
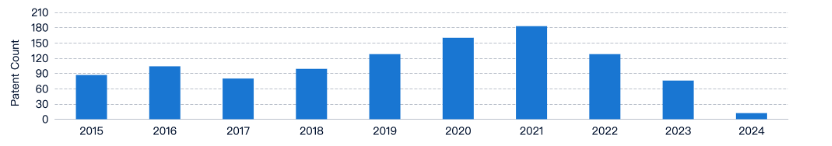
Smart TPE Development Goals and Background
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) combines the properties of thermoplastics and elastomers, offering flexibility, elasticity, and processability. The integration of smart functions into TPE materials aims to incorporate intelligent features such as self-healing, shape memory, stimuli-responsiveness, and sensing capabilities. By leveraging material science advancements, smart TPE can adapt to environmental conditions, respond to external stimuli, and potentially self-repair or self-modify. This development expands their application scope across industries like automotive, aerospace, healthcare, robotics, and consumer electronics. The background involves material science, nanotechnology, and advanced manufacturing techniques, with approaches including functional nanoparticles, stimuli-responsive polymers, and additive manufacturing.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of tpe, try Eureka.
Market Demand for Smart TPE Applications
The market demand for smart TPE applications is driven by the need for advanced materials with enhanced functionalities across various industries. Smart TPEs offer unique advantages, enabling product innovation and performance improvement.
- Automotive Industry: Used in interior components like instrument panels and door trims, and exterior applications like bumpers, providing self-healing, self-cleaning, and temperature regulation.
- Healthcare Sector: Employed in medical devices, prosthetics, and wearables, offering biocompatibility, antimicrobial properties, and moisture management.
- Consumer Electronics: Integrated into smartphone cases and wearable devices for impact resistance, self-healing, and temperature regulation.
- Sports and Leisure Industry: Used in athletic equipment and protective gear for breathability, moisture management, and self-cleaning capabilities.
- Sustainability Focus: Biodegradable or recyclable smart TPEs align with the global push towards a circular economy and environmental consciousness.
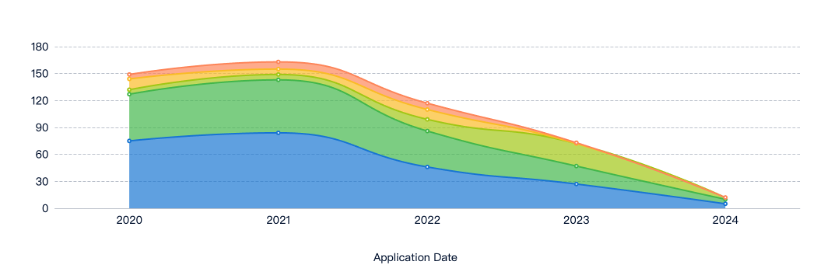
Current State and Challenges of Smart TPE
Integrating smart functions into TPEs presents several challenges:
- Homogeneous Dispersion: Achieving uniform distribution of functional fillers like conductive particles or responsive polymers without compromising mechanical properties.
- Maintaining Smart Properties: Ensuring stability and durability of smart functionalities under various environmental conditions.
- Processing Conditions: Controlling shear forces, temperature profiles, and residence times during manufacturing to prevent degradation or loss of functionality.
- Compatibility: Addressing interfacial adhesion or chemical incompatibility between the TPE matrix and functional additives.
- Commercial Availability: Limited availability and high production costs of smart TPEs, and scaling up manufacturing processes while maintaining quality.
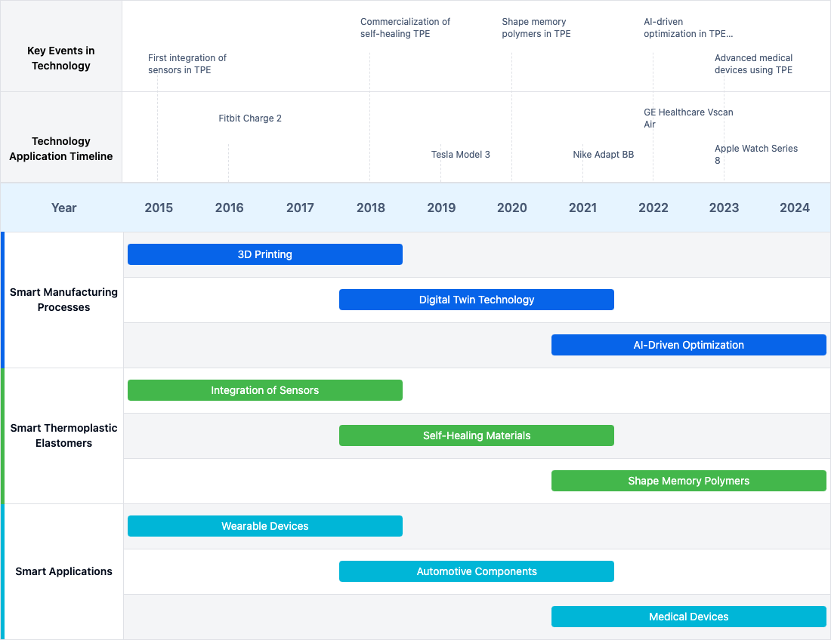
Evolution of Smart TPE Technologies
Existing Smart TPE Solutions
TPE Materials with Thermal Properties
These materials exhibit enhanced thermal properties such as heat resistance, temperature resistance, or thermochromic properties. They are designed for high-temperature applications or to change color in response to temperature changes.
TPE Materials with High Temperature Resistance
Designed to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation, achieved through careful selection of polymer components and additives.
TPE Materials with Self-Reinforcing or Self-Crosslinking Properties
Formulated to enhance thermal and mechanical properties through internal crosslinking or reinforcement during processing or use.
TPE Materials with Thermal Insulation or Heat Dissipation Capabilities
Designed to either insulate against heat transfer or facilitate heat dissipation, depending on specific requirements.
TPE Materials with Thermochromic or Thermosensitive Properties
Change color or other properties in response to temperature changes, used in applications like temperature indicators or smart packaging.
TPE Materials for Thermal Management in Electronic Devices
Formulated for thermal management applications in electronic devices, providing suitable thermal properties and electrical insulation.
TPE Materials for Specific Applications
Tailored for applications such as medical supplies, non-pneumatic tires, refrigerator sealing strips, voltage-withstanding cables, or washing machine drain pipes.
TPE Materials for Cable Sheathing and Insulation
Formulated with additives and modifications for properties like flame retardancy, electromagnetic shielding, and environmental resistance.
TPE Materials for Medical and Healthcare Applications
Meeting requirements for medical applications such as infusion tubes and catheters, offering properties like antibacterial and skin-friendly characteristics.
TPE Materials for Automotive and Transportation Applications
Tailored for applications like non-pneumatic tires and sealing strips, offering properties like high elasticity and weather resistance.
TPE Materials with Advanced Functionalities
Incorporating properties like moisture-wicking, sunlight degradability, or texture mimicry for applications in sportswear, packaging, or decorative products.
TPE Materials with Improved Processing and Manufacturing Capabilities
Enhanced for processing and manufacturing, improving production processes and enabling new TPE products with unique properties.
TPE Materials with Conductive or Dielectric Properties
Possessing enhanced conductive or dielectric properties for applications requiring electrical conductivity, low dielectric constant, or fire resistance.
TPE Materials with Improved Mechanical Properties
Exhibiting enhanced mechanical properties like high elasticity, wear resistance, or scratch resistance for durability and improved grip.
TPE Composite Materials and Blends
Combining TPE with other materials like nylon, glass fibers, fullerene, or graphene for synergistic properties or enhanced performance.
Key Players in Smart TPE Industry
Virginia Tech
Research on programmable shape change in bio-inspired TPE bilayers for applications in soft robotics, biomedical devices, and adaptive structures.
Apple Inc.
Patent portfolio for TPE-based components with haptic feedback, shape memory, and self-healing properties for consumer electronics and wearable devices.
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
Research on smart TPEs with stimuli-responsive properties like shape memory and self-healing abilities for applications in actuators, coatings, and smart textiles.
ResMed Pty Ltd.
Patents for TPE-based components with shape memory, breathability, and antimicrobial properties for medical devices like respiratory masks and tubing.
Ningbo Renhe Technology Co. Ltd.
Patents for TPE-based components with shape memory, self-healing, and thermal insulation properties for automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
Core Innovations in Smart TPE
Patent 1: Cold-Resistant High-Elasticity Flame-Retarding TPE Composite Material
- Core Invention Points:
- Carbon fiber treated with polyamide wax improves elasticity.
- Compounding SEBS, POE, PP, and other raw materials for high-elastic TPE with cold and high-temperature resistance.
- Simple preparation process suitable for industrial production.

Patent 2: High-Fogging Halogen-Free Flame-Retardant TPE for Electric Wires and Cables
- Core Invention Points:
- In-situ micro-crosslinking technology using the double bond in SBS for a high matte effect.
- Achieving a full matte appearance while maintaining other properties of the TPE cable material.

Paper 1: Deformation- and Temperature-Responsive Elastomer Composites for Smart Device Applications
- Core Invention Points:
- Electrical properties of carbon whisker reinforced TPE composites vary with temperature and deformation.
- Potential electromechanical and electrothermal applications due to significant resistivity changes.

Paper 2: Programmable Shape Change in Bio-Inspired TPE Bilayers
- Core Invention Points:
- TPE bilayers can bend, curl, and twist upon strain release.
- Reversible deformations through low-temperature heat application.

Future Directions for Smart TPE
TPE Materials with Conductive Properties
Designed for electrical conductivity, achieved by incorporating conductive fillers, useful for applications like electrical shielding and antistatic properties.
TPE Materials with Thermal Regulation Capabilities
Exhibiting heat resistance or thermochromic behavior, suitable for high-temperature or temperature-sensing applications.
TPE Materials with Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Engineered for high elasticity, wear resistance, or scratch resistance through specific polymer blends and reinforcing fillers.
TPE Materials with Functional Surface Properties
Designed for hydrophobicity, anti-fouling, or self-cleaning capabilities, achieved through surface modification techniques.
TPE Materials for Specialized Applications
Tailored for specific applications like medical devices, non-pneumatic tires, or electronic component encapsulation.
Regulatory Landscape for Smart TPE
The regulatory landscape for smart TPEs involves:
- Material Safety and Environmental Impact: Compliance with guidelines from agencies like the EPA and ECHA.
- Product Safety and Consumer Protection: Standards from bodies like the CPSC and GPSD.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Securing patents through offices like the USPTO and EPO.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Compliance with sector-specific regulations from agencies like the FDA and FAA.
Environmental Impact of Smart TPE
The environmental impact of smart TPEs involves:
- Hazardous Substances: Proper handling and disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
- Energy Consumption: Evaluating and optimizing energy use during production and operation.
- End-of-Life Management: Developing recycling technologies and circular economy strategies.
- Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs): Quantifying environmental impact throughout the TPE life cycle.
Collaboration between industry, academia, and regulatory bodies is essential to establish guidelines and best practices for sustainable smart TPE production and use.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

