Introduction
Sodium bisulfate is essential in various industries due to its pH adjusting, fungicidal, herbicidal, and microbiocidal properties. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of sodium bisulfate, encompassing its chemical properties, production methods, key applications, pros and cons, recent research developments, and health and safety regulations.
What is Sodium Bisulfate?
Sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4), also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HNaO4S. It typically appears in crystal, granular, or powder form.
Sodium bisulfate is closely related to sulfuric acid and its other salts, sharing similar acidic properties. Because of its effective pH adjusting and preservative qualities, this compound is highly valuable across multiple sectors, including cleaning, swimming pool maintenance, food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and metal finishing.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of sodium bisulfate, check Eurkea.

Production Methods of Sodium Bisulfate
Traditional Methods of Sodium Bisulfate producing
Traditionally, sodium bisulfate is produced by reacting sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) with sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The production process involves dissolving sodium sulfate in water, and then adding sulfuric acid to precipitate sodium bisulfate crystals. This method is widely used due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, it has environmental drawbacks, primarily due to the generation of acidic effluents.
Sustainable and Cost-effective Production
Coal Chemical Industry Solid Slag
Solid slag from the coal chemical industry can react with sulfuric acid to produce sodium bisulfate. This method aligns with sustainable development by utilizing waste resources, therefore, it can reduce environmental impact.
Lithium Salt Production By-products
Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) generated as a by-product in the lithium salt production process can be converted into potassium sulfate (K2SO4) and sodium bisulfate by reacting with potassium chloride (KCl). This method valorizes the by-product and reduces environmental pollution.
Hydrazine Hydrate Production
Sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3·10H2O) is a by-product from hydrazine hydrate production. It can be used as a raw material to replace soda ash in sodium bisulfate production, reducing raw material costs and providing a way to utilize this by-product
Key Applications of Sodium Bisulfate
💡 Want to explore the key applications of sodium bisulfate? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its use in water treatment, cleaning agents, and pH regulation, helping you understand its benefits and industrial significance.
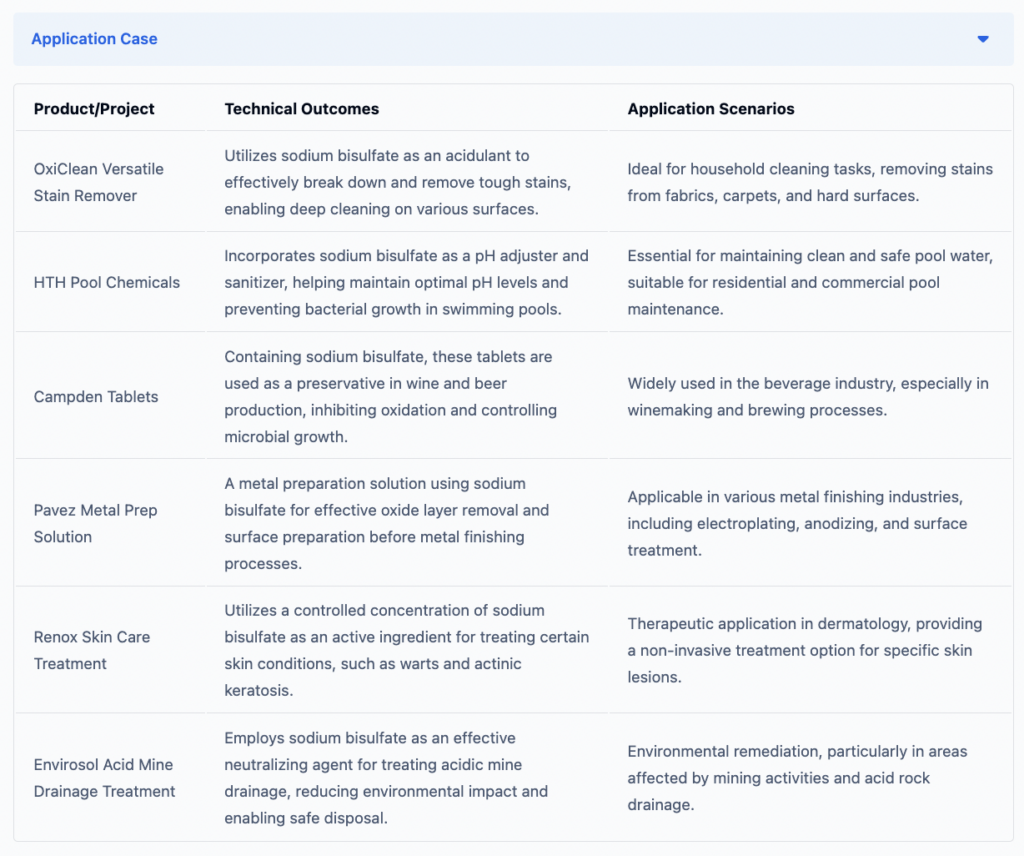
Household Cleaning Products
Sodium bisulfate is commonly used in household cleaning products due to its acidic nature. It is quite effective in removing stains, scale, and deposits. It is a key ingredient in toilet bowl cleaners, grout cleaners, and other acidic cleaning solutions.
Swimming Pool Maintenance
In swimming pool maintenance, people often use sodium bisulfate to adjust the pH levels of pool water, ensuring it remains within the optimal range for swimmer comfort and safety. Additionally, it helps control bacterial growth, keeping the water clean and safe.
Food and Pharmaceutical Preservatives
Sodium bisulfate acts as a preservative in food and pharmaceutical industries by inhibiting microbial growth and oxidation. It is used in products like beverages, baked goods, and medications.
Metal Finishing
Sodium bisulfate finds applications in metal finishing processes, such as electroplating, metal cleaning, and pickling. It helps remove oxide layers and prepare metal surfaces for further processing.

Therapeutic Applications
Acute Cyanide Poisoning
Sodium bisulfate is being explored for treating acute cyanide poisoning due to its acidic properties, which can help neutralize cyanide ions.
Cisplatin Toxicities
Research indicates that sodium bisulfate can help mitigate toxicities associated with cancer therapy drugs like cisplatin, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Calciphylaxis
Sodium bisulfate is in use for treating calciphylaxis, a serious condition affecting dialysis patients, by helping to reduce calcium deposits in soft tissues.
Environmental Applications
Emission Control Agent
Sodium bisulfate is effective in reducing ammonia and alcohol emissions from dairy slurry, contributing to environmental pollution control. Its use in emission control helps mitigate the environmental impact of agricultural practices.
Agriculture and Animal Husbandry
In agriculture and animal husbandry, sodium bisulfate can reduce pH levels in calf bedding, preventing bacterial growth and creating an unfavorable environment for fly larvae. This application helps improve animal health and hygiene.
If you want to know more about applications of sodium bisulfate, to help improve your research and development projects or innovations, ask Eureka Tech-Seek
Pros and Cons of Sodium Bisulfate
Pros
- Effective pH Adjuster: Sodium bisulfate is widely used in various industries for its ability to regulate pH levels effectively. Its acidic properties make it a reliable choice for pH adjustment.
- Multifunctional Use: This compound serves multiple purposes, ranging from cleaning and preservation to therapeutic and environmental applications, making it a versatile and valuable compound across industries.
- Environmental Benefits: The development of sustainable production methods utilizing waste resources aligns sodium bisulfate with eco-friendly practices, reducing environmental pollution and promoting resource efficiency.
Cons
- Potential Health Risks: Sodium bisulfate can pose health risks if mishandled. It can cause respiratory and skin irritation, and in severe cases, chemical burns. Proper handling and protective measures are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Regulatory Considerations: The use of sodium bisulfate must comply with various safety and environmental regulations. Ensuring compliance can be challenging and may require additional resources and monitoring.
Achievements in Research and Developments of Sodium Bisulfate
Sustainable Production Advancements
- Solid Slag Utilization: Researchers have successfully developed methods to produce sodium bisulfate from solid slag, a waste product of the coal chemical industry. This approach not only reduces waste but also minimizes the environmental footprint of sodium bisulfate production.
- By-products of Lithium Salt Production: Utilizing sodium sulfate, a by-product of lithium salt production, to produce sodium bisulfate has shown promise. This method reduces waste and promotes a circular economy by converting by-products into valuable chemicals.
- Gas-Liquid Reactions: Innovations in production techniques, such as gas-liquid reactions, have improved the efficiency and yield of sodium bisulfate production. These methods offer more controlled and efficient reactions, enhancing overall production processes.
Therapeutic Research
- Cyanide Poisoning Treatment: Researchers are investigating the use of sodium bisulfate in treating acute cyanide poisoning. Preliminary studies suggest that its acidic properties can help neutralize cyanide ions, offering a potential treatment option for this life-threatening condition.
- Cisplatin Toxicity Mitigation: Sodium bisulfate is being studied for its potential to mitigate toxicities associated with cisplatin, a chemotherapy drug. Early research indicates that it may help reduce side effects and improve patient outcomes during cancer treatment.
- Calciphylaxis Treatment: In the field of nephrology, sodium bisulfate is being evaluated for its effectiveness in treating calciphylaxis, a serious condition affecting dialysis patients. Its role in reducing calcium deposits in soft tissues is being explored as a potential therapeutic approach.
Preservative Research
- Enhanced Stability: Researchers are investigating formulations that enhance the stability of sodium bisulfate in various products, ensuring consistent preservative action over extended periods.
- Synergistic Effects: By combining sodium bisulfate with other preservatives and additives, researchers have explored to achieve synergistic effects, enhancing overall preservation and safety.

For detailed scientific explanations and in-depth research of innovations of sodium bisulfate, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research
Health and Safety Regulations of Using Sodium Bisulfate
FDA and EPA Monitoring
The use of sodium bisulfate is subject to regulatory oversight by agencies such as the FDA and EPA:
- FDA Regulation: As a food preservative, FDA regulates sodium bisulfate to ensure safe consumption levels. Adherence to FDA guidelines is essential to prevent adverse health effects.
- EPA Monitoring: The EPA monitors industrial effluents containing sulfur compounds, including sodium bisulfate, to prevent environmental pollution. Compliance with EPA regulations is critical to minimize environmental impact.
Safety Guidelines
To ensure safe handling and use of sodium bisulfate, you need to follow the safety guidelines below:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and protective clothing, to prevent skin and eye exposure.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in work areas to avoid inhalation of fumes. Use fume hoods or exhaust systems in confined spaces.
- Spill Containment: Implement procedures to contain and clean up spills promptly to minimize environmental contamination and prevent workplace accidents.
Green Cleaning Alternatives
To reduce reliance on sodium bisulfate:
- Vinegar: Acetic acid in vinegar is an effective, natural alternative for cleaning and pH adjustment.
- Baking Soda: Sodium bicarbonate is a versatile, non-toxic cleaner and pH regulator, suitable for various household applications.
- Plant-based Surfactants: Natural surfactants derived from plants offer environmentally friendly cleaning solutions with minimal health risks.
Conclusion
Sodium bisulfate is a versatile and essential compound, renowned for its pH adjusting, preservative, and cleaning properties. This comprehensive article has detailed its key applications and sustainable production methods. With ongoing research and innovation, sodium bisulfate continues to hold promise for future advancements across various industries.

