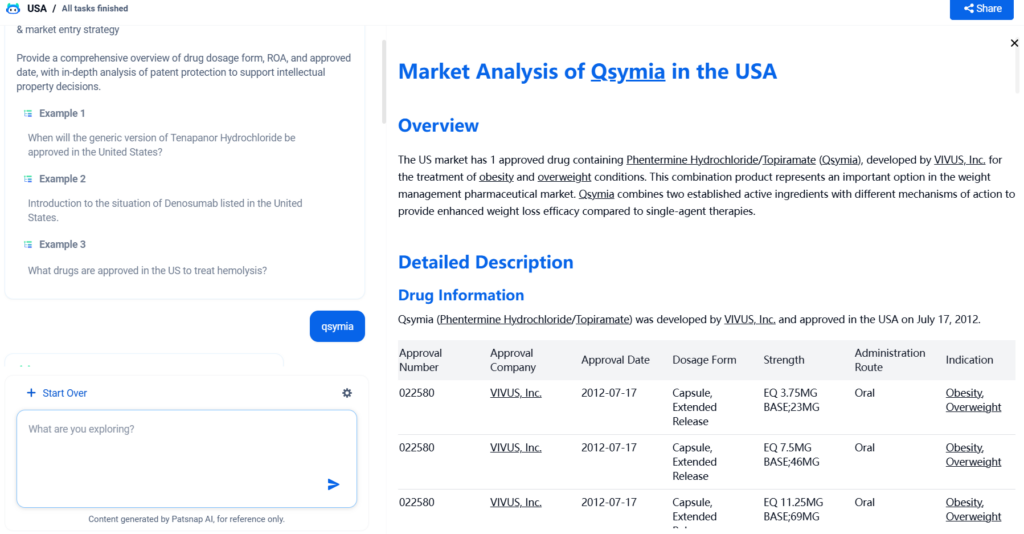
The US market has 1 approved drug containing Phentermine Hydrochloride/Topiramate (Qsymia), developed by VIVUS, Inc. for the treatment of obesity and overweight conditions. This combination product represents an important option in the weight management pharmaceutical market. Qsymia combines two established active ingredients with different mechanisms of action to provide enhanced weight loss efficacy compared to single-agent therapies.
Detailed Description
Drug Information
Qsymia (Phentermine Hydrochloride/Topiramate) was developed by VIVUS, Inc. and approved in the USA on July 17, 2012.
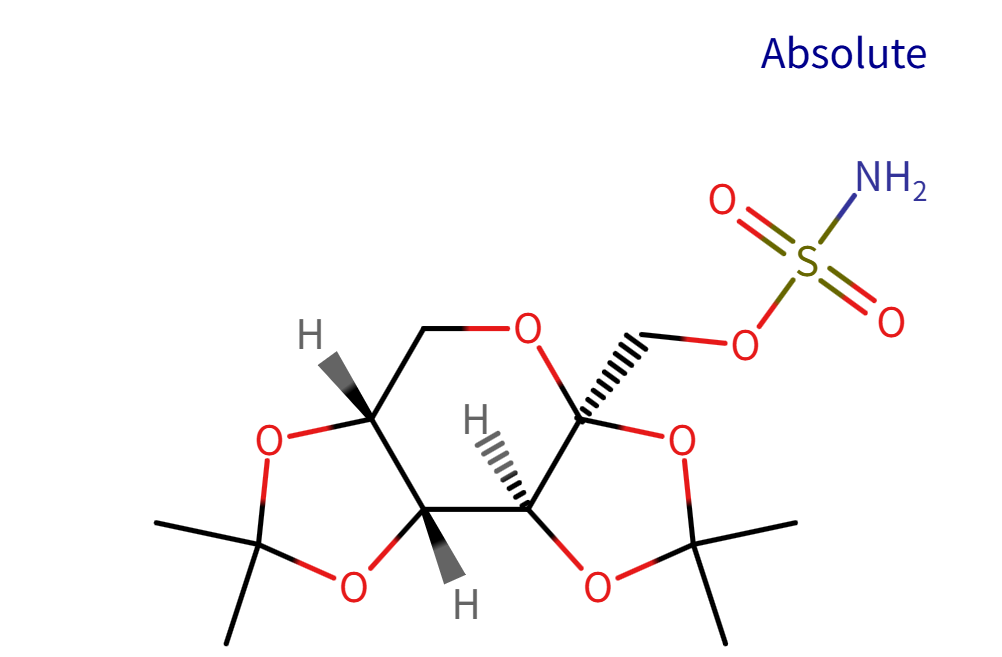
Structure
Mechanism of Action
Qsymia works through multiple mechanisms including:
- CA2 inhibitors
- CA4 inhibitors
- GABRA1 agonists
- TAAR1 agonists
Patent Statement Information
There is 1 patent statement for Qsymia, submitted on July 18, 2013.

Registration Patent Barrier Analysis
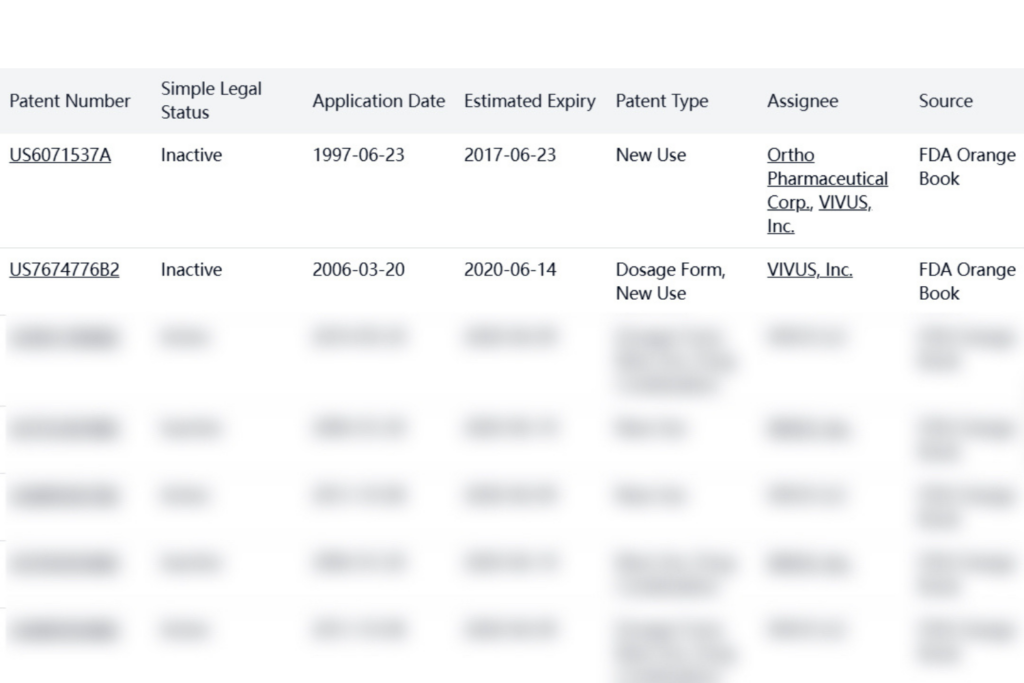
FDA Orange Book patents for Qsymia are held by VIVUS, Inc. (now VIVUS LLC). Several patents remain active until 2028-2029, providing significant protection against generic competition.
Other Patent Barrier Analysis
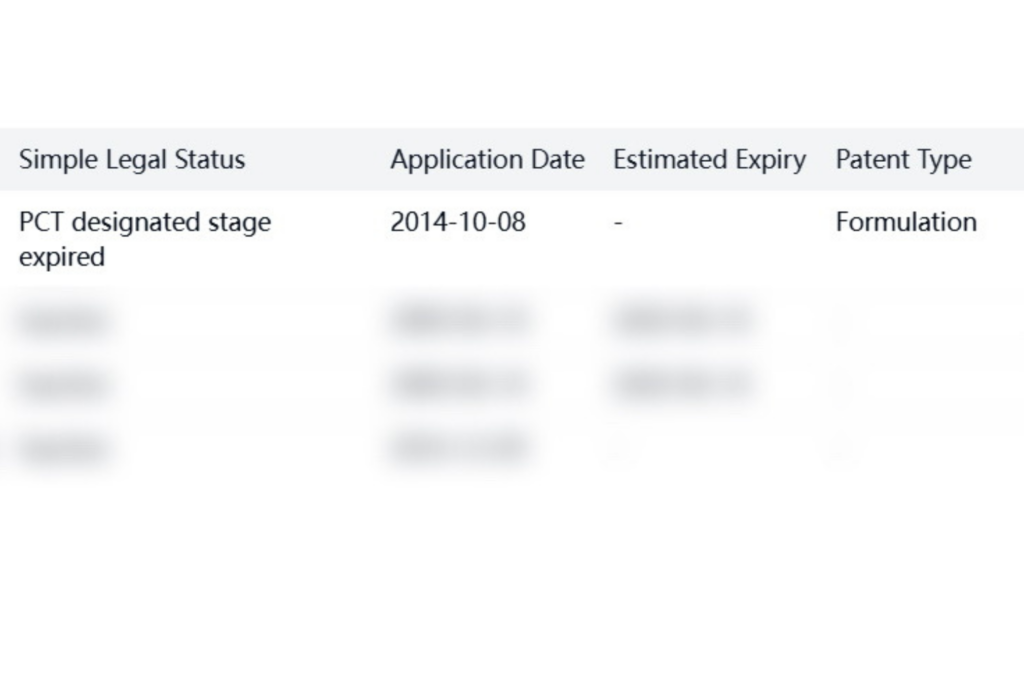
Additional patents held by VIVUS, Inc. include international filings, though many are now inactive.
Clinical Results
Nonclinical (Animal) Toxicology and Reproductive Studies
- Carcinogenicity, Mutagenicity, and Fertility: Individual studies with phentermine and topiramate showed no evidence of carcinogenicity or genotoxicity for phentermine. Topiramate was not mutagenic but was associated with increased urinary bladder tumors in mice at very high doses, believed to be species-specific.
- Embryo-Fetal Development and Reproductive Toxicity: Studies in rats and rabbits showed that lower doses (2-3 times clinical exposures) did not produce fetal malformations but resulted in reduced fetal weights. Higher doses led to maternal toxicity, decreased pup survival, limb and tail malformations, and delayed developmental milestones, indicating that topiramate is teratogenic.
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
- Mechanism of Action: Phentermine works through central sympathomimetic effects similar to amphetamine for appetite suppression. Topiramate’s effects involve GABAergic modulation, ion channel modulation, and carbonic anhydrase inhibition.
- Pharmacokinetic Studies: Studies in patients with hepatic impairment showed phentermine AUC increased by 37% and 60% in mild and moderate impairment respectively, while topiramate exposure remained unchanged. In patients with renal impairment, both drugs showed inverse correlation with creatinine clearance, with severe impairment resulting in significantly higher exposure.
Clinical Efficacy Studies
- Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials: Two major clinical studies demonstrated significant weight loss efficacy:
- Study 1: In obese patients (BMI ≥35 kg/m²), high-dose Qsymia produced up to approximately 16% mean weight loss over 56 weeks compared to placebo.
- Study 2: In obese and overweight patients (BMI ≥27 kg/m²) with at least one weight-related comorbidity, both dosing regimens (7.5 mg/46 mg and 15 mg/92 mg) achieved meaningful weight loss compared to placebo.
Drug Interaction Studies
- Antidiabetic Medications: Co-administration with glyburide and pioglitazone led to small changes in the pharmacokinetic profiles of these agents, warranting careful monitoring of glycemic control.
- Oral Contraceptives: Qsymia slightly increased norethindrone exposure (by around 16%) and decreased ethinyl estradiol exposure (by about 16%), which may contribute to irregular bleeding but not necessarily reduced contraceptive efficacy.
Infringement Cases
Based on the available information, no specific patent infringement incidents involving Phentermine Hydrochloride/Topiramate have been identified.
Policy and Regulatory Risk Warning
After a comprehensive search, no specific market exclusivity or data protection period beyond patent protection was identified for Qsymia in the USA.
Market Entry Assessment & Recommendations
- Patent Protection Analysis: Qsymia maintains strong patent protection until 2029, with several key patents (US9011906B2, US8895057B2, US8895058B2, US8580298B2, US9011905B2, US8580299B2) remaining active. Generic manufacturers should focus on developing non-infringing formulations or consider licensing agreements.
- Formulation Challenges: The extended-release formulation presents technical challenges for generic developers. Investment in specialized drug delivery technology would be necessary to achieve bioequivalence.
- Market Positioning:
- For Innovators: VIVUS should focus on:
- Reinforcing brand loyalty through patient support programs
- Developing new formulations or combination therapies to extend product lifecycle
- Expanding indications to other obesity-related conditions
- Emphasizing clinical benefits over potential generic competitors
- For Generic Entrants: Companies should:
- Begin preparing for entry after 2029 when key patents expire
- Consider challenging the validity of existing patents through Paragraph IV certifications
- Develop alternative formulations that may avoid patent infringement
- Form strategic partnerships with organizations experienced in extended-release technology
- For Innovators: VIVUS should focus on:
- Regulatory Strategy:
- Monitor FDA guidance on weight management drugs
- Address safety concerns preemptively in development programs
- Consider Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) requirements
- Commercial Considerations:
- The obesity market is growing rapidly due to increasing prevalence rates
- Payer restrictions remain a challenge for weight management medications
- Direct-to-consumer marketing has proven effective in this therapeutic area
- Consider value-based contracting models to improve market access
In conclusion, Qsymia maintains significant patent protection in the US market until 2029, creating a substantial barrier to generic entry. Companies interested in this space should develop comprehensive strategies addressing both technical formulation challenges and market access considerations while monitoring the evolving regulatory landscape for weight management medications.