
Introduction: LTE vs 5G
LTE vs. 5G: The evolution from LTE to 5G marks a significant leap in mobile network technology. LTE (Long-Term Evolution) has been the backbone of mobile connectivity, delivering reliable speeds and widespread coverage. 5G, on the other hand, promises ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and massive capacity, redefining how we interact with technology. Let’s break down the differences between these two networks.

What Is LTE?
LTE is a 4G mobile communication standard that provides high-speed internet access and supports a variety of mobile services. It was developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and is designed to offer improved data rates, reduced latency, and enhanced network efficiency compared to its predecessors.
Key Features
- Speed: LTE offers download speeds up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds up to 50 Mbps.
- Latency: LTE has a latency of around 50 ms, which is significantly lower than 3G networks.
- Capacity: LTE supports a large number of devices and provides high spectral efficiency.
- Use Cases: Suitable for mobile broadband, streaming, online gaming, and IoT applications.
Advantages
- High data rates and low latency make it ideal for mobile broadband services.
- Supports a wide range of devices and applications.
- Efficient use of spectrum resources.
Limitations
- As the number of connected devices increases, LTE networks can become congested, leading to reduced performance.
- Limited ability to support the massive number of devices expected in the future.
What Is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile network technology, designed to provide even faster data speeds, ultra-low latency, and greater connectivity than its predecessors. It is also developed by the 3GPP and is intended to support a vast number of devices and new use cases such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Key Features
- Speed: 5G offers download speeds up to 20 Gbps and upload speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Latency: 5G aims to reduce latency to as low as 1 ms.
- Capacity: 5G can support millions of devices per square kilometer.
- Use Cases: Supports a wide range of applications including IoT, autonomous vehicles, augmented and virtual reality, and more.
Advantages
- Extremely high data rates and low latency make it suitable for mission-critical applications.
- Can support a massive number of devices, enabling widespread IoT adoption.
- Enhanced network slicing capabilities allow for customized network performance for different applications.
Limitations
- Requires significant infrastructure investments, including the deployment of small cells and the use of millimeter wave frequencies.
- Coverage and performance can be affected by obstacles such as buildings and vegetation.
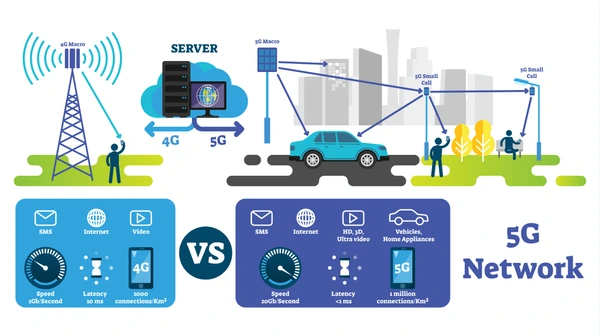
Key Differences Between LTE and 5G
Speed and Capacity
- LTE: Provides high data rates and capacity compared to previous generations but is limited in meeting the growing demand for data traffic.
- 5G: Offers significantly increased bandwidth, broadening the cellular market beyond smartphones to provide last-mile connectivity to various devices, including desktops, set-top boxes, and IoT devices.
Spectral Efficiency
- LTE: Achieves a certain level of spectral efficiency but faces challenges in spectrum scarcity with the exponential growth of connected devices.
- 5G: Enhances spectral efficiency and supports more simultaneous connections, addressing the spectrum limitations by utilizing millimeter wave frequencies.
Latency
- LTE: Provides lower latency compared to earlier generations but still struggles to meet the ultra-low latency requirements of some applications.
- 5G: Significantly reduces latency, enabling real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
Use Cases
- LTE: Suitable for traditional mobile services, HD video streaming, and videoconferencing.
- 5G: Designed to support a wide range of new use cases, including smart cities, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and mission-critical communications.
Network Architecture
- LTE: Implements an all-IP network architecture, providing higher data rates and end-to-end Quality of Service (QoS).
- 5G: Introduces a reconfigurable core network with a multitechnology convergent core, supporting an all-IP platform for a large number of simultaneous connections.
When to Use LTE vs 5G
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
- LTE: Suitable for high-speed data transmission and multimedia services. It provides a minimum downlink data rate of 100 Mbps, which is sufficient for most current mobile broadband applications.
- 5G: Offers significantly higher data rates, with the potential to reach gigabit speeds, making it ideal for applications requiring very high bandwidth, such as advanced augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences, and high-definition video streaming.
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC)
- LTE: While LTE can provide low latency, it may not meet the stringent requirements of ultra-low latency needed for applications like remote medical surgery, industrial automation, and autonomous vehicles.
- 5G: Designed to offer ultra-low latency, with latency as low as 1 ms, making it essential for mission-critical applications that require real-time communication.
Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC)
- LTE: Suitable for a large number of connected devices, but may not be efficient for extremely large-scale IoT deployments due to limitations in device density and power consumption.
- 5G: Optimized for massive connectivity, supporting a vast number of devices with low power consumption, making it ideal for applications like smart cities, industrial IoT, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications.
In summary, use LTE when you need reliable mobile broadband for general use cases, and use 5G when you require high-speed, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity for advanced and mission-critical applications.
FAQs
- Is 5G faster than LTE?
Yes, 5G offers speeds over 1 Gbps, significantly faster than LTE’s 20-100 Mbps. - Does 5G improve battery life compared to LTE?
5G can be more energy-efficient in newer devices, but older devices may experience faster battery drain. - Can my current phone use 5G?
Only phones with 5G-compatible hardware can connect to 5G networks. - How does 5G improve latency over LTE?
5G achieves latency as low as 1 ms, compared to LTE’s average of 50 ms, enabling near-instantaneous responses. - Will LTE be phased out with the rollout of 5G?
LTE will coexist with 5G for years, providing fallback coverage where 5G isn’t available.
To get detailed scientific explanations of LTE vs. 5G, try Patsnap Eureka.

