-resistant coatings that do not compromise transparency.
- Additives and Fillers: Investigate the impact of additives on light transmittance and find strategies to mitigate negative effects.
- Long-term Performance: Address issues like yellowing and degradation due to UV exposure to maintain high transmittance over the product’s lifetime.
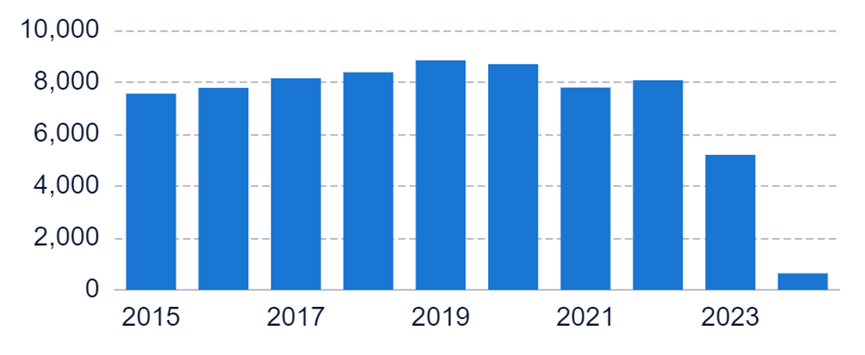
To get a detailed scientific explanations of polycarbonate, try Eureka.
Market Demand for High Transmittance Materials
The demand for high transmittance materials is growing across multiple industries due to their need for optical clarity.
Automotive and Construction Industries
- Automotive Sector: Increasing demand for lightweight, high-strength materials like polycarbonate for windshields and sunroofs, which improve fuel efficiency and safety.
- Construction Industry: High transmittance polycarbonate is used in large glass facades and skylights to create bright, energy-efficient spaces.
Electronics and Emerging Technologies
- Consumer Electronics: Polycarbonate is crucial in optical components like lenses and displays, driven by the need for high-resolution devices.
- Emerging Technologies: Fields like solar energy systems and medical devices require high transmittance materials for optimized performance.
Current State and Challenges of Polycarbonate
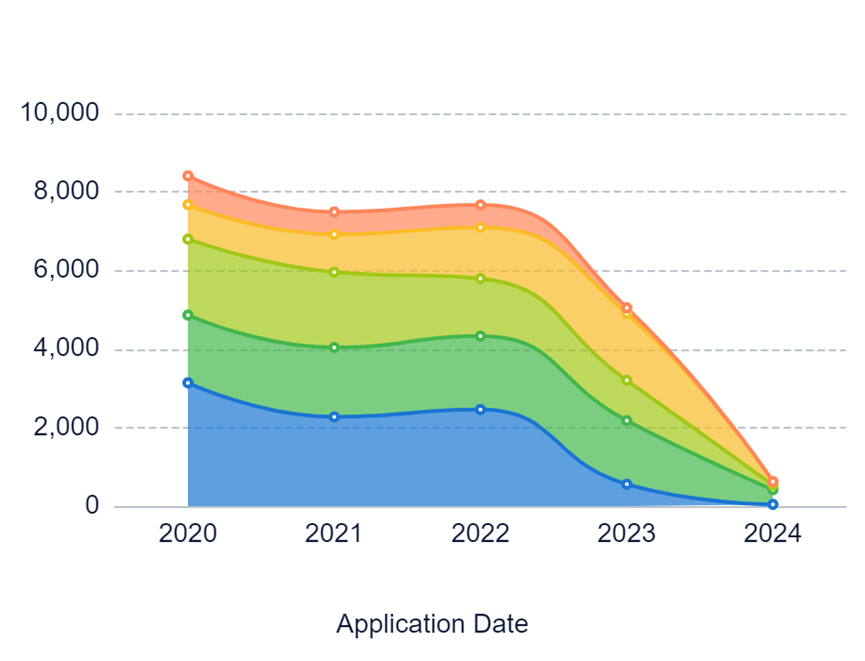
Polycarbonate is known for its optical properties, but achieving high light transmittance is challenging.
Impurities and Processing
- Contaminants: Even trace impurities can cause light scattering, reducing transparency. Maintaining high purity and precise control is essential.
- Manufacturing Conditions: Factors like temperature and shear stress can lead to defects like haze. Optimizing these parameters is crucial for clarity.
Surface Quality and Environmental Resistance
- Surface Defects: Scratches and irregularities reduce transparency, requiring effective surface treatments.
- Environmental Degradation: Exposure to UV radiation and chemicals can cause discoloration over time, affecting light transmittance.
Evolution of Polycarbonate Transmittance Technologies
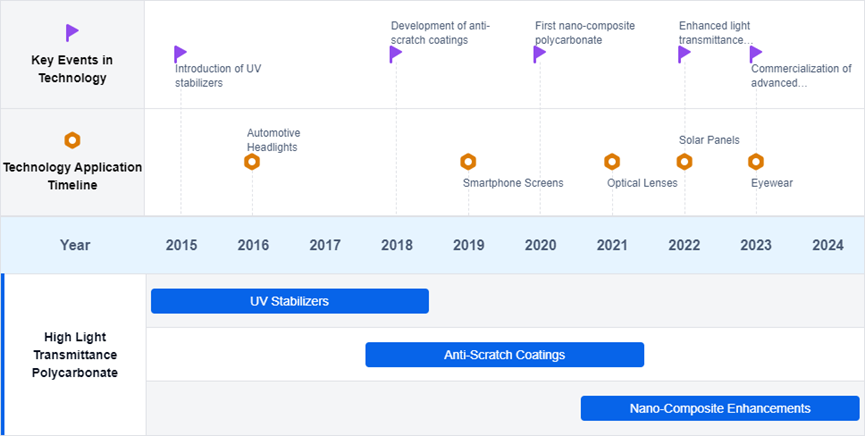
Existing Solutions for Enhancing Light Transmittance
High Transmittance Compositions
Polycarbonate materials with high light transmittance, particularly in the visible light range, have been developed. These materials exhibit excellent optical properties, making them suitable for various applications such as lighting displays and optical components.
Light-Diffusing Compositions
These compositions incorporate agents or fillers to create a diffused light effect, useful in backlight diffusers and light-diffusing films.
Flame-Retardant Compositions
Polycarbonate resins combined with flame retardants maintain high light transmittance while ensuring fire safety, making them ideal for lighting fixtures and electrical enclosures.
Infrared Light Management
Compositions designed for infrared light management are used in applications like remote control lenses and heat management systems, allowing either transmission or blocking of infrared light.
Key Players in Polycarbonate Industry
The competitive landscape for high light transmittance polycarbonate is driven by leading companies with advanced R&D capabilities.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co. Ltd.
Wanhua has developed high-performance polycarbonate with enhanced light transmittance by optimizing the polymer matrix and incorporating advanced additives.
Mitsubishi Engineering-Plastics Corp.
Mitsubishi Engineering-Plastics offers polycarbonate solutions with high light transmittance, achieved through proprietary resin formulations and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Covestro has introduced a polycarbonate grade with superior light transmittance, utilizing precise polymerization control and high-purity raw materials, including UV stabilization.
SABIC Global Technologies BV
SABIC has developed a polycarbonate material with high light transmittance by leveraging advanced copolymerization techniques and nano-scale additives.
Teijin Limited
Teijin offers high-transmittance polycarbonate using a unique polymer blend and advanced extrusion processes to achieve excellent optical clarity.
Core Innovations in Polycarbonate Transmittance
Patent 1: Polycarbonate Resin Composition
This patent covers a composition that combines dyes with different maximum absorption wavelengths to achieve a high visible-light blocking rate and high transmittance at 1550 nm.
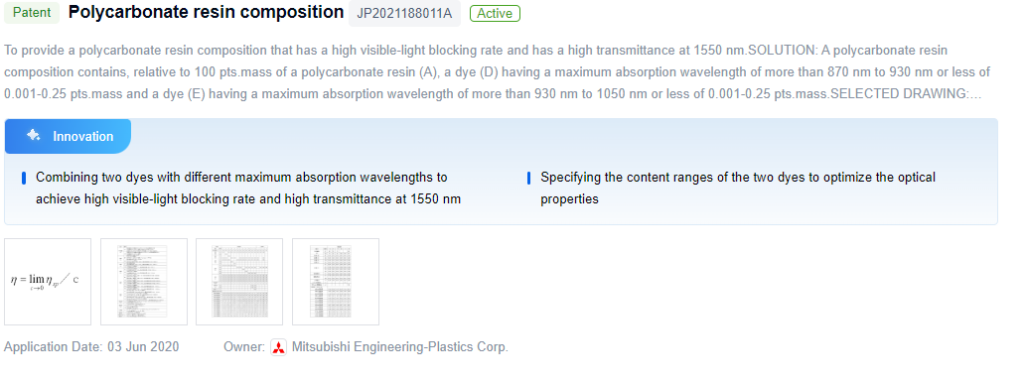
Patent 2: Polycarbonate Resin Composition
Another patent describes a polycarbonate composition with specific dyes to enhance visible-light blocking and transmittance at 1550 nm.
Paper 1: Broadband Anti-Reflection Structures
This study explores fabricating broadband anti-reflection structures on polycarbonate to improve transmittance, increasing it by up to 6%.
Paper 2: Transparent Polymers
Research on transparent polymers with high light transmittance, achieving up to 96% at 450 nm and excellent performance at communication wavelengths.
Potential Breakthroughs in Polycarbonate Applications
High Transmittance Compositions
These compositions focus on enhancing light transmittance for applications requiring high transparency.
Preparation Methods
These methods describes techniques for manufacturing polycarbonate with improved light transmittance, such as polymerization conditions and light-diffusing particles.
Composites with Additional Properties
Polycarbonate composites combine high light transmittance with other properties like flame retardancy and weather resistance.
Light Diffusion and Control
These materials and techniques manage light diffusion or transmission in polycarbonate through specific additives or surface treatments.
Environmental Impact of Polycarbonate Production
Polycarbonate production raises environmental concerns, including greenhouse gas emissions and hazardous waste. The energy-intensive process often relies on fossil fuels, contributing to these issues. Manufacturers are exploring sustainable production methods and implementing waste management strategies to mitigate environmental impact. Regulatory frameworks and industry standards play a crucial role in promoting these practices.
Regulatory Landscape for Polycarbonate Materials
The regulatory landscape for polycarbonate materials is complex, with various national and international bodies overseeing production, use, and disposal. Compliance with regulations such as the EPA and FDA in the U.S., REACH in the EU, and similar frameworks in Asia is essential. Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to fines, recalls, and reputational damage. As regulations evolve, staying informed and compliant is crucial for businesses operating in the polycarbonate industry.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

