UWQHD, or Ultra-Wide Quad HD, is a popular ultra-wide display resolution standard commonly used in monitors designed for immersive gaming, professional work, and multimedia consumption. It offers a wider field of view compared to traditional resolutions, making it highly attractive for multitasking and immersive experiences.
This article explores the technology trends and patent landscapes driving UWQHD innovations, uncovering strategic insights to stay ahead in display technology development through PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.
What is UWQHD?
UWQHD stands for Ultra-Wide Quad High Definition. It typically refers to a display resolution of 3440 x 1440 pixels, combining ultra-wide aspect ratios (21:9) with Quad HD vertical resolution (1440p). This ultra-wide format is designed to provide significantly more horizontal screen real estate compared to standard 16:9 WQHD (2560 x 1440), enhancing productivity and immersive viewing.

Key Specifications of UWQHD
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Resolution | 3440 x 1440 pixels |
| Aspect Ratio | 21:9 |
| Pixel Density | Typically ~110 PPI (varies) |
| Refresh Rate | Ranges from 60Hz to 144Hz+ |
| Panel Types | IPS, VA, OLED |
| Color Gamut | Up to 100% sRGB or higher |
| Response Time | Typically 1ms to 5ms |
| Connectivity | HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C |
Real-World Applications & Use Scenarios
- Gaming: UWQHD’s wide aspect ratio delivers immersive gameplay with expanded peripheral vision, popular among gamers who demand realistic and panoramic visuals.
- Professional Work: Video editors, graphic designers, and programmers benefit from more horizontal space for timelines, multiple windows, and coding interfaces.
- Entertainment: Ultra-wide monitors provide cinematic viewing experiences, replicating movie theater aspect ratios without black bars.
- Multitasking: Business users enjoy enhanced productivity by viewing multiple applications side-by-side on a single screen, reducing the need for dual monitors.
Market Relevance & Competitive Positioning
UWQHD monitors have gained substantial popularity as ultra-wide displays become more affordable and mainstream. Brands like Dell, LG, Samsung, and Asus aggressively compete in this market segment, targeting gamers and professionals alike.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent reveals a growing patent activity in ultra-wide display manufacturing, panel innovations, and adaptive refresh technologies — emphasizing UWQHD’s increasing technological relevance and innovation momentum.
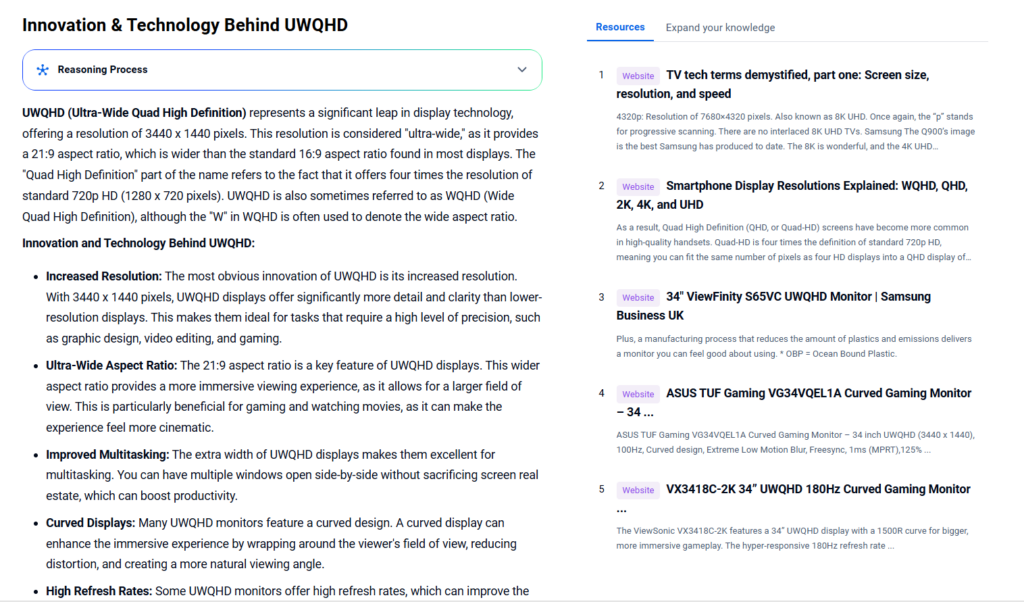
Innovation & Technology Behind UWQHD
- Increased Resolution: One of the most notable innovations is the higher resolution. With 3440 x 1440 pixels, these ultra-wide displays offer significantly more detail and clarity than lower-resolution screens. This makes them ideal for tasks requiring precision, such as graphic design, video editing, and gaming.
- Ultra-Wide Aspect Ratio: A key feature is the 21:9 aspect ratio. This wider format provides a more immersive viewing experience. It allows a larger field of view, which is especially beneficial for gaming and watching movies, creating a cinematic feel.
- Improved Multitasking: The extra horizontal space makes multitasking easier. Users can open multiple windows side-by-side without sacrificing screen space. This leads to improved productivity.
- Curved Displays: Many models feature a curved design. The curve wraps around the viewer’s field of vision. It enhances immersion, reduces distortion, and creates a more natural viewing angle.
- High Refresh Rates: Some monitors support high refresh rates. This improves motion smoothness in games and videos. For instance, the ViewSonic VX3418C-2K offers a 180Hz refresh rate.
- Advanced Panel Technologies: Various panel types are used, including IPS (In-Plane Switching) and VA (Vertical Alignment). These improve color accuracy, contrast, and viewing angles.
- Quantum Dot Technology: Certain displays use quantum-dot technology, such as Samsung’s SUHD TVs. This enhances color reproduction and brightness.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Some manufacturers, like Samsung, emphasize sustainable processes. They reduce plastic use and emissions during production.

Challenges and Considerations:
- Content Availability: While UWQHD displays offer stunning visuals, the availability of content that takes full advantage of the resolution and aspect ratio is still limited. Many movies and games are still produced in standard aspect ratios, and upscaling lower-resolution content can sometimes result in a loss of quality.
- Hardware Requirements: Running games and applications at UWQHD resolution requires a powerful graphics card, as rendering images at such a high resolution can be demanding on hardware.
- Cost: UWQHD displays are generally more expensive than lower-resolution displays.
In summary, UWQHD represents a significant advancement in display technology, offering improved resolution, an ultra-wide aspect ratio, and enhanced multitasking capabilities. However, it’s essential to consider factors like content availability, hardware requirements, and cost when deciding if an UWQHD display is the right choice for you.
UWQHD vs. WQHD: Feature-by-Feature Comparison
Understanding the differences between UWQHD (Ultra Wide Quad High Definition) and WQHD (Wide Quad High Definition) requires a deep dive into their specifications and use cases. Below is a comprehensive comparison of the two, highlighting their key features and differences.
1. Resolution
- WQHD: WQHD, or Wide Quad High Definition, has a resolution of 2560 x 1440 pixels. This means it has 2,560 horizontal pixels and 1,440 vertical pixels, resulting in a total of 3,686,400 pixels (2,560 x 1,440). It is sometimes referred to as 2K, with the idea that it’s half the 4K HD resolution (more about that later).
- UWQHD: UWQHD, or Ultra Wide Quad High Definition, typically has a resolution of 3440 x 1440 pixels. This means it has 3,440 horizontal pixels and 1,440 vertical pixels, resulting in a total of 4,972,800 pixels (3,440 x 1,440). Some ultra-wide variants of this resolution go up to 5120 x 1440 pixels.
2. Aspect Ratio
- WQHD: WQHD has an aspect ratio of 16:9. The “Wide” or “W” in WQHD explicitly emphasizes the widescreen 16:9 aspect ratio.
- UWQHD: UWQHD has a wider aspect ratio, typically 21:9. This makes it suitable for tasks that require a wider field of view, such as video editing, gaming, or multitasking with multiple windows side by side.
3. Screen Size
- WQHD: WQHD is commonly found on monitors ranging from 27 to 32 inches. A 34-inch ultrawide monitor with a 3440×1440 (WQHD) resolution is also mentioned as an industry standard.
- UWQHD: UWQHD is typically found on larger, ultrawide monitors, ranging from 34 inches to 49 inches. A 34 Inch ultrawide 21:9 WQHD (3440x1440p) IPS curved monitor is one example.
4. Use Cases
- WQHD: WQHD is a good balance between resolution and performance, making it suitable for a wide range of tasks, including general computing, gaming, and multimedia consumption. It is also a good choice for users who want a higher resolution than Full HD but don’t want to sacrifice too much in terms of performance or power consumption.
- UWQHD: UWQHD is ideal for tasks that require a lot of screen real estate, such as video editing, graphic design, programming, or multitasking with multiple windows open simultaneously. The wider aspect ratio allows for more content to be displayed on the screen at once, which can improve productivity and immersion. UWQHD monitors are great if your work demands having two applications open at once – you can see the contents of both without having to shift between tabs.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages
- WQHD:
- Advantages: Good balance between resolution and performance; widely available; compatible with a variety of devices.
- Disadvantages: May not provide enough screen real estate for some tasks; lower pixel density compared to higher resolutions.
- UWQHD:
- Advantages: Provides a lot of screen real estate; ideal for multitasking and immersive experiences; higher pixel density compared to WQHD.
- Disadvantages: Requires a more powerful graphics card to drive the higher resolution; may be more expensive; less portable due to larger screen size.
6. Other Considerations
- Graphics Card Requirements: Both WQHD and UWQHD require a dedicated graphics card for optimal performance, especially for gaming or graphic-intensive tasks. The higher resolution of UWQHD will require a more powerful graphics card.
- Power Consumption: Higher resolution displays typically consume more power. UWQHD displays will generally have higher power consumption than WQHD displays.
- Availability and Cost: WQHD monitors are more common and generally more affordable than UWQHD monitors. UWQHD monitors are typically premium products and come with a higher price tag.
- Connectivity: Many modern WQHD and UWQHD monitors come with a variety of connectivity options, including HDMI, DisplayPort, and USB-C. Some monitors have USB hubs that let you plug USB thumb drives or other devices into more convenient ports on the monitor instead of reaching around the back of your PC; such a display will have both a USB upstream port (for connecting the monitor and computer) and one or more USB downstream ports (for thumb drives and other peripherals). On USB Type-C-capable monitors, sometimes that same connection can act as the video signal carrier and the data conduit, and often can supply power to run or charge your computer as well. A USB Type-C port with up to 90W charging power can link to business laptops and transmit data with just one cable, reducing clutter often associated with old monitors.
In summary, the choice between WQHD and UWQHD depends on your specific needs and preferences. If you prioritize a balance between resolution and performance and don’t need a lot of screen real estate, WQHD is a great choice. If you require a lot of screen space for multitasking or immersive experiences and have a powerful graphics card, UWQHD is the way to go.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent is a powerful tool for analyzing the ultra-wide display market. It provides:
- Patent Landscape Analysis: Discover key patents related to UWQHD technology.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Understand market leaders’ IP strategies and innovation hotspots.
- Trend Detection: Monitor emerging technologies in display manufacturing and panel tech.
- Strategic Insights: Support R&D and product development with actionable data.
By integrating PatSnap Eureka, companies and researchers can gain an edge in understanding and innovating within the ultra-wide display segment.
Conclusion
UWQHD is reshaping the display industry by offering a wider, more immersive experience that appeals to gamers, professionals, and content consumers alike. Its technological advancements and increasing market penetration underscore its importance in modern computing. Leveraging AI-powered tools like PatSnap Eureka can accelerate insight generation and innovation, ensuring stakeholders stay competitive in this dynamic field.
FAQs
A: It depends on your needs. UWQHD offers more horizontal space and immersive viewing, ideal for multitasking and gaming, while WQHD is more affordable and sufficient for general use.
A: Mostly desktop monitors, some high-end laptops, and gaming setups support UWQHD resolution.
A: To drive higher resolutions and refresh rates smoothly, a modern GPU with adequate power is recommended.
A: It provides patent analytics, market trend insights, and competitive intelligence specifically for display technologies including UWQHD.
By harnessing PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, your organization can navigate the fast-evolving UWQHD display landscape with data-driven confidence—driving innovation and strategic growth in the ultra-wide revolution.