
Haptic Feedback Technology Background and Goals
Haptic feedback technology, also known as tactile feedback or force feedback, has been evolving over several decades. Its integration into automotive applications, particularly steering wheels, is a relatively new and rapidly advancing field. The primary goal of incorporating haptic feedback into steering wheels is to enhance driver safety and awareness by providing tactile alerts and cues that complement visual and auditory warnings. This technology development is driven by the increasing demand for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and the need to reduce accidents caused by driver distraction or inattention.
The integration of haptic feedback technology into steering wheels aims to achieve several objectives:
- Intuitive Alerts: Provide non-intrusive tactile alerts to warn drivers of potential hazards, lane departures, or critical situations.
- Enhanced Driving Experience: Offer a more immersive and responsive control interface that improves the overall driving experience.
- Navigational Assistance: Convey navigational cues effectively, reducing cognitive load on drivers.
As the automotive industry continues to prioritize safety and user experience, the integration of haptic feedback technology into steering wheels is expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of driving.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of the integration of haptic feedback technology into steering wheels, try Eureka.
Market Demand for Tactile Alerts in Vehicles
The market demand for tactile alerts in vehicles has been growing due to the increasing emphasis on driver safety and awareness. As vehicles become more technologically advanced and driver distractions increase, innovative solutions that can effectively capture the driver’s attention and convey critical information are needed.
Key factors driving this demand include:
- Limitations of Visual and Auditory Alerts: Visual alerts can be missed if the driver’s attention is elsewhere, and auditory alerts can be drowned out by external noise. Tactile alerts provide a direct and intuitive means of communication that bypasses these limitations.
- Integration with ADAS: As ADAS technologies become more prevalent, tactile alerts delivered through the steering wheel offer a natural extension of these systems, enhancing the driving experience.
- User Experience and Personalization: Consumers seek vehicles that prioritize safety and provide a comfortable and engaging driving experience. Tactile alerts can be tailored to individual preferences, enhancing the overall experience.
Moreover, tactile alerts have potential applications beyond safety, such as navigation assistance and enhancing in-vehicle entertainment systems.
Current State and Challenges of Haptic Feedback in Steering Wheels
The integration of haptic feedback technology into steering wheels faces several challenges:
- Balance Between Feedback and Distraction: Poorly implemented haptic systems could inadvertently distract drivers, compromising safety.
- Complexity of Design: Designing haptic feedback systems that accurately convey various types of alerts and information requires sophisticated algorithms and control mechanisms.
- Ergonomic Factors: Drivers have varying sensitivity levels, requiring customizable systems to accommodate individual needs.
- Compatibility and Integration: Haptic feedback systems must seamlessly interface with other vehicle systems, such as ADAS, without causing conflicts.
- Durability and Reliability: Steering wheels are subject to harsh environmental conditions, requiring robust and long-lasting haptic components.
- Cost and Scalability: Manufacturers must balance the benefits of enhanced safety with the associated costs and manufacturing complexities.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful implementation and widespread adoption of haptic feedback in the automotive industry.
Evolution of Haptic Feedback Technologies
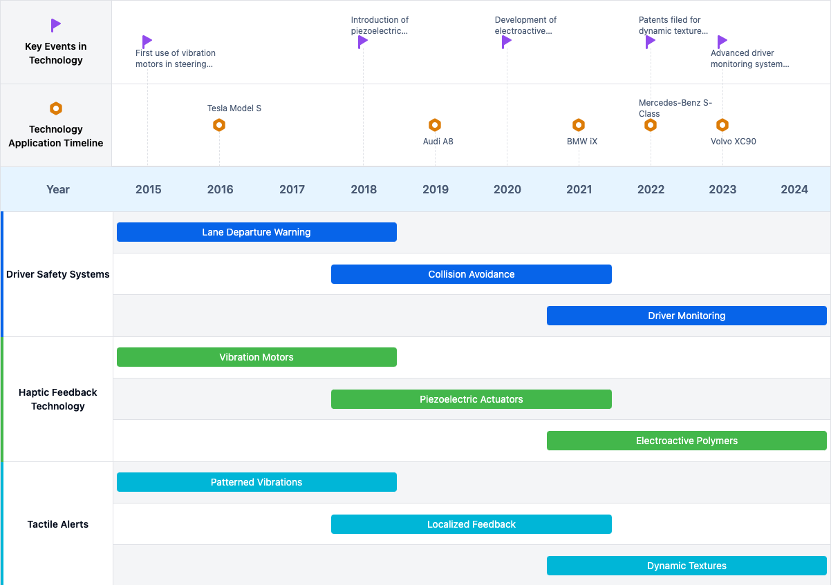
Existing Solutions for Tactile Alerts in Vehicles
Haptic Feedback Systems for Steering Wheels
These systems provide tactile feedback to the driver through the steering wheel, enhancing awareness and safety by alerting them to various situations, such as lane departures or potential hazards, through vibrations or force feedback.
Steer-by-Wire Systems with Haptic Feedback
In steer-by-wire systems, where there is no mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, haptic feedback mechanisms simulate the tactile sensations of traditional steering systems, improving driver experience and situational awareness.
Haptic Feedback for Driver Assistance and Navigation
Haptic feedback provides directional cues, alerts, or guidance to the driver during navigation or when using driver assistance features, helping maintain situational awareness and respond appropriately.
Haptic Feedback for Vehicle Interfaces and Displays
Integrating haptic feedback into vehicle interfaces, such as touchscreens and control panels, enhances user experience by providing tactile confirmation or feedback when interacting with these interfaces.
Haptic Feedback Systems for Rehabilitation and Training
These systems leverage haptic feedback technology for rehabilitation or training purposes, simulating driving scenarios and providing feedback on driving techniques.
Key Players in Automotive Haptic Technology
Toyota Research Institute Inc.
Developing advanced haptic actuators for steering wheels to provide tactile alerts in various driving scenarios, enhancing driver safety and awareness.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG (BMW)
BMW has developed a haptic feedback system for steering wheels that uses precise vibrations to alert drivers about critical driving information, aiming to improve response times and safety.
Immersion Corp.
Specializes in haptic technology, providing versatile systems for automotive steering wheels that offer customizable tactile alerts for different driving conditions.
Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Implemented haptic feedback technology in their steering wheels to provide tactile alerts for driver assistance systems, improving situational awareness.
Volvo Car Corp.
Volvo’s haptic feedback technology enhances driver safety by providing tactile alerts for lane departure warnings, collision avoidance, and other critical driving information.
Core Innovations in Haptic Feedback for Driver Safety
Patent 1: System and Method for Reinforcing Continuous Caution in Vehicle by Using Tactile Feedback
- Core Points:
- A system comprising sensors that detect environmental and vehicle conditions, outputting signals to a processor.
- The processor determines the appropriate tactile feedback, which is then delivered to the driver via a tactile output device.
- This continuous and intuitive method improves driver awareness and response to emergency situations.

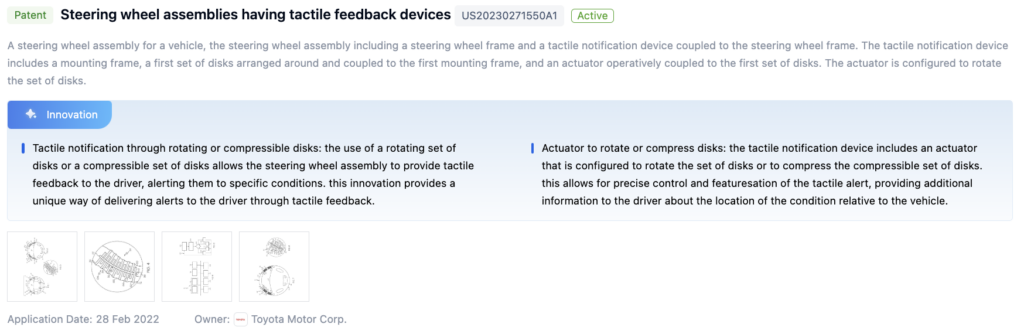
Patent 2: Steering Wheel Assemblies with Tactile Feedback Devices
- Core Points:
- Incorporates tactile notification through rotating or compressible disks in the steering wheel assembly.
- An actuator controls the disks, providing precise tactile alerts to the driver, enhancing their awareness of specific conditions.
Potential Breakthroughs in Haptic Steering Wheel Technology
Haptic Feedback Systems for Steering Wheels
Systems that generate tactile sensations on the steering wheel to alert the driver or convey information about the vehicle’s status or surroundings, improving driver awareness and safety.
Steer-by-Wire Systems with Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback simulates the feel and response of traditional steering systems in steer-by-wire setups, enhancing the driving experience and providing critical cues.
Driver Notification and Alert Systems with Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback provides tactile warnings or alerts to the driver, particularly useful for safety-related information such as lane departure or collision avoidance.
Haptic Feedback for Enhanced Driver Experience
Integrating haptic feedback into various driving aspects, including navigation and entertainment, creates a more immersive and intuitive experience.
Regulatory Landscape for Automotive Safety Technologies
The regulatory landscape for automotive safety technologies, including haptic feedback, is shaped by stringent standards and guidelines. In the U.S., the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) regulates automotive safety, while the European Union enforces the General Safety Regulation (GSR), covering advanced safety features like lane departure warnings and driver monitoring systems. Compliance with these regulations is essential for market entry and consumer trust.
Human Factors and Ergonomics in Haptic Feedback Design
Effective haptic feedback design must consider:
- Sensory Integration: Seamlessly integrating haptic feedback with visual and auditory cues to enhance situational awareness without overwhelming the driver.
- Intuitive Mapping: Tactile signals should be mapped intuitively to specific events, minimizing the need for extensive training.
- Customization and Adaptability: Systems should accommodate individual driver preferences for intensity, frequency, and patterns.
- Ergonomic Considerations: Ensuring that haptic actuators do not compromise grip comfort or control precision.
- Context Awareness: The system should adapt to driving conditions, providing relevant alerts without causing distractions.
- User Acceptance and Trust: Designing feedback that is perceived as helpful and reliable.
- Robustness and Reliability: Ensuring long-term performance in various environmental conditions.
By addressing these factors, haptic feedback technology can effectively enhance driver safety and awareness while maintaining a natural driving experience.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

