
In research, experimental designs are essential for establishing cause-and-effect relationships. However, conducting true experiments is not always feasible due to ethical, logistical, or financial constraints. This is where quasi-experimental design plays a crucial role.
Quasi-experimental designs allow researchers to study causal relationships without randomly assigning participants to groups. These designs are commonly used in social sciences, healthcare, education, and public policy when randomization is impractical or unethical.
This guide explores:
- What quasi-experimental design is
- Types of quasi-experimental designs
- Examples and real-world applications
- How AI-powered tools like Eureka enhance quasi-experimental research
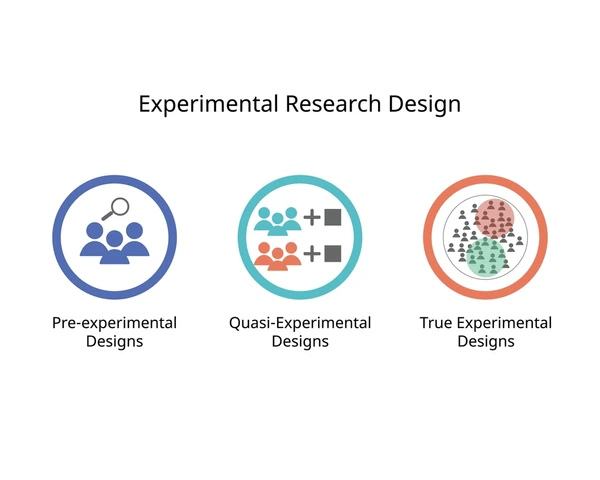
What is a Quasi-Experimental Design?
🔹 Definition
A quasi-experimental design is a research approach that examines cause-and-effect relationships but lacks random assignment of participants.
Unlike true experiments, where subjects are randomly placed into control and experimental groups, quasi-experiments rely on naturally occurring groups or pre-existing conditions.
🔹 Key Characteristics
- No random assignment – Participants belong to pre-existing groups.
- Control and treatment groups exist – But they may not be perfectly equivalent.
- Observes causal relationships – But may have confounding variables affecting results.
- Used when experiments are impractical – Common in real-world settings.
🔹 Example of Quasi-Experimental Design
📌 Education Policy Study:
A school district implements a new teaching method in one school, while another continues with traditional teaching. Since researchers cannot randomly assign students, they use a quasi-experimental design to compare student performance.
Challenge: Socioeconomic background differences may impact results, but statistical adjustments help control for these factors.
Types of Quasi-Experimental Designs
Want to explore different quasi-experimental designs? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into various types, including nonequivalent groups, time-series, and regression discontinuity designs, helping you understand their applications and limitations in research.
1️⃣ Non-Equivalent Groups Design
✅ Definition: Compares two or more groups without randomization.
✅ Example: A hospital introduces a new treatment to one group, while another receives standard care.
2️⃣ Interrupted Time Series Design
✅ Definition: Measures outcomes before and after an intervention over time.
✅ Example: A city implements a new traffic law, and researchers analyze accident rates before and after the law is enforced.
3️⃣ Regression Discontinuity Design
✅ Definition: Assigns treatment based on a pre-determined cutoff point.
✅ Example: Students with test scores above a threshold qualify for a scholarship, while those below do not.
4️⃣ Matched Pairs Design
✅ Definition: Participants in different groups are matched based on key characteristics to reduce bias.
✅ Example: In a study on exercise and heart disease, researchers match sedentary participants with active participants based on age, BMI, and medical history.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Quasi-Experimental Design
✅ Strengths
- Ethical feasibility – Used when randomization is impossible (e.g., public policies).
- Real-world applicability – Studies natural behaviors in authentic environments.
- Cost-effective – Reduces the need for complex laboratory setups.
- Useful in large-scale studies – Government, healthcare, and education frequently use quasi-experimental designs.
❌ Weaknesses
- Lack of randomization – Introduces selection bias.
- Confounding variables – External factors may influence results.
- Lower internal validity – Harder to prove causation compared to true experiments.
🔍 How Eureka Helps:
By leveraging AI-driven insights, patent data, and trend analysis, Eureka can:
- Identify hidden biases in quasi-experimental designs.
- Automate confounding variable adjustments.
- Improve study replication with AI-based simulations.
How to Strengthen a Quasi-Experimental Study
- Use Matching Techniques – Control for differences between groups.
- Include a Comparison Group – Even if randomization is not possible.
- Apply Statistical Controls – Regression models help reduce biases.
- Leverage AI for Data Validation – Eureka provides data-driven risk analysis.
- Test Findings Across Different Contexts – Ensuring external validity.
Example:
📌 A company wants to test a new remote work policy. By using Eureka’s AI-powered insights, they can:
- Compare productivity trends before and after implementation.
- Control for industry-wide fluctuations using global business trend data.
- Optimize employee matching to ensure valid comparisons.
Conclusion
Quasi-experimental designs provide a powerful alternative when randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not possible. They allow researchers to study real-world interventions, but they require careful planning and statistical control.
Eureka’s AI-driven capabilities empower researchers to:
- Enhance study design with predictive modeling
- Detect confounding variables with AI-driven analysis
- Improve research validity with large-scale data comparisons
By leveraging AI-powered research tools like Eureka, researchers can strengthen quasi-experimental designs, validate findings, and optimize decision-making.
🔍 Want to enhance your research? Explore Eureka today for AI-powered research validation!
FAQs
1️⃣ How is quasi-experimental research different from experimental research?
Quasi-experimental research lacks random assignment, while true experiments use randomized groups to ensure strong causal inference.
2️⃣ What are common applications of quasi-experimental designs?
Education, healthcare, business strategies, and public policies frequently use quasi-experimental designs when randomization is not feasible.
3️⃣ How can I minimize bias in quasi-experimental research?
Use statistical controls, matched pairs, and AI-powered data analysis tools like Eureka to adjust for confounding variables.
4️⃣ What is the best quasi-experimental design for policy evaluation?
Interrupted Time Series is often used for analyzing policy changes over time.
5️⃣ How does Eureka improve quasi-experimental research?
Eureka provides real-time trend analysis, AI-powered bias detection, and predictive modeling, enhancing the reliability of research findings.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Quasi-Experimental Design, try Patsnap Eureka.


