
The Raptor 3 engine is the latest iteration of SpaceX’s high-performance, methane-fueled rocket engine, designed to power the Starship launch system. Building on the advancements of Raptor 1 and Raptor 2, this new version delivers higher thrust, improved efficiency, and a streamlined design that enhances the reusability of SpaceX’s next-generation rockets. With record-breaking chamber pressures and an optimized structure, Raptor 3 represents a major leap forward in rocket propulsion technology. This article explores its specifications, design improvements, performance milestones, and impact on the Starship program.
What Is the Raptor 3 Engine?
What is the Raptor 3 engine? Eureka Technical Q&A explores its advanced rocket propulsion technology, increased efficiency, and role in SpaceX’s next-generation space missions.
The Raptor 3 is a full-flow staged combustion cycle engine powered by liquid methane and liquid oxygen. It is specifically designed to power SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy booster, forming the core of the company’s ambition to make space travel more sustainable, cost-effective, and reusable.
Raptor engines are unique because they use methane, a fuel that can potentially be produced on Mars via in-situ resource utilization, making long-term interplanetary missions more feasible.
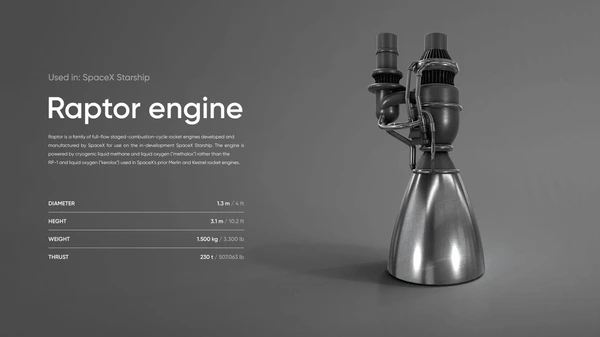
Raptor 3 Engine Specifications
| Specification | Raptor 3 | Raptor 2 | Raptor 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thrust (Sea Level) | 280 metric tons | 230 metric tons | 185 metric tons |
| Chamber Pressure | 350 bar | 300 bar | 270 bar |
| Specific Impulse (ISP) | approximately 350 seconds | approximately 330 seconds | approximately 320 seconds |
| Engine Mass | 1,525 kg | approximately 1,600 kg | approximately 2,000 kg |
| Thrust-to-Weight Ratio | 183.6 | 160 | 110 |
| Fuel Type | Liquid Methane / Liquid Oxygen | Liquid Methane / Liquid Oxygen | Liquid Methane / Liquid Oxygen |
(Image Source: SpaceX)
- Thrust and Efficiency:
- The Raptor 3 engine has gained an additional 50 ton-force (tf) of thrust compared to the Raptor 2 engine.
- Raptor 3 has 1.5 times the thrust of Raptor 1 and still has room for improvement.
- Raptor 2 offers 25% more thrust than Raptor 1 while being 20% lighter.
- Design and Manufacturing:
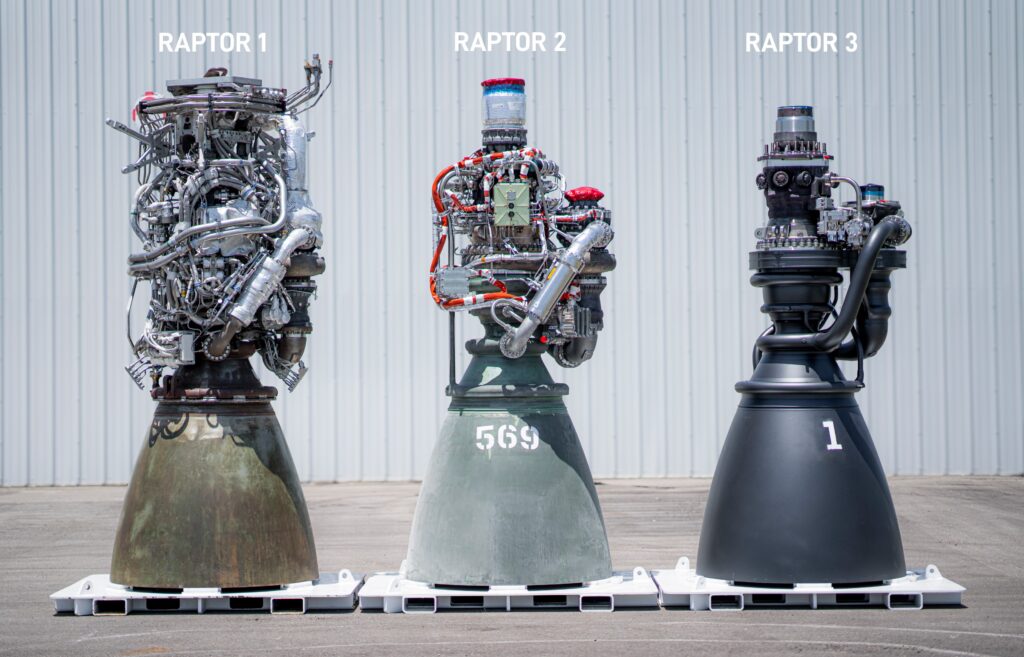
- Raptor 3 features a more streamlined and consolidated design, which could have been made possible with additive manufacturing (AM).
- Raptor 2 has undergone extensive part consolidation and uses internalized secondary flow paths and regenerative cooling for exposed components.
- Raptor 1 has a more complex design with a lot of external components compared to Raptor 2 and 3.
- Weight and Complexity:
- Raptor 3 is lighter than Raptor 2 and provides higher thrust and efficiency.
- Raptor 2 is 20% lighter than Raptor 1.
- Raptor 1 is heavier and more complicated than Raptor 2 and 3.
- Testing and Reliability:
- SpaceX has been testing Raptor engines to extreme levels to understand their performance.
- Raptor 2 engines have been successfully fired up in static fire tests.
- Raptor 1 engines were used in earlier Starship test flights.
- Future Developments:
- SpaceX is developing Raptor 3 engine variants for future Starship missions.
- The ultimate goal is to reduce the cost of Raptor 2 production to $1000 per ton of thrust.
Key Design Improvements in Raptor 3
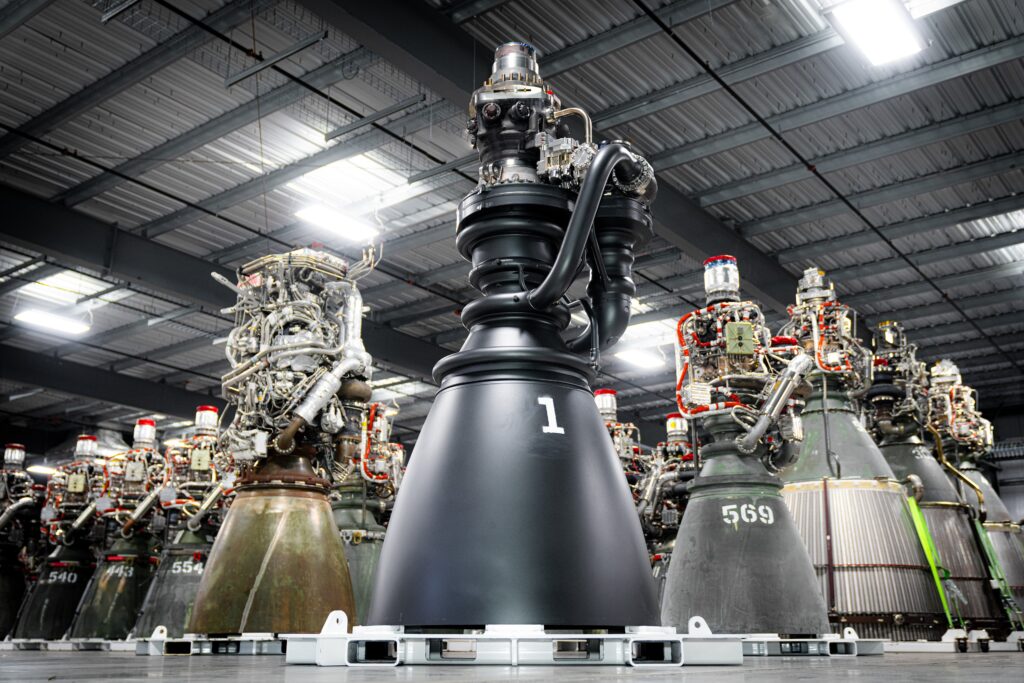

(Image Source: SpaceX)
Higher Efficiency and Thrust
The increase in thrust from 230 to 280 metric tons allows Raptor 3 to generate more power while maintaining a similar size and weight. This improvement enhances Starship’s payload capacity, making it more effective for cargo missions, lunar landings, and Mars colonization efforts.
Simplified Engine Design
Compared to earlier versions, Raptor 3 eliminates unnecessary components, reducing weight and manufacturing complexity. Key changes include:
- fewer external plumbing and sensors, reducing failure points
- enhanced thermal resilience, eliminating the need for an external heat shield
- more efficient combustion cycle, improving fuel efficiency
Improved Reusability
One of the major goals of Starship and Super Heavy is full reusability. Raptor 3 is designed to endure multiple launches and landings with minimal refurbishment, significantly reducing launch costs.
Performance Milestones of Raptor 3
Record-Breaking Chamber Pressure
In May 2023, Raptor 3 achieved a chamber pressure of 350 bar during a static fire test, producing 269 metric tons of thrust—a milestone never reached by any other operational rocket engine.
Optimized Manufacturing and Scalability
SpaceX has streamlined production, making Raptor 3 faster and cheaper to manufacture. This allows higher production rates, ensuring a steady supply of engines for Starship’s ambitious orbital and deep-space missions.
Raptor 3’s Role in Starship and Super Heavy
Increased Engine Count and Performance
With Raptor 3’s improved thrust-to-weight ratio, SpaceX can increase the number of engines on both Starship and Super Heavy:
- Super Heavy Booster: Up to 35 Raptor 3 engines, increasing liftoff thrust
- Starship Upper Stage: Uses 6 Raptor engines, with 3 optimized for vacuum and 3 for sea level
Supporting Lunar and Mars Missions
NASA has selected Starship for the Artemis Program, making Raptor 3 crucial for crewed lunar landings. With its high efficiency and potential for methane refueling on Mars, it is also essential for SpaceX’s Mars colonization plans.
Reduced Launch Costs
By improving reusability, efficiency, and manufacturing speed, Raptor 3 significantly lowers launch costs, making Starship one of the most cost-effective space vehicles ever built.
FAQs
What makes Raptor 3 different from Raptor 2?
Raptor 3 offers higher thrust, greater efficiency, and a more streamlined design, making it more powerful and reliable.
How powerful is the Raptor 3 engine?
At 280 metric tons of thrust, Raptor 3 is among the most powerful operational rocket engines, surpassing even NASA’s RS-25 and SpaceX’s Merlin engines.
Why does Raptor 3 use methane instead of hydrogen or kerosene?
Methane is clean-burning, allows for reusability, and can be synthesized on Mars, making it ideal for long-term space missions.
How many Raptor 3 engines will Starship use?
The Super Heavy booster can have up to 35 Raptor 3 engines, while Starship’s upper stage will use 6 Raptor engines.
What is the future of the Raptor engine series?
Raptor 3 is expected to power all upcoming Starship launches. SpaceX may continue developing even more advanced versions for interplanetary missions and heavier payloads.
Conclusion
The Raptor 3 engine represents a major leap in rocket propulsion, offering higher thrust, efficiency, and reusability compared to its predecessors. As the driving force behind SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy, it plays a critical role in revolutionizing space travel, reducing costs, and enabling missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
With its record-breaking performance and innovative design, Raptor 3 sets the foundation for a new era of space exploration, bringing humanity closer to becoming a multi-planetary species.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Raptor 3 Engine, try Patsnap Eureka.


