
Innovation is the foundation of progress, driving advancements in technology, healthcare, sustainability, and consumer products. Whether it’s a new gadget, a groundbreaking medical device, or a revolutionary business model, the best inventions address real-world problems while offering a competitive edge. However, coming up with innovative invention ideas is often a challenge. It requires creativity, research, market awareness, and strategic execution. This article provides a structured approach to generating and developing invention ideas, highlighting the role of AI-powered platforms like PatSnap Eureka in streamlining research, validation, and commercialization.
The Invention Process
Looking for your next big invention idea? PatSnap Eureka helps you uncover market gaps, analyze emerging trends, and track competitor innovations, giving you the insights needed to develop groundbreaking products.
Every invention starts as an idea, but transforming that idea into a real-world product or technology involves several crucial steps. By following a structured innovation process, inventors and businesses can maximize their chances of success while reducing risks.
Step 1: Identifying Problems and Needs
The foundation of every great invention is solving a problem or fulfilling an unmet need. The best ideas arise from observing everyday challenges, whether in personal life, industry inefficiencies, or global issues.
Best Practices for Identifying Problems
- Observe daily life challenges and note repetitive issues
- Conduct market research to find gaps in existing products and services
- Explore consumer feedback, online reviews, and complaint forums to identify pain points
- Stay updated on technological advancements and emerging industry trends
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- AI-driven market insights identify unmet consumer needs and technology gaps
- Competitor analysis reveals which industries are evolving and where innovation is lacking
- Scientific literature tracking uncovers emerging problems in science, engineering, and sustainability
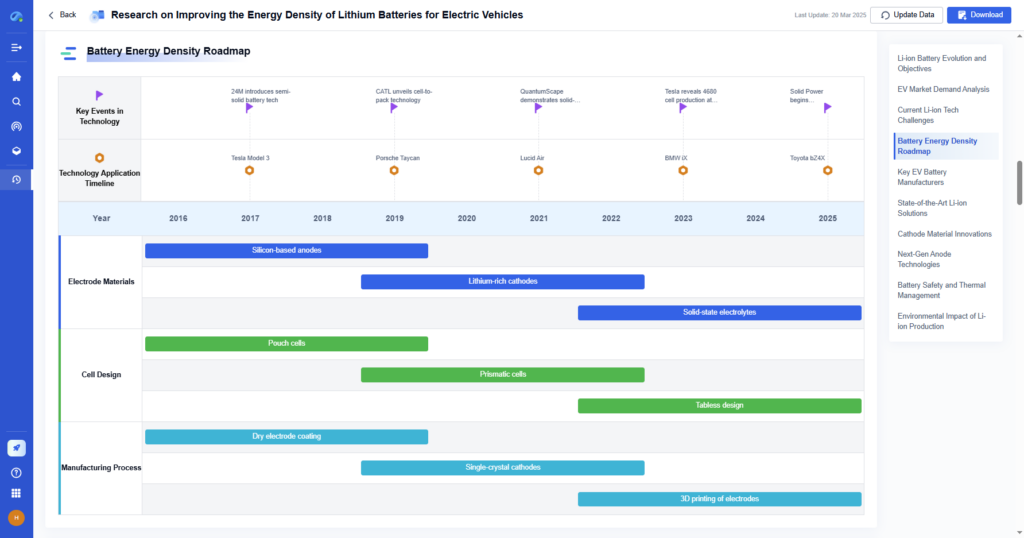
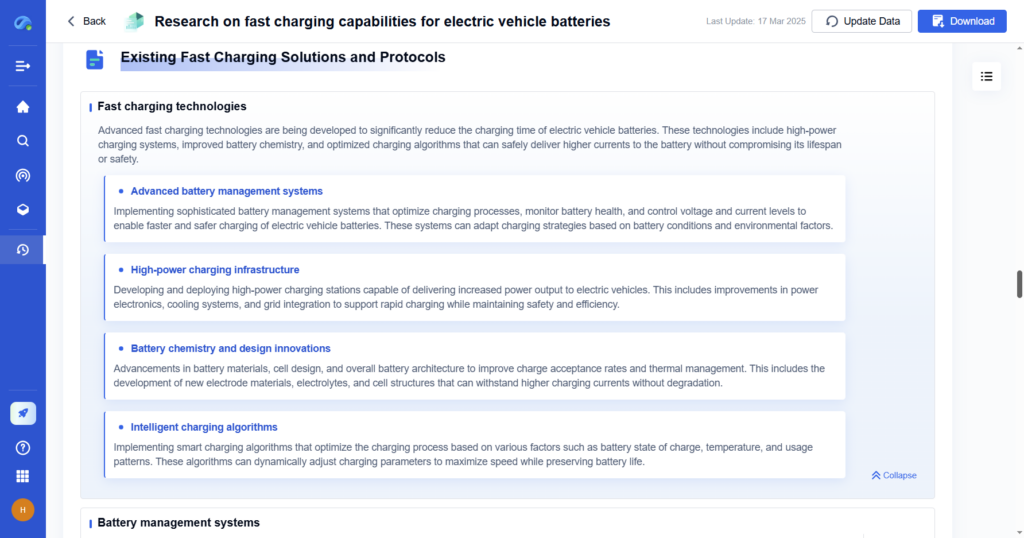
Step 2: Researching Existing Solutions
Before investing time in an invention, it’s essential to analyze the existing market and understand previous solutions. This prevents reinventing the wheel and helps build upon current innovations.
Best Practices for Research
- Conduct patent searches to avoid legal conflicts
- Analyze scientific and technical papers to understand past research
- Study market trends and competitor innovations to identify opportunities
- Investigate government grants and industry funding trends to see what innovations are getting financial backing
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- Comprehensive patent database enables quick searches for similar inventions
- AI-powered literature review extracts key insights from millions of scientific and technical papers
- Competitive intelligence tracks industry leaders’ R&D investments to help identify areas ripe for innovation
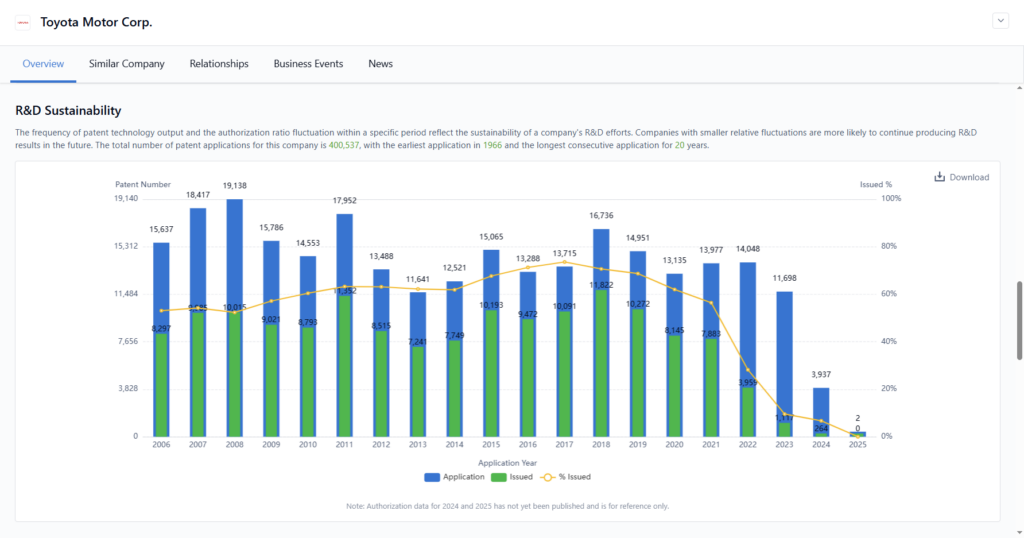
Step 3: Brainstorming and Conceptualizing Ideas
Once problems and existing solutions are analyzed, the next step is to brainstorm and refine invention ideas.
Best Practices for Brainstorming
- Use creative techniques like mind mapping and SCAMPER (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse)
- Combine existing technologies to create new applications
- Look at emerging industries where technology is still developing
- Seek collaboration with experts, engineers, or scientists to refine technical feasibility
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- AI-powered idea validation suggests potential areas of improvement based on patent and literature analysis
- Technology landscape mapping shows how different fields intersect, helping inventors combine innovations in unique ways
- Data-driven brainstorming tools recommend invention ideas based on existing market trends and future projections
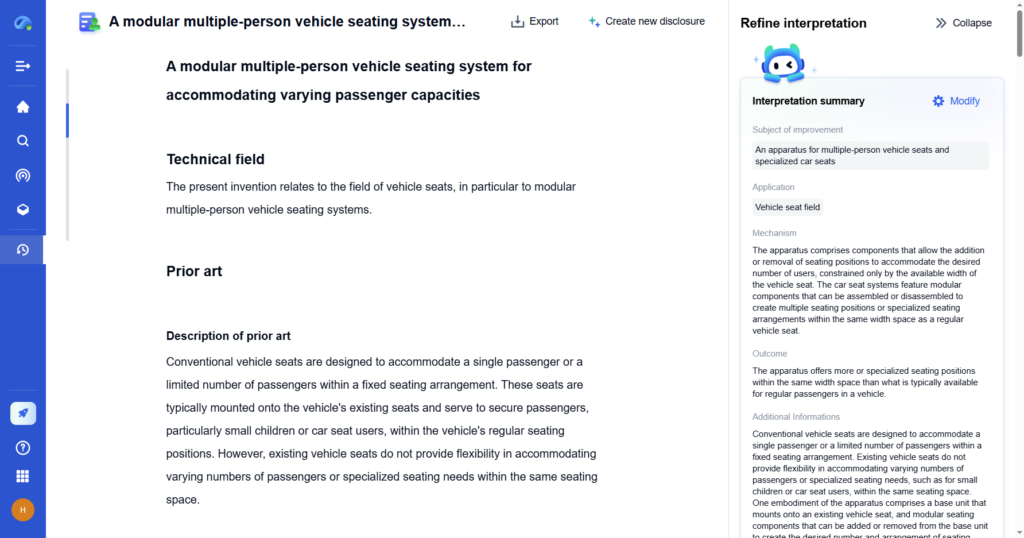
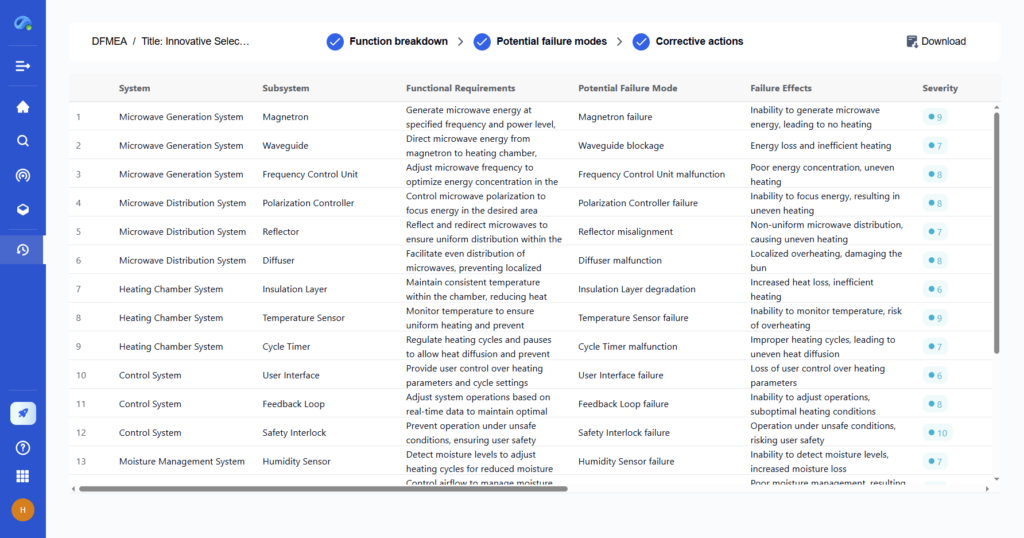
Step 4: Developing a Prototype
Turning an idea into a working prototype is a crucial phase. A prototype helps test feasibility, refine functionality, and attract investors or partners.
Best Practices for Prototyping
- Start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) – a basic version with core features
- Use 3D modeling software and rapid prototyping tools to test early concepts
- Conduct small-scale testing to refine design and performance
- Gather feedback from early testers or industry experts before mass production
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- Material selection databases provide information on optimal materials for durability, efficiency, and sustainability
- Patent similarity search helps inventors refine their design by analyzing similar prototypes
- Technology performance benchmarking compares new inventions against existing industry standards
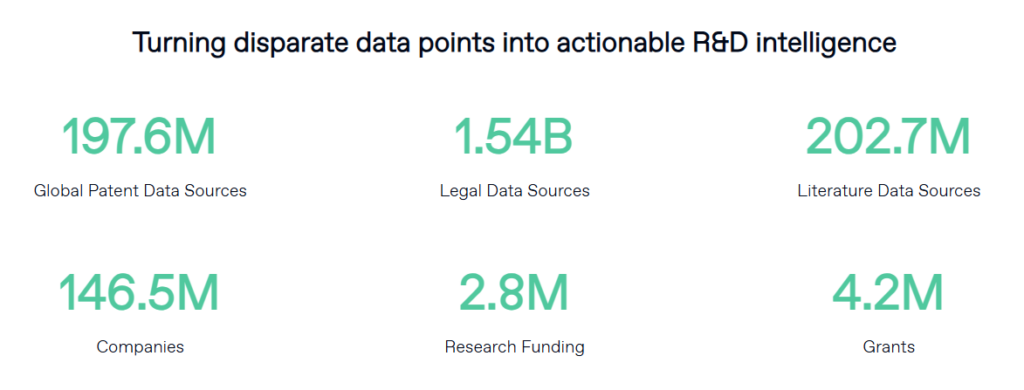
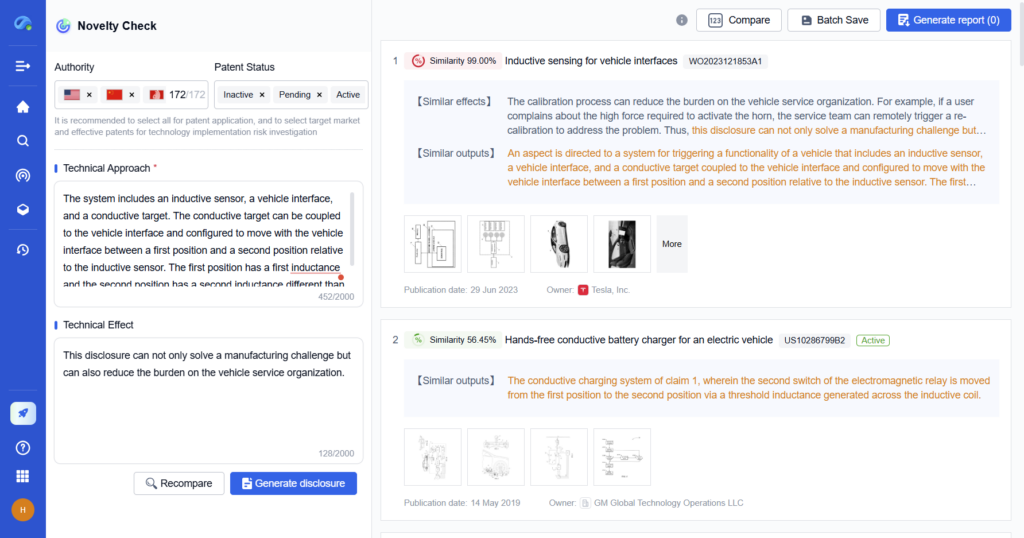
Step 5: Protecting Intellectual Property (IP)
Securing intellectual property rights prevents competitors from copying your invention and ensures market exclusivity.
Best Practices for IP Protection
- Conduct a prior art search to check if your invention is truly unique
- File for a patent early to establish ownership
- Consider trademarking your invention’s name for branding protection
- Monitor global patent filings to track competitor activity
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- Automated prior art searches find existing patents that may impact your invention’s patentability
- IP risk assessment tools identify potential legal conflicts or licensing opportunities
- Patent monitoring dashboards track competitor filings in real-time
Step 6: Testing and Refining the Invention
Before launching the product, rigorous testing and refinement ensure that the invention meets quality, safety, and consumer needs.
Best Practices for Testing
- Perform real-world testing under different conditions
- Use third-party experts for unbiased validation
- Iterate based on user feedback to optimize the final design
- Address regulatory compliance and industry standards
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- User feedback analysis tools collect insights from market testing and competitor reviews
- AI-driven performance tracking monitors key metrics to evaluate efficiency, durability, and usability
- Regulatory compliance databases provide up-to-date legal requirements across different countries and industries
Step 7: Commercializing and Scaling the Invention
Once the invention is refined and protected, the final step is bringing it to market.
Best Practices for Commercialization
- Develop a go-to-market strategy, including pricing, branding, and sales channels
- Identify potential licensing or partnership opportunities with industry leaders
- Secure funding from investors or government grants
- Continuously monitor market feedback and be ready to adapt
How PatSnap Eureka Helps
- Market readiness assessment tools evaluate whether your product is viable for mass adoption
- Investment and funding tracking identifies potential venture capital firms or grant opportunities
- Competitor pricing analysis provides insights on optimal pricing strategies for market penetration
Conclusion
The process of generating and developing invention ideas requires a mix of creativity, research, strategic execution, and market intelligence. By following this structured step-by-step approach, inventors can increase their chances of success and avoid common pitfalls. By leveraging advanced AI-driven insights, inventors and businesses can turn great ideas into commercially viable products with confidence. Want to accelerate your invention process? Start using PatSnap Eureka today.


