I. Introduction
Sodium percarbonate, a powerful and versatile cleaning agent, plays a pivotal role in various industries. This article aims to delve deeply into the chemistry of sodium percarbonate, exploring its definition, properties, and applications. We will also discuss its advantages and limitations, along with the latest advancements in its research and development.

II. What is Sodium Percarbonate?
Sodium percarbonate, known chemically as 2Na₂CO₃•3H₂O₂, is an adduct formed by the reaction of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide. This compound comprises sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide in a 2:3 molar ratio, acting as a solid source of hydrogen peroxide, wherein peroxide molecules are stabilized by sodium carbonate. When dissolved in water, it decomposes to release hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate:
2??2??3•3?2?2+?2?→2??2??3+3?2?22Na2CO3•3H2O2+H2O→2Na2CO3+3H2O2
The released hydrogen peroxide serves as a robust oxidizing agent. Sodium percarbonate boasts greater stability and safety compared to liquid hydrogen peroxide, making it suitable for various applications, including detergents, bleaching agents, and environmental remediation. Its versatility and environmental friendliness further enhance its value across multiple industries.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of sodium percarbonate, check Eurkea.
III. Chemical Properties and Mechanism of Action
Properties of Sodium Percarbonate
– High active oxygen content (typically >14%), making it an effective oxidizing agent.
– Stability as a solid, with improved stability through additives, coatings, and controlled manufacturing processes.
– Solubility in water, enabling the release of hydrogen peroxide for oxidation and bleaching applications.
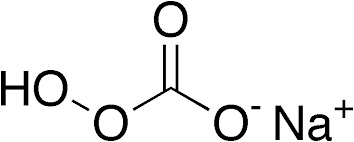
Mechanism of Action
Sodium percarbonate (2Na2CO3·3H2O2) acts as an oxidizing agent and bleaching agent due to its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. The key chemical reactions involved are:
- 1. Dissociation in water: 2Na2CO3·3H2O2 + 3H2O → 2Na2CO3 + 3H2O2
- This releases hydrogen peroxide, which is the active oxidizing species.
- 2. Oxidation reactions: H2O2 undergoes various oxidation reactions, such as:
- Oxidation of organic compounds, leading to bleaching and decolorization.
- Oxidation of inorganic compounds, e.g., Fe(II) → Fe(III), leading to disinfection.
- 3. Decomposition: H2O2 can decompose into water and oxygen, especially in the presence of catalysts or at high temperatures.
IV. Key Applications of Sodium Percarbonate
Sodium Percarbonate for Household Cleaning and Laundry
- Brightening and Stain Removal: Sodium percarbonate is widely used in laundry detergents and cleaning formulations due to its potent oxidizing and bleaching properties. It effectively brightens colors and removes stains.
- Eco-friendly Alternative: It serves as a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to chlorine bleach.
Food Industry
- Beyond Fruit and Vegetable Washing: Sodium percarbonate finds applications in fruit and vegetable washing solutions, where it aids in removing pesticide residues and contaminants. Its antimicrobial properties also make it useful for food processing and disinfection purposes.
Environmental Applications of Sodium Percarbonate
- Water Treatment and Remediation: Sodium percarbonate is employed in water treatment processes for fast oxygenation and disinfection. Its ability to release oxygen and hydrogen peroxide makes it beneficial for wastewater treatment, sewage treatment, and other environmental remediation applications.
- Environmental Impact: While it offers significant benefits, its eco-toxicity must be managed properly to avoid adverse effects.
Textile Processing
- Application in Textile Industry: Its oxidizing properties are leveraged for dyeing, bleaching, and finishing fabrics, contributing to textile processing innovations.
Medical and Personal Care
- Applications: Sodium percarbonate is used in controlled release formulations for skin treatments and wound care, providing targeted delivery of hydrogen peroxide for antimicrobial and healing benefits.

If you want to know more about applications of sodium percarbonate, to help improve your research and development projects or innovations, ask Eureka Tech-Seek
V. Coated vs. Uncoated Sodium Percarbonate
Stability & Shelf Life
Coated sodium percarbonate offers enhanced stability and a longer shelf life compared to the uncoated. The coating acts as a protective barrier against moisture, heat, and other environmental factors that can cause premature decomposition of the sodium percarbonate. Coatings commonly used include inorganic compounds like sodium silicates, borates, magnesium compounds, or organic polymers.
Uncoated sodium percarbonate, on the other hand, is more susceptible to degradation and loses its active oxygen content faster, leading to a shorter shelf life.
Handling & Storage
Coated sodium percarbonate is easier to handle and store due to reduced dustiness and better flow properties. It is less prone to caking and abrasion, making it more user-friendly.
Uncoated sodium percarbonate, being more sensitive to moisture and temperature fluctuations, may require more careful handling and storage conditions to maintain its quality.
VI. Pros and Cons of Sodium Percarbonate
Advantages
- Eco-friendly: It breaks down into harmless components like water and oxygen.
- Effective Cleaning: Releases strong oxygen for efficient stain removal and disinfection.
- Versatility: Applicable across various industries, from household cleaning to medical care.
Disadvantages
- Handling Risks: Potential for skin, eye, and respiratory irritation if not handled properly.
- Environmental Concerns: Risk of eco-toxicity if not managed correctly, necessitating careful handling and disposal protocols.

VII. Latest Achievements in Research and Development
Therapeutic Substances for Dissolving Bath Products
Solid sodium percarbonate is incorporated into packaging for bath products, which can be dissolved in water to produce a hydrogen peroxide solution. This provides beneficial effects to the user in a controlled release manner.
Coated Sodium Percarbonate
Coating technologies have been developed to improve the storage stability of sodium percarbonate particles in detergents and cleaning products. The coatings, often containing reaction products of borates and hydrogen peroxide, provide a controlled release mechanism and enhance shelf life.
Water Fast Oxygenation and Disinfection Products
Sodium percarbonate preparations in the form of tablets, blocks, or pellets have been designed for fast dissolution and controlled release of oxygen in water treatment applications, providing effective disinfection and oxygenation from bottom to top.
Synergistic Deodorant Formulations
Coated sodium percarbonate has been combined with microorganisms like Propionibacterium freudenreichii and lactic acid bacteria, along with fragrances, to create synergistic deodorant formulations with controlled release of active oxygen and beneficial bacteria.
Improved Production Processes
Various patents have been filed for optimized production processes of sodium percarbonate, focusing on improving reaction stability, increasing active oxygen content, enhancing particle properties (size, density, etc.), and achieving better control over the release of active oxygen.
Other notable advancements include research on the synthesis methods, applications in fruit and vegetable washing, and medical/healthcare uses of sodium percarbonate or its byproduct, hydrogen peroxide.
For detailed scientific explanations and in-depth research of innovations of sodium percarbonate, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research

VIII. Conclusion
Sodium percarbonate stands out as a valuable, eco-friendly oxidizing agent, harnessing its stability, efficiency, and environmental benefits to revolutionize various industries. This comprehensive article has explored the key infomation of sodium percarbonate. Its future remains promising with continued innovation and applications.
