Triethylene glycol (TEG) is a widely used polyether compound with the molecular formula C₆H₁₄O₄. It appears as a clear, colorless, and odorless viscous liquid. Owing to its high boiling point, low volatility, and excellent hygroscopicity, TEG serves many vital roles in industry. It acts primarily as a dehydrating agent in natural gas processing, a plasticizer in polymers, a humectant in cosmetics, and a solvent in pharmaceutical and electronic applications.
With growing demand for safer and more sustainable chemicals, TEG’s role is expanding beyond traditional uses. Researchers and manufacturers are focusing on greener production methods and improved formulations to meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
This article explores triethylene glycol’s chemical structure, physical and functional properties, and industry-grade specifications through PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.
What is Triethylene Glycol?
Triethylene glycol is a clear, colorless, and odorless viscous liquid. It belongs to the polyether class and consists of three ethylene glycol units linked together.
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₄O₄
- CAS Number: 112-27-6
- Appearance: Viscous, colorless liquid
- Solubility: Miscible with water and many organic solvents
TEG’s unique molecular structure grants it high thermal stability, low volatility, and excellent hygroscopicity. These features make it a popular choice in dehydration processes and formulation chemistry.

Composition & Properties/Performance
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 150.17 g/mol |
| Density | 1.124 g/cm³ (at 20°C) |
| Boiling Point | 285°C |
| Melting Point | -8.5°C |
| Viscosity | 48 cP (at 25°C) |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.04 mmHg (at 20°C) |
| pH (10% aqueous) | Neutral (~7) |
Key Functional Properties:
- Excellent dehydrating agent in natural gas processing
- Acts as a plasticizer enhancing flexibility in polymers
- Serves as a humectant, retaining moisture in cosmetics and coatings
- High thermal and chemical stability ensures durability under harsh conditions
- Low volatility reduces losses during processing
Material Grades & Designations
Common triethylene glycol grades include:
- Industrial Grade: Used in chemical synthesis, natural gas dehydration
- Pharmaceutical Grade: High purity for medical and cosmetic formulations
- Electronic Grade: Ultra-pure for electronic cooling and manufacturing
| Standard System | Grade Name/Designation | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM D1927 | Industrial TEG | Gas dehydration, solvents |
| USP/NF | Pharmaceutical Grade | Personal care, pharma |
| JIS K 2201 | Electronic Grade | Semiconductor cooling fluids |
Application Landscape
Triethylene glycol finds use in diverse industries:
- Natural Gas Industry: Primary dehydrating agent to remove water vapor
- Plastics and Polymers: As a plasticizer and intermediate in polymer synthesis
- Cosmetics & Personal Care: Humectant in lotions, creams, and deodorants
- Pharmaceuticals: Solvent and stabilizer in drug formulations
- Electronics: Cooling fluids in semiconductor manufacturing
Example Use Cases:
- A major natural gas plant uses industrial-grade TEG for efficient dehydration.
- Cosmetic brands incorporate pharmaceutical-grade TEG for moisture retention.
- Electronics firms rely on ultra-pure TEG in thermal management fluids.
Emerging Trends:
- Development of bio-based TEG from renewable feedstocks
- Innovations in TEG blends to improve environmental profiles
- Regulations driving adoption of low-toxicity, safer glycols
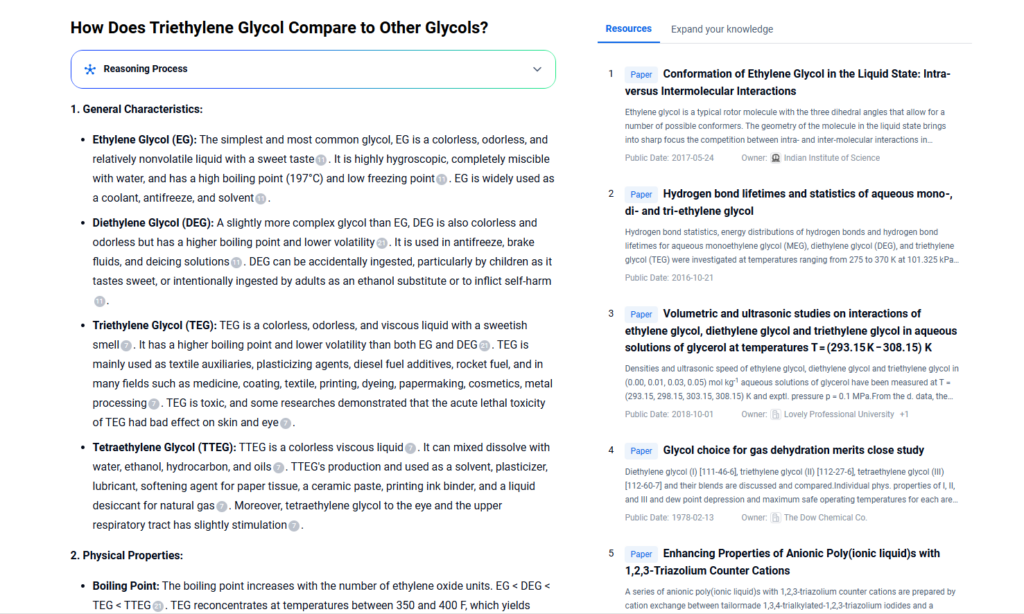
Triethylene Glycol vs Other Similar Materials
| Feature | Triethylene Glycol (TEG) | Ethylene Glycol (EG) | Diethylene Glycol (DEG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 150.17 g/mol | 62.07 g/mol | 106.12 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 285°C | 197°C | 245°C |
| Toxicity | Low | Moderate | Higher |
| Typical Uses | Gas dehydration, cosmetics | Antifreeze, coolants | Solvent, plasticizers |
Advantages of TEG:
- Higher boiling point provides thermal stability
- Lower toxicity compared to DEG, safer in consumer products
- Superior moisture absorption capacity
- Versatile across multiple industries
Innovations & Technology
Triethylene glycol’s continued relevance is driven by active innovation in production, formulation, and application. Here are key technological advancements shaping its future:
1. Sustainable and Bio-Based Production
- New methods use renewable biomass feedstocks, such as plant sugars, to produce TEG via green chemical routes.
- These approaches reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Pilot projects demonstrate fermentation-based synthesis and enzymatic catalysis, enhancing sustainability.
2. High-Purity and Specialty Grades
- Advances in purification technology enable production of ultra-high purity TEG for sensitive electronics and pharmaceutical uses.
- Techniques like distillation under reduced pressure and membrane filtration improve impurity removal.
- Specialty grades meet stringent standards for moisture, acidity, and contaminant levels.
3. Advanced Formulation Technologies
- TEG blends with other glycols and additives optimize performance in antifreeze, plasticizers, and solvent systems.
- Researchers develop TEG-based polymer plasticizers with enhanced flexibility and reduced toxicity.
- In cosmetics, formulation scientists use TEG to create moisture-retentive, non-irritating products.
4. Green Chemistry and Process Intensification
- Catalysts and solvents are being replaced with environmentally benign alternatives to improve process safety and reduce waste.
- Novel reactor designs, including microreactors and continuous flow systems, increase efficiency and scalability.
- Process intensification reduces energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Sustainability & Environmental Impact
- TEG is biodegradable and generally considered safe for the environment.
- The shift toward bio-based TEG reduces carbon footprint and supports circular economy goals.
- Production improvements lower energy consumption and emissions.
- Compliance with REACH, RoHS, and FDA standards ensures safe use in consumer and industrial products.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent. helps companies innovate with TEG by:
- Providing patent landscape mapping and competitor monitoring
- Identifying regulatory changes affecting TEG applications
- Tracking emerging technologies and green chemistry trends
- Offering data-driven insights to accelerate R&D and reduce risk
Conclusion
Triethylene glycol remains an indispensable chemical due to its versatile properties and broad application scope. Its thermal stability, low toxicity, and excellent moisture management qualities enable its use in natural gas dehydration, plastics, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
At the same time, the industry faces increasing pressure to enhance sustainability and meet tighter regulations. The shift towards bio-based TEG, high-purity specialty grades, and greener manufacturing processes illustrates the sector’s commitment to environmental responsibility and product safety. In summary, triethylene glycol’s future looks promising as innovation and technology drive it toward safer, greener, and higher-performing applications across industries.
FAQs
It is used in gas dehydration, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and electronics cooling.
TEG has low toxicity but should still be handled per safety guidelines.
TEG has a higher boiling point, lower toxicity, and better moisture retention.
Yes, bio-based production methods are emerging to reduce environmental impact.
Natural gas, personal care, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and electronics.
For more scientific explanations of triethylene glycol , try PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.