
Torque Wrench Technology Background and Goals
Torque wrenches are essential tools used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing to ensure proper tightening of fasteners. Accurate torque measurement is crucial for maintaining the integrity of assembled components and preventing failures. The goal of improving torque wrench measurement accuracy is to enhance precision, reliability, and safety in critical applications.
Over the years, the evolution of torque wrench technology has been driven by the need for higher precision and repeatability in torque measurement. Early designs relied on mechanical mechanisms like deflecting beams or torsion bars, which were susceptible to wear, temperature variations, and human error, leading to inaccuracies over time. Advancements in electronics and sensor technology have led to modern torque wrenches incorporating digital displays, strain gauges, and other electronic components, improving measurement accuracy and enabling real-time torque monitoring, data logging, and calibration.
Despite these improvements, challenges remain in achieving higher levels of measurement accuracy. Factors such as friction, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical wear can still introduce errors and inconsistencies in torque readings. The need for frequent calibration and maintenance can also be time-consuming and costly, particularly in high-volume production environments.
To get detailed scientific explanations of torque wrenches, try Patsnap Eureka TechResearch.
Market Demand for Accurate Torque Measurement
Accurate torque measurement is crucial across industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. The demand arises from the need to ensure proper assembly, prevent over-tightening or under-tightening of fasteners, and maintain product quality and safety standards.
In the automotive world, precise torque measurement is crucial for assembling key parts like engines, suspensions, and wheels. Likewise, in aerospace, torque control becomes critical for assembling aircraft components, where small errors can be disastrous. Construction also depends on accurate torque for installing structural elements, ensuring stability and strength. Similarly, manufacturing demands consistent torque application to fit parts correctly, avoiding damage and boosting product durability.
As industries focus on quality control and meeting standards, demand for precise torque tools keeps rising. Regulatory bodies enforce strict torque rules, requiring calibrated wrenches for crucial tasks. With the rise of automation and robotics, industries are increasingly driven to prioritize accuracy, safety, and efficiency.
Current State and Challenges of Torque Wrench Technology
While torque wrenches are indispensable tools in various industries, several challenges impact their accuracy:
- Wear and Tear: The internal components of torque wrenches experience friction and wear over time, leading to inaccurate torque readings. Exposure to harsh environments like extreme temperatures and chemicals can accelerate this degradation.
- Calibration Challenges: Proper calibration is crucial for maintaining accuracy, but inconsistencies in calibration equipment, procedures, and operator skills can introduce errors.
- Design and Manufacturing Issues: Variations in material properties, manufacturing tolerances, and assembly processes can result in deviations from intended specifications, affecting accuracy.
- Geographical Factors: Different regions may have varying standards, regulations, and environmental conditions, influencing the performance and accuracy requirements of torque wrenches.
To address these challenges, the industry is exploring new technologies and approaches, such as advanced materials, improved manufacturing processes, and innovative calibration techniques. The integration of digital technologies like sensors and data analytics is also being explored to enable real-time monitoring and adjustment of torque measurements.
Evolution of Torque Measurement Technologies
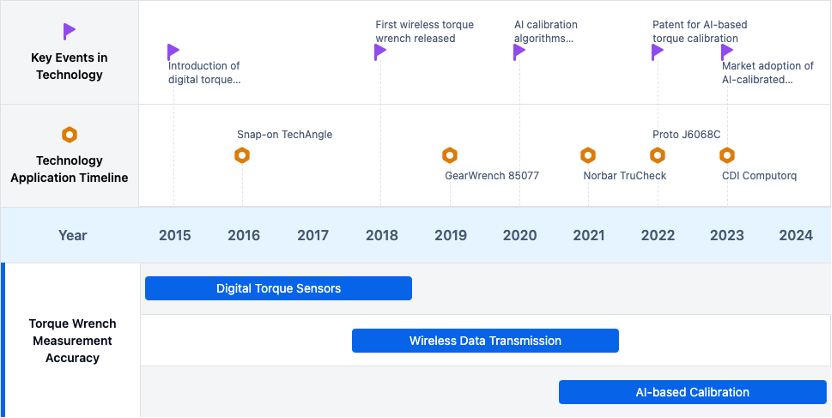
Existing Solutions for Torque Measurement Accuracy
Torque Wrench Accuracy Measurement Devices:
Various devices and methods are used to measure and test the accuracy of torque wrenches, including calibration consoles, testing devices, and measurement instruments designed to evaluate precision. These devices typically apply a known torque to the wrench and compare the measured value with the applied torque to determine accuracy. Some devices also allow for calibration and adjustment of the torque wrench.
Torque Wrench Calibration and Adjustment Mechanisms:
Several patents describe mechanisms and methods for calibrating and adjusting the torque value of a torque wrench. These may involve adjustable components within the wrench or external calibration devices to ensure accurate and consistent torque measurements.
Torque Wrench with Integrated Torque Measurement and Display:
Some torque wrenches incorporate electronic components and sensors to directly measure and display the applied torque, improving accuracy and providing real-time feedback to the user.
Torque Wrench with Angle Measurement and Control:
In addition to torque measurement, some wrenches include angle measurement capabilities, allowing for precise control of the tightening angle, important in certain applications.
Portable and Compact Calibration Devices:
Portable calibration devices are designed for convenient, on-site calibration of torque wrenches, making them easier to transport and use in various field settings.
Key Players in Torque Wrench Industry
Atlas Copco Industrial Technique AB:
Developed advanced torque wrenches with integrated sensors and digital interfaces to improve measurement accuracy, utilizing real-time data analytics and feedback systems to ensure precise torque application.
NSK Ltd.:
Known for precision engineering and ergonomic designs in torque wrenches, NSK products are reliable and accurate, utilizing advanced mechanical and electronic components.
Robert Bosch GmbH:
Offers torque wrenches equipped with Bluetooth connectivity and advanced calibration technologies, focusing on user-friendly interfaces and robust data logging capabilities.
Snap-On Inc.:
Provides torque wrenches with digital displays and programmable settings, featuring advanced strain gauge technology for high precision.
ABB Group:
Focuses on integrating torque wrenches with industrial automation systems, including smart torque wrenches that can be monitored and controlled remotely for high accuracy and efficiency.
Core Innovations in Torque Measurement
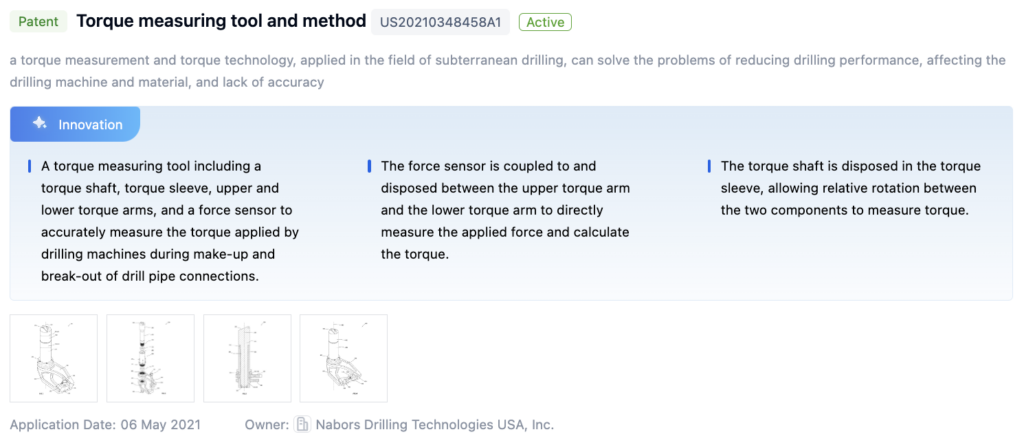
Patent 1: Torque Measuring Tool and Method
- Core Points:
- Includes a torque shaft, torque sleeve, upper and lower torque arms, and a force sensor to measure the torque applied by drilling machines.
- The force sensor is coupled to and disposed between the upper and lower torque arms to directly measure the applied force and calculate torque.
- The torque shaft is disposed in the torque sleeve, allowing relative rotation between components to measure torque.
Patent 2: Torque Wrench with Force Indication
- Core Points:
- Utilizes pressure-sensitive material in the gripping portion to exhibit a signal when a predetermined force is applied.
- The signal can be electric, color-based, motion-based, or audio-based, allowing simple and direct torque measurement.
- The pressure-sensitive material is non-toxic and compatible for hand-use, suitable for repeated use.

Potential Breakthroughs in Torque Wrench Technology
Torque Wrench Calibration and Accuracy Testing Devices:
Devices designed to calibrate torque wrenches include consoles and testing tools, comparing applied torque to ensure precise accuracy.
Torque Measurement Methods and Techniques:
Various methods and techniques, such as sensors, angle measurement, and peak hold measurement, are employed to accurately measure the torque applied by a torque wrench, particularly at lower torque values.
Torque Wrench Design and Components for Improved Accuracy:
Optimizing the design and components of torque wrenches to enhance measurement accuracy, including features like precise torque-measuring devices and manual operating torque sensing.
Torque Wrench Calibration and Adjustment Methods:
Methods and systems developed for calibrating and adjusting torque wrenches to maintain their accuracy over time, involving adjustment devices, calibration procedures, or techniques for setting and verifying torque values.
Regulatory Landscape for Torque Tools
In the field of torque tools, regulatory bodies ensure safety, accuracy, and standardization. The regulatory landscape includes various national and international standards, guidelines, and certification requirements governing the design, manufacturing, and calibration of torque wrenches.
Key standards include the ISO 6789 series, which specifies requirements for hand torque tools, including design, performance, and testing procedures. Compliance with these standards ensures consistent quality, accuracy, and reliability across different manufacturers and models.
Regional organizations like the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the British Standards Institution (BSI) also provide standards and guidelines for torque tools. Regular calibration and certification processes are mandated by regulatory bodies to maintain the accuracy of torque wrenches.
Industry-specific regulations may apply to torque tools used in critical applications, imposing stricter requirements for traceability, documentation, and quality control. Compliance with these standards is essential for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users to ensure product safety, quality, and acceptance in different markets.
Environmental Impact of Torque Wrench Technologies
The environmental impact of torque wrench technologies is a crucial consideration throughout their lifecycle. The production of torque wrenches involves resource extraction, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the use of hazardous materials in manufacturing can pose environmental risks.
During operation, maintenance and calibration processes may involve the use of lubricants, solvents, or chemicals that can harm the environment if not properly managed. At the end of their useful life, torque wrenches pose challenges in terms of disposal or recycling, particularly electronic components.
Mitigating the environmental impact requires sustainable practices, including using eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, proper waste management, and recycling programs. Research and development should focus on designing torque wrenches with improved durability, easier disassembly for recycling, and the use of renewable or biodegradable materials.
By addressing these aspects and continuously innovating, torque wrench technology can significantly improve, leading to more efficient, reliable, and environmentally sustainable tools for various industries.
If you want in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Patsnap Eureka TechResearch. Try now!

