
In research, collecting data from an entire population is often impractical and expensive. This is where sampling techniques come into play. One effective method is cluster sampling, which allows researchers to divide a population into groups (clusters) and randomly select clusters for study. Cluster sampling is widely used in survey research, epidemiology, business analytics, and education due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. However, it requires careful design and analysis to minimize bias and maintain accuracy.
This guide will cover:
- What cluster sampling is and how it works
- Types of cluster sampling
- Advantages and limitations
- Real-world examples
- How AI-powered tools like Eureka enhance cluster sampling research
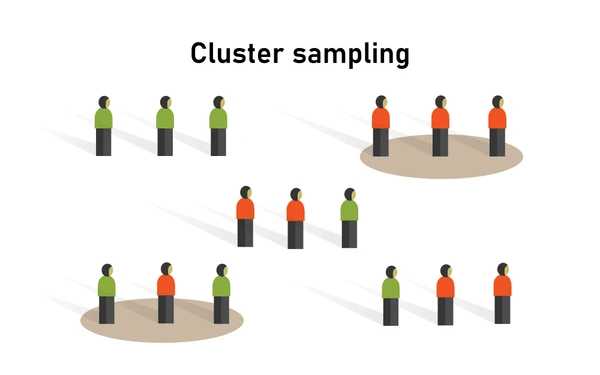
What is Cluster Sampling?
🔹 Definition
Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers divide a population into groups (clusters) and then randomly select entire clusters instead of individual members.
This technique is particularly useful when a population is large, geographically dispersed, or difficult to access individually.
🔹 Key Characteristics
- Divides a population into clusters – Each cluster should represent the overall population.
- Randomly selects clusters – Ensures unbiased representation.
- Studies all individuals within selected clusters – Reduces cost and time compared to simple random sampling.
- Used when population-wide sampling is impractical.
Curious about cluster sampling? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its methodology, advantages, and real-world applications, helping you understand how this sampling technique enhances research efficiency and accuracy.
🔹 Example of Group sampling in Research
📌 National Education Survey
A government agency wants to study student performance nationwide. Instead of selecting random students from each school, they randomly select entire schools (clusters) and collect data from all students within those selected schools.
🔍 Challenge: If selected clusters are not representative, results may be biased.
Types of Cluster Sampling
1️⃣ Single-Stage Cluster Sampling
✅ Definition: The researcher randomly selects entire clusters and studies all individuals within those clusters.
✅ Example: A healthcare study selects 10 hospitals randomly and collects patient data from all admitted patients.
2️⃣ Two-Stage Cluster Sampling
✅ Definition: After randomly selecting clusters, researchers then randomly select individuals within those clusters.
✅ Example: A company surveys random employees from randomly selected branches rather than all employees in those branches.
🔍 Want to optimize your research sampling? Explore Eureka today and elevate your study design with AI-driven insights!
3️⃣ Multistage Cluster Sampling
✅ Definition: Researchers select clusters at multiple levels before choosing individual participants.
✅ Example: A study on consumer behavior randomly selects states, then cities within those states, then stores within cities, and finally customers within stores.
Advantages and Limitations of Cluster Sampling
✅ Advantages
- Cost-effective – Reduces travel and administrative costs.
- Faster data collection – Fewer sampling units make studies more manageable.
- Practical for large populations – Suitable for geographically dispersed groups.
❌ Limitations
- Risk of cluster bias – If clusters are not diverse, findings may not accurately represent the population.
- Higher sampling error – Compared to stratified or simple random sampling.
- Requires careful design – Poorly chosen clusters can distort results.
How to Implement Cluster Sampling in Research
🔹 Step 1: Define the Population
Clearly outline who or what will be studied.
📌 Example: A market research firm studying customer behavior in retail chains.
🔹 Step 2: Identify Clusters
Divide the population into logical, naturally occurring groups.
📌 Example: Clusters could be cities, schools, or hospitals.
🔹 Step 3: Select Clusters Randomly
Use random selection methods to ensure fairness.
📌 Example: Using AI-powered tools like Eureka to eliminate selection bias.
🔹 Step 4: Choose Sampling Technique
Decide whether to use single-stage, two-stage, or multistage sampling.
📌 Example: If a researcher needs specific age groups, two-stage sampling is preferable.
🔹 Step 5: Collect and Analyze Data
Gather data only from selected clusters and perform statistical adjustments.
📌 Example: AI-driven data cleaning in Eureka ensures higher accuracy.
How Eureka Enhances Cluster Sampling Research
🔍 What is Eureka?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that helps researchers:
- Identify optimal sampling techniques for different populations.
- Analyze global trends in research methodology.
- Improve data accuracy with AI-driven validation tools.
🔍 How Eureka Helps in Group sampling
- Cluster Optimization – AI-driven geospatial analysis ensures clusters are truly representative.
- Bias Reduction – Identifies hidden biases in selected clusters before research begins.
- Predictive Sampling Models – Uses machine learning algorithms to predict sampling outcomes.
- Real-Time Data Adjustments – Adapts sample sizes based on new insights during research.
📌 Example of Eureka in Action:
A public health organization using this method to study disease outbreaks can:
- Use AI to select clusters with diverse demographics.
- Compare historical disease trends to validate sampling accuracy.
- Adjust for biases in real-time using Eureka’s dynamic modeling tools.
Conclusion
Cluster sampling is an efficient and cost-effective method for large-scale research. However, choosing the right clusters and ensuring representation are key to avoiding bias.
🚀 Eureka’s AI-powered tools revolutionize this method by:
- Optimizing cluster selection for better representativeness.
- Reducing sampling errors with machine learning-driven corrections.
- Enhancing data reliability through real-time validation.
🔍 Want to optimize your research sampling? Explore Eureka today and elevate your study design with AI-driven insights!
FAQs
1️⃣ What is the main advantage of cluster sampling?
✅ This method is cost-effective and efficient for studying large, geographically dispersed populations.
2️⃣ How does cluster sampling differ from stratified sampling?
✅ This method selects entire groups, while stratified sampling selects individuals from each group.
3️⃣ What are the risks of using cluster sampling?
✅ Cluster bias and higher sampling error are common risks, but AI-powered tools like Eureka help mitigate them.
4️⃣ How does AI improve Group sampling?
✅ AI-powered tools like Eureka analyze global datasets, detect biases, and optimize cluster selection for higher accuracy.
5️⃣ Can Group sampling be used for business analytics?
✅ Yes! Many companies use this method for consumer behavior analysis, market segmentation, and operational efficiency studies.
To get detailed scientific explanations of cluster sampling, try Patsnap Eureka.


