
Perchloric acid (HClO₄) is a highly corrosive and powerful oxidizing agent commonly used in industrial and laboratory processes. Its strong acidity and reactivity make it an essential chemical for applications such as rocket propulsion, analytical chemistry, and metal processing. However, due to its hazardous nature, proper handling and storage are critical. This article explores the properties, uses, safety measures, and real-world case studies related to this acid.
What is Perchloric Acid?
This acid is a mineral acid known for its high reactivity and ability to form explosive compounds under certain conditions. It exists in various concentrations, with higher concentrations exhibiting strong oxidizing behavior.

Chemical Properties
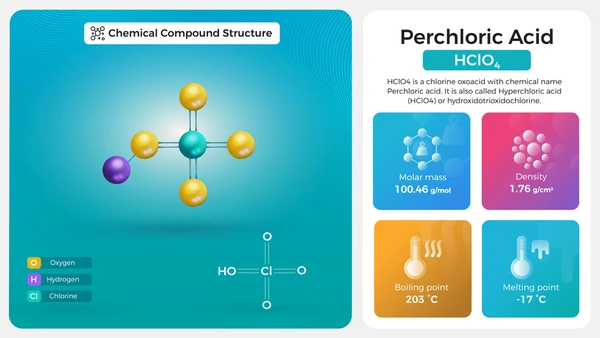
- Molecular Formula: HClO₄
- Molar Mass: 100.46 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- Boiling Point: ~203°C (72.5% solution)
- Oxidizing Power: High at concentrations above 85%
Physical States
- Aqueous Solutions: The most stable form is a 72.5% solution, which forms an azeotrope with water.
- Anhydrous Perchloric Acid: Unstable and rarely encountered due to its explosive potential.
Perchloric Acid vs. Other Strong Acids
| Property | Perchloric Acid (HClO₄) | Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) | Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing Strength | High (above 85%) | Moderate | Low |
| Corrosiveness | Very high | High | Moderate |
| Industrial Use | Rocket fuel, etching | Battery acid, dehydration | Cleaning, metal treatment |
Uses of Perchloric Acid
1. Industrial Applications
- Rocket Propellants: Used to produce ammonium perchlorate, a critical oxidizer in solid rocket fuels.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Acts as an etchant for semiconductors and printed circuit boards.
- Metal Refining: Helps dissolve metals for analysis and ore extraction.
2. Laboratory and Chemical Research
- Analytical Chemistry: Used to prepare perchlorate salts and for titration procedures.
- Synthesis of Perchlorates: Essential for manufacturing various perchlorate compounds in research.
3. Medical and Pharmaceutical Use
- Radiopharmaceuticals: Used in select medical imaging applications.
Hazards and Safety Considerations
Need guidance on handling perchloric acid safely? Eureka Technical Q&A offers expert insights on its hazards, proper storage, and safety precautions, helping you minimize risks and ensure compliance with handling protocols in laboratories and industrial settings.
1. Reactivity and Explosion Risks
Perchloric acid becomes a strong oxidizer at concentrations above 85%, which can lead to violent reactions, particularly with:
- Organic materials (e.g., paper, oil)
- Reducing agents
- Metals such as aluminum and magnesium
2. Corrosive Effects
- Causes severe burns upon skin or eye contact.
- Inhalation of fumes can lead to serious respiratory issues.
- Ingestion results in internal damage and is potentially fatal.
3. Notable Incidents: O’Connor Plating Works Disaster (1947)
One of the deadliest accidents involving this acid occurred in Los Angeles when a bath containing 75% this acid and acetic anhydride exploded, killing 17 people and injuring over 150. The explosion was caused by organic contamination, highlighting the importance of safe handling.
Safe Handling and Storage Practices
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Chemical splash goggles and face shields
- Acid-resistant gloves (neoprene, PVC)
- Protective clothing (lab coats, aprons)
2. Engineering Controls
- Fume Hoods with Wash-Down Systems: Prevents accumulation of reactive perchlorates.
- Explosion-Proof Storage Cabinets: Reduces risk of accidental ignition.
3. Storage Guidelines
- Store separately from organic materials and reducing agents.
- Use glass or ceramic containers, as plastics may degrade over time.
- Regularly inspect for leaks or discoloration, which may indicate decomposition.
4. Emergency Procedures
- Spill Response: Neutralize small spills with sodium bicarbonate and rinse thoroughly with water.
- Fire Response: Do not use organic fire suppressants; use water or non-combustible dry extinguishers.
FAQs About Perchloric Acid
1. What is perchloric acid used for?
It is primarily used in producing ammonium perchlorate for rocket fuels, as well as in metal refining, electronics, and analytical chemistry.
2. Why is perchloric acid dangerous?
Its strong oxidizing properties at high concentrations make it highly reactive, and it can cause severe burns, explosions, and toxic fumes.
3. How should perchloric acid be stored safely?
It should be stored in non-reactive containers, separate from organic and flammable materials, in a well-ventilated area with secondary containment.
4. Can perchloric acid explode?
Yes, especially in concentrated or anhydrous form, when contaminated with organic compounds or under heat.
5. How do you neutralize a spill of perchloric acid?
Neutralize with an inorganic acid neutralizer like sodium bicarbonate, then rinse the area thoroughly with water.
Conclusion
Perchloric acid is a powerful chemical with critical applications in industrial, laboratory, and aerospace settings. However, its strong oxidizing properties and corrosive nature make proper handling and storage essential. By following safety protocols and understanding its risks, this acid can be used effectively while minimizing potential hazards.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Perchloric Acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


