
Phosphorous acid plays a crucial role in multiple industries, ranging from agriculture to chemical manufacturing. It serves as a reducing agent, a precursor in the production of phosphonates, and an effective component in plant nutrition. But what makes phosphorous acid different from other phosphorus-containing compounds, and why is it essential in various applications. This article explores the chemical structure, industrial significance, advantages, challenges, and the latest innovations related to H₃PO₃.
What is Phosphorous Acid?
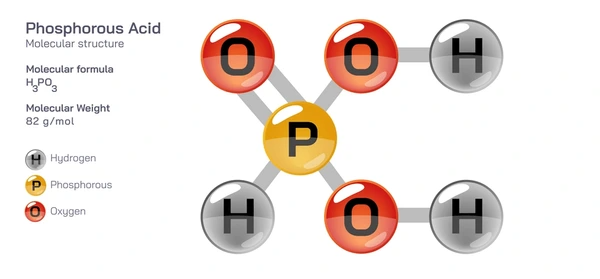
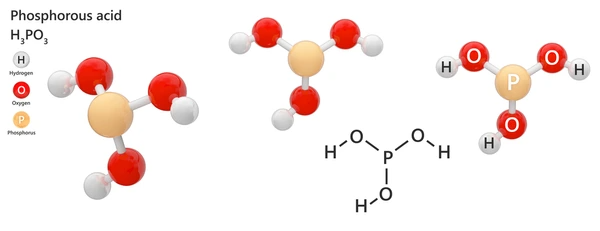
Phosphorous acid (H₃PO₃) is a phosphorus-containing inorganic acid with strong reducing properties. It is a colorless, crystalline substance that is highly soluble in water and decomposes upon heating.
Key Chemical Characteristics
- Molecular Formula: H₃PO₃
- Molecular Weight: 82 g/mol
- Acidity: Moderately strong acid, stronger than phosphoric acid
- Solubility: Completely dissolves in water and forms acidic solutions
- Reducing Properties: Converts metal oxides into pure metals and reacts with oxidizing agents
💡 Did You Know?
Phosphorous acid is often confused with phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄), but they differ in oxidation states. Phosphorous acid contains trivalent phosphorus (P³⁺), while phosphoric acid has pentavalent phosphorus (P⁵⁺).
How Phosphorous Acid Works in Chemical Reactions
Phosphorous acid is widely recognized for its reducing ability and reactivity with metal ions, organic compounds, and oxidizers. Some of its critical functions include:
- Acts as a Reducing Agent: Converts metal oxides into pure metals through redox reactions.
- Precursor for Phosphonates: Plays a key role in the synthesis of organophosphorus compounds used in industrial and agricultural applications.
- Prevents Oxidation: Used in chemical formulations to protect against oxidation.
Chemical Reaction Example:
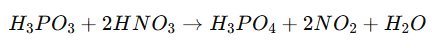
In this reaction, H₃PO₃ donates electrons, reducing nitric acid (HNO₃) while converting into phosphoric acid.
Industrial Applications of Phosphorous Acid
Agriculture and Plant Nutrition 🌱
- Fungicidal Properties: Used as an active ingredient in plant protection to combat fungal diseases like downy mildew and Phytophthora.
- Phosphite Fertilizers: Enhances plant resistance to environmental stress, boosting crop yield and health.
Chemical Manufacturing 🏭
- Production of Phosphonates: Acts as a precursor for synthesizing phosphonate-based detergents, water treatment agents, and flame retardants.
- Antioxidant in Plastics: Prevents oxidative degradation in polymer and plastic production.
Water Treatment 💧
- Corrosion Inhibitor: Used in cooling systems and industrial water treatment to protect metal pipes from rust.
- pH Stabilizer: Helps maintain the desired acidity level in water purification processes.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Use 💊
- Used in Drug Synthesis: Serves as an intermediate in the production of certain phosphorus-based medicines.
Phosphorous Acid vs. Phosphoric Acid: Key Differences
While both acids contain phosphorus, they differ significantly in chemical structure and industrial use.
| Feature | Phosphorous Acid (H₃PO₃) | Phosphoric Acid (H₃PO₄) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation State of P | +3 (Trivalent) | +5 (Pentavalent) |
| Acid Strength | Stronger, more reactive | Weaker, more stable |
| Chemical Use | Reducing agent, phosphonates | Fertilizers, food additives |
| Industrial Application | Fungicides, water treatment | Soft drinks, detergents |
💡 Tip: If you’re looking for a reducing agent, H₃PO₃ is the better choice. If you need a stabilizer for food and fertilizers, phosphoric acid is more suitable.
Challenges and Safety Considerations
Concerned about the challenges and safety considerations of phosphorous acid? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert guidance on its handling, potential hazards, and safe usage in industrial and agricultural applications, helping you minimize risks and ensure proper safety measures.
Handling and Storage Risks ❌
- Highly corrosive and can cause skin and eye irritation.
- Needs proper ventilation as it may release toxic fumes.
Limited Stability ❌
- Decomposes when heated, producing phosphine gas, which is hazardous.
- Reacts with strong oxidizers, leading to potential combustion risks.
Regulatory Restrictions ❌
- In some regions, phosphorous acid-based plant protection products require strict regulatory approval before use.
⚠️ Safety Tip: Always store H₃PO₃ in sealed, non-metallic containers away from heat and oxidizing agents.
Future Trends in Phosphorous Acid Research and Innovation
Advanced Agricultural Solutions 🔹
- Development of next-generation phosphite-based biofertilizers to enhance sustainable farming practices.
Green Chemistry Applications 🔹
- Increased use of eco-friendly phosphorus derivatives in industrial production to minimize environmental impact.
Enhanced Corrosion Protection 🔹
- Innovations in water treatment formulations that use H₃PO₃ for better metal protection without harmful byproducts.
How Eureka by PatSnap Accelerates Phosphorous Acid Research
What is Eureka by PatSnap?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that assists researchers in discovering the latest advancements in H₃PO₃ technologies.
How It Benefits Phosphorous Acid R&D
✅ Patent Analysis: Tracks cutting-edge patents related to H₃PO₃ applications.
✅ Competitive Intelligence: Helps industries benchmark against top competitors in chemical manufacturing.
✅ Technology Roadmapping: Provides insights into emerging research trends and new industrial applications.
🚀 For professionals in chemical engineering, agriculture, and water treatment, Eureka by PatSnap accelerates research and optimizes innovation strategies.
Conclusion
Phosphorous acid is a versatile compound with applications in agriculture, chemical production, and water treatment. Its strong reducing properties and effectiveness in plant nutrition make it an essential chemical in multiple industries. While H₃PO₃ presents handling and stability challenges, ongoing research and innovation are expanding its applications in sustainable agriculture, corrosion protection, and green chemistry. By leveraging AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap, researchers and manufacturers can stay ahead of industry trends and drive innovation in H₃PO₃ technologies.
🚀 Want to explore the latest advancements in phosphorous acid research? Sign up for Eureka by PatSnap today and accelerate your innovation journey!
FAQs
1️⃣ Is phosphorous acid the same as phosphoric acid?
No, H₃PO₃ contains trivalent phosphorus (P³⁺), while phosphoric acid has pentavalent phosphorus (P⁵⁺). They differ in chemical behavior and industrial use.
2️⃣ What is H₃PO₃ used for?
It is widely used in agriculture (fungicides, fertilizers), chemical synthesis (phosphonates), and water treatment (corrosion prevention).
3️⃣ Is phosphorous acid toxic?
Yes, it is highly corrosive and should be handled with protective gear to avoid burns and inhalation hazards.
4️⃣ Can H₃PO₃ be used in organic farming?
Some phosphite-based fertilizers are approved for organic farming, but regulations vary by country.
5️⃣ How can I stay updated on H₃PO₃ research?
Using AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap helps track the latest patents, innovations, and industrial applications in H₃PO₃ research.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Phosphorous Acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


