PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent clarity, toughness, and ease of processing. It is a popular choice for packaging, medical devices, and 3D printing filaments. Chemically similar to PET, it includes glycol modification to improve durability and eliminate brittleness.
This blog dives into PETG’s composition, performance characteristics, and material grades. We also explore real-world applications, innovation trends, and sustainability profiles—empowered by PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, which enables in-depth patent analysis and market intelligence for materials R&D.
What is PETG?
It is a copolyester derived from PET (polyethylene terephthalate) by incorporating cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM) as a comonomer. This modification reduces crystallinity, enhancing clarity and impact resistance.
- Chemical Name: Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol
- Common Form: Transparent pellets or filaments
- Key Attributes: Clarity, ductility, low shrinkage, chemical resistance

Composition & Properties / Performance
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | (C10H8O4)n with CHDM units |
| CAS Number | 25640-14-6 |
| Density | ~1.27 g/cm³ |
| Melting Temperature | 230–260°C |
| Glass Transition Temp | 80–85°C |
| Tensile Strength | 45–50 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 100–200% |
| Optical Clarity | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis |
| Biocompatibility | Yes (used in medical applications) |
Functional Strengths:
- High impact resistance (tougher than acrylic)
- Excellent thermoformability and machinability
- Minimal shrinkage during extrusion or molding
Material Grades & Designations
It is available in various grades depending on application:
| Grade Type | Designation | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| FDA-Compliant | Eastar™ GN001 | Food packaging, medical trays |
| 3D Printing | PETG 3D Filament | Rapid prototyping, end-use parts |
| Flame-Retardant | PETG FR | Electronics, displays |
| UV-Resistant | PETG UV | Outdoor signage, automotive parts |
Standards:
- ASTM D1003 for transparency
- ISO 527 for tensile properties
- RoHS, FDA, and REACH compliant in many grades
Application Landscape
PETG’s unique blend of clarity, strength, and chemical resistance makes it ideal across many industries. Its popularity continues to grow thanks to its balance between ease of processing and durability.
1. 3D Printing
- Use: Widely used in FDM/FFF 3D printing for functional prototypes, mechanical parts, and consumer goods.
- Advantages: Low warping, excellent layer adhesion, and minimal odor.
- Notable Trend: It is replacing ABS in many applications due to its better ease of use and fewer emissions.
2. Medical & Healthcare
- Use: Medical packaging (trays, blister packs), protective shields, diagnostic device housings.
- Advantages: Easy sterilization via gamma radiation or ethylene oxide. Excellent clarity for visibility.
- Case Example: During COVID-19, it was widely used for face shields and diagnostic kits.
3. Packaging Industry
- Use: Transparent food containers, clamshell packaging, display cartons.
- Advantages: FDA-compliant grades offer food safety, clarity, and impact resistance.
- Trend: Shift toward mono-material its structures to enhance recyclability.
4. Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Use: Transparent bottles, jars, and dispensers.
- Advantages: Superior gloss, chemical resistance, and shatterproof nature.
- Scenario: Premium personal care brands use it to provide luxury packaging feel while being recyclable.
5. Signage & Displays
- Use: Light-diffusing panels, indoor/outdoor signage, POP displays.
- Advantages: UV-resistant grades offer long-term weatherability. It can be vacuum-formed and printed on directly.
- Application Insight: It is replacing acrylic in applications where impact resistance is more important than scratch resistance.
6. Industrial and Mechanical Parts
- Use: Machine guards, housings, durable components.
- Advantages: Toughness, machinability, and chemical resistance make it suitable for industrial use.
- Trend: Increasing use in applications requiring clear mechanical safety enclosures.
Application Trends:
- Growth in customized 3D printing solutions
- Increasing medical-grade PETG demand post-pandemic
- Development of recyclable multilayer packaging using PETG barrier layers
PETG vs Other Similar Materials
| Feature | PETG | PLA | ABS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biodegradable | No | Yes | No |
| Impact Resistance | High | Low | Medium |
| Clarity | Excellent | Moderate | Poor |
| Printability | Good | Very Good | Moderate (requires heated bed) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Fair | Good |
PETG strikes a balance between the easy printability of PLA and the strength of ABS.
Advantages of PETG
- Excellent Clarity: Suitable for transparent and glossy applications
- Impact Resistance: Withstands mechanical stress and rough handling
- Low Shrinkage: Maintains dimensional stability after molding or printing
- Easy to Process: Compatible with extrusion, injection molding, and 3D printing
- FDA-Approved Grades: Safe for food contact and medical usage
- Strong Chemical Resistance: Performs well in industrial and lab settings
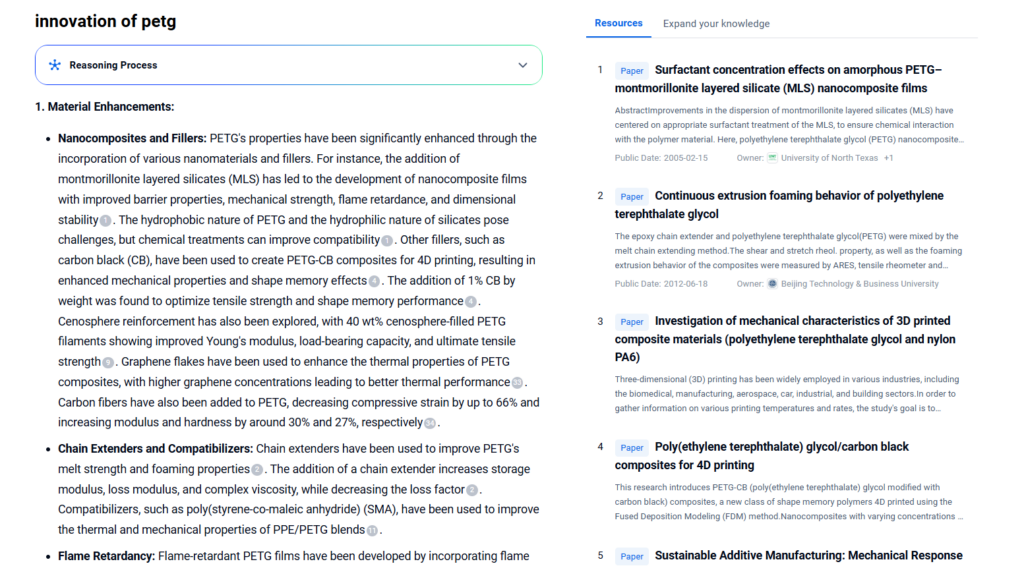
Innovations & Technology
Innovation around PETG is rapidly evolving, driven by sustainability, customization, and functionality. Below are key innovation directions:
1. Bio-Based PETG & Recycled PETG (rPETG)
- Goal: Reduce dependency on virgin petrochemical sources.
- Innovation: Several companies now produce PETG using renewable raw materials like sugarcane-derived glycol.
- Impact: Maintains original PETG properties while reducing carbon footprint.
2. Advanced Additive Formulations
- Nanocomposites: It reinforced with nano-silica or graphene to enhance flame resistance, stiffness, and conductivity.
- Anti-bacterial PETG: Incorporates silver-ion or zinc-based agents for use in high-touch surfaces and medical environments.
3. Recyclable Multilayer Structures
- Problem Solved: Traditional multilayer packaging is hard to recycle.
- Solution: PETG-based mono-material multilayer films now allow separation and remanufacturing.
- Example: Eastman’s Tritan™ Renew incorporates molecular recycling to reclaim PETG waste.
4. Smart Manufacturing & Digital Customization
- Digital Printing Compatibility: PETG accepts direct UV printing and ink adhesion, allowing fast product customization.
- Smart Tooling: Use of PETG in jigs and fixtures for smart assembly lines thanks to its low shrinkage and toughness.
Sustainability & Environmental Impact
- Recyclability: It is fully recyclable in stream RIC 1 (with PET) if uncontaminated
- Environmental Profile: Lower energy use than polycarbonate and ABS
- Compliance: Widely meets REACH, RoHS, and FDA standards
- Challenges: Not biodegradable, but developments in bio-PETG are emerging
- Lifecycle Consideration: Long usable life reduces need for frequent replacements
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
- Patent Intelligence: Analyze PETG patents by formulation, use, and geography
- Competitor Monitoring: Track new entrants and technologies in 3D printing, packaging, and medical devices
- White Space Discovery: Identify unmet needs and potential formulation areas
- Regulatory Tracking: Stay updated on changes in its safety and compliance across regions
Conclusion
PETG has cemented its place as a versatile and high-performance plastic. From consumer goods to industrial applications, its clarity, durability, and ease of use make it a material of choice across sectors. As demand for recyclable and high-strength plastics rises, PETG’s role will only expand.
By leveraging tools like PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, R&D teams can make informed decisions faster—identifying trends, avoiding IP risks, and staying ahead of competitors.
FAQs
PETG offers greater durability and chemical resistance, making it better for functional parts.
Yes, PETG is recyclable and often accepted in PET recycling streams.
FDA-approved PETG grades are safe for food and medical use.
It prints better with a heated bed but is more forgiving than ABS.
For more scientific explanations of PETG , try PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.