Waymo LLC, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., is a trailblazer in autonomous vehicle (AV) technology. Originally launched as Google’s self-driving car project in 2009, Waymo has since evolved into a full-scale mobility company focused on robotaxis, freight automation, and AV platforms.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of Waymo’s corporate structure, product portfolio, business model, innovation footprint, and market position. Powered by insights from the PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, we also explore how intellectual property (IP) trends reflect Waymo’s competitive advantage in autonomous driving and perception systems.
Company Overview of Waymo
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Company Name | Waymo LLC |
| Founded | 2009 (as Google Self-Driving Car Project) |
| Headquarters | Mountain View, California, USA |
| Parent Company | Alphabet Inc. |
| CEO (2025) | Tekedra Mawakana (Co-CEO), Dmitri Dolgov (Co-CEO) |
| Core Focus Areas | Robotaxi services, autonomous driving software, AV platforms |
| Key Products | Waymo Driver, Waymo One, Waymo Via |

Corporate Structure
| Unit / Segment | Role / Focus |
|---|---|
| Waymo Driver | Autonomous driving system stack used in all Waymo vehicles |
| Waymo One | Robotaxi ride-hailing service available in Phoenix and expanding |
| Waymo Via | Autonomous freight and delivery logistics platform |
| Perception & AI | Neural network training, sensor fusion, behavior prediction |
| Simulation & Safety | Virtual testing, scenario generation, safety case validation |
Waymo operates as a semi-autonomous subsidiary of Alphabet, with access to Google Cloud, machine learning infrastructure, and engineering talent.
Products and Services of of Waymo
Waymo Driver
A modular, AI-based autonomous driving system designed to be integrated into various vehicle platforms (e.g., Chrysler Pacifica, Jaguar I-PACE, Freightliner trucks). It includes:
- Perception Module: Sensor fusion, 3D object detection, semantic segmentation
- Behavior Prediction: ML models forecasting the actions of pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles
- Planning & Control: Route optimization, trajectory generation, emergency response handling
Waymo One
Commercial robotaxi service currently operational in Phoenix, Arizona, and parts of Los Angeles and San Francisco (limited). Features:
- App-based hailing
- Fully driverless rides
- Remote assistance integration

Waymo Via
Focuses on autonomous freight delivery, with pilot programs on long-haul trucking routes in Texas. Partners include UPS, JB Hunt, and Daimler Trucks.
Business Model
Waymo follows a multi-tiered monetization strategy targeting urban mobility and logistics:
| Stream | Description |
|---|---|
| B2C Robotaxi Services | Waymo One generates fare-based revenue via app-based rides |
| B2B Freight Solutions | Waymo Via partners with logistics companies and fleets |
| Licensing (Future) | Plans to license Waymo Driver to OEMs for autonomous vehicles |
| Data Services | Potential monetization of driving behavior, HD mapping, and traffic data |
Waymo’s long-term vision includes deploying autonomous driving across all forms of ground mobility, including last-mile delivery and ride-hailing at scale.
Market Position of Waymo
| Factor | Status |
|---|---|
| Robotaxi Deployment | First U.S. company to offer fully autonomous rides (no safety driver) |
| Freight Pilots | Active in Texas; competitive with Aurora, Kodiak, and TuSimple |
| Geographic Footprint | Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles; testing in Texas and Nevada |
| OEM Partners | Chrysler (Stellantis), Jaguar, Daimler, Volvo, Geely |
| Fleet Size | Over 300 robotaxis, 100+ autonomous trucks (as of 2024) |
Waymo leads in real-world miles driven, having logged over 40 million autonomous miles on public roads and billions more in simulation.
Innovation & Technology of of Waymo
Waymo’s innovation engine is built on a deeply integrated stack of perception, decision-making, and control technologies, underpinned by a rich portfolio of high-impact patents. Using PatSnap Eureka, we can uncover Waymo’s technical edge across five core domains—each reflecting strategic investments in safety, intelligence, and scalability.
1. Sensor Fusion and Perception Systems
At the heart of the Waymo Driver lies its custom-designed multi-modal sensor suite, consisting of:
- Long-range LiDAR: For 360° distance mapping at up to 300m
- Short-range LiDARs: Mounted at lower corners for curb/close object detection
- Radar: Penetrates adverse weather; measures object velocity
- High-resolution cameras: Capture color, lane markings, road signs, traffic lights
- Ultrasonic sensors: Used at low speeds for parking and proximity awareness
These sensors are fused using proprietary software and edge AI accelerators.
Patent Highlights :
- Occlusion compensation: Detecting partially obscured objects (e.g., child behind a car)
- Dynamic sensor alignment: Real-time calibration across temperature shifts or road vibration
- 3D environmental reconstruction: Fusing radar and LiDAR for volumetric scene understanding
- Reflected beam filtering: Isolating relevant signals from reflective surfaces
2. Deep Learning and Behavior Prediction
Waymo’s behavior prediction module uses spatiotemporal deep neural networks to forecast the motion and intent of dynamic actors (pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles) up to several seconds in advance.
Key innovations include:
- Keypoint recognition: Identifying human pose (e.g., arm raised to cross street) using CNNs
- Social interaction modeling: Predicting vehicle-pedestrian negotiation at intersections
- Multi-modal prediction: Modeling multiple plausible paths and assigning confidence values
- Behavioral classification: Detecting aggressive drivers, confused pedestrians, yielding behavior
Patent Highlights:
- Training methods combining real-world sensor logs + synthetic adversarial data
- Reinforcement learning agents to model unstructured human intent
- Vehicle motion prediction in multi-agent environments
3. Mapping and Localization
Waymo builds and maintains ultra-high-definition (HD) maps for localization, route planning, and context-aware behavior. These maps include:
- Lane-level detail: Width, curvature, lane types, and barrier information
- Semantic data: Road signs, traffic lights, yield zones, crosswalks
- Topological rules: Right-of-way logic, U-turn legality, construction zones
Localization is achieved using sensor-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), inertial measurements, and GPS correction.
Patent Highlights:
- Dynamic localization without GPS (e.g., in tunnels or urban canyons)
- Map confidence indexing: Real-time quality control based on sensor feedback
- Real-time updates using fleet sensor crowdsourcing
- Automated map stitching across adjacent geographic tiles
4. Planning and Control
The planning layer is responsible for trajectory generation, goal fulfillment, and risk-aware decision-making, based on real-time data from the perception and prediction modules.
Key system capabilities include:
- Multi-agent negotiation: Real-time adjustment of speed/trajectory in complex interactions
- Yield & stop logic: Policy-driven response to signals, crosswalks, and stopped vehicles
- Emergency protocol library: Fall-back behavior (e.g., controlled stop, reroute) when anomalies arise
- Smooth trajectory planning: Jerk-minimization for comfort and safety
Patent Highlights:
- Human-aware control smoothing for passenger comfort
- Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) awareness in multi-Waymo scenarios
- Remote override system with human-in-the-loop interfaces for rare edge cases
- Energy-optimized trajectory adjustment for EVs
5. Simulation and Edge Case Testing
Waymo’s testing pipeline includes billions of simulated miles per year—more than any other AV developer. The simulator is capable of generating highly realistic traffic scenarios, and includes:
- Edge case generators: Simulate rare events (e.g., a ball rolling into the road)
- Weather overlays: Rain, snow, glare conditions modeled using generative techniques
- Full-stack validation: From raw sensor input to actuator command response
- Behavior diversity injection: Simulating different human driver styles and responses
Patent Highlights:
- Adversarial testing frameworks for non-deterministic scenario replay
- Behavior switching engines to modify simulation actor logic mid-test
- Real-time logging and training of behavior predictors from simulated miles
Technical Differentiation via PatSnap Eureka AI Agent
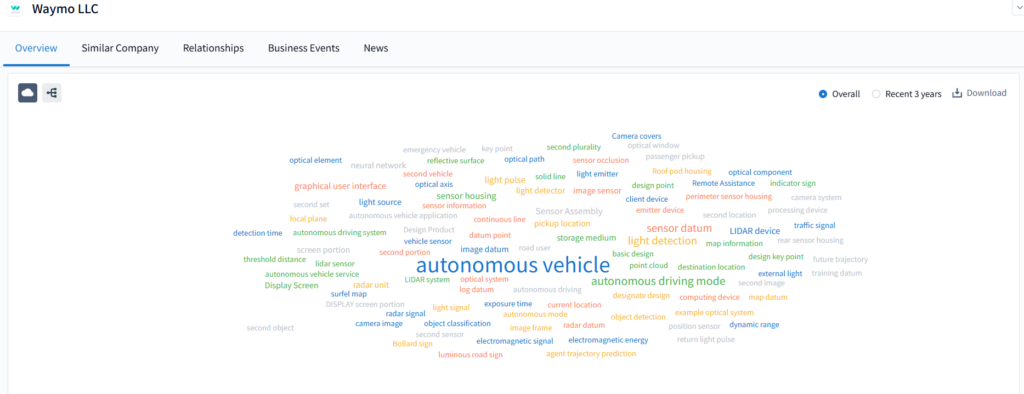
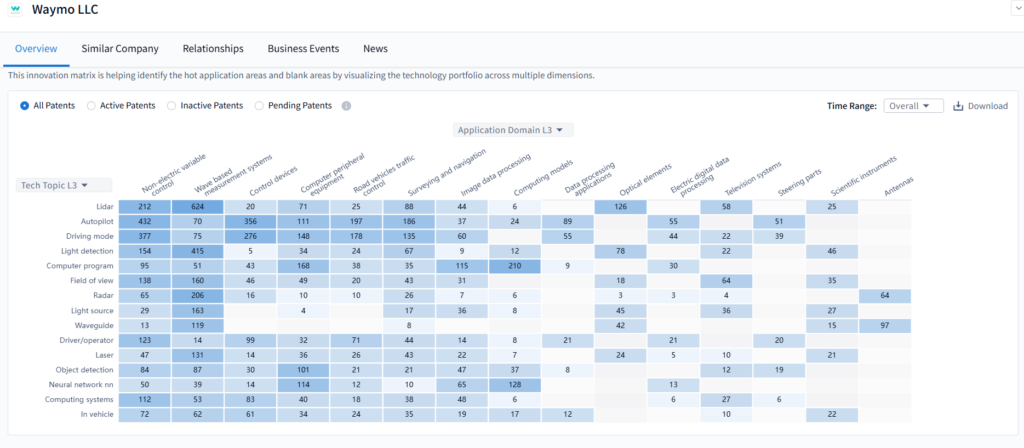
Waymo’s IP heatmap via PatSnap Eureka’s Company Search AI Agent shows:
- Strongest clusters in sensor occlusion handling, multi-agent trajectory planning, and map-based localization
- Dense filings from 2020–2024 in deep learning-based intent prediction and remote override systems
- Active innovation around roof pod design, camera cleaning, and heat dissipation for prolonged AV operation
Market Presence and Financials of of Waymo
| Metric | Estimated Value / Status (2024–2025) |
|---|---|
| Annual R&D Spending | $1.1–1.3 billion (Alphabet allocation) |
| Revenue | Not yet profitable; modest ride-hailing income |
| Valuation (Private) | $30–40 billion (based on internal Alphabet estimates) |
| Ride Volume | 200,000+ robotaxi trips completed in Phoenix and SF |
| Major Partners | Uber (robotaxi integration), Stellantis, Volvo, Daimler, JB Hunt |
Despite not being commercially profitable yet, Waymo continues to lead in data scale, technical depth, and regulatory testing.
Waymo Competitors Analysis in the Autonomous Vehicle and Robotaxi Market
In the rapidly evolving autonomous vehicle industry, Waymo faces competition from several strong players in both robotaxi services and self-driving technology development.
- Is Waymo better than Cruise for robotaxi services?
Cruise, backed by General Motors, has launched urban robotaxi operations in San Francisco, leveraging GM’s large-scale automotive resources. While Cruise excels in dense city navigation, Waymo leads in total autonomous miles driven, multi-city deployment experience, and more integrated self-driving technology stacks, giving it an advantage in scaling robotaxi services nationwide.
- How does Waymo compare to Aurora in autonomous driving?
Aurora Innovation specializes in autonomous freight trucking and partners with FedEx and Uber Freight for logistics. However, Waymo’s strength lies in passenger ride-hailing services, proprietary sensor technology, and a more mature robotaxi deployment network, making it stronger in urban and suburban mobility markets.
- Waymo vs Tesla FSD – which self-driving technology is safer?
Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) Beta uses a camera-only vision system with frequent over-the-air software updates. In contrast, Waymo applies multi-sensor fusion—combining LiDAR, radar, and high-resolution cameras—plus a safety-first engineering approach, which has consistently demonstrated higher reliability in fully driverless operations.
- What advantages does Waymo have over Motional in robotaxis?
Motional, backed by Hyundai and Aptiv, tests autonomous taxis in Las Vegas with Hyundai’s manufacturing support. While Motional benefits from large-scale production, Waymo owns its entire self-driving software stack and custom-built sensors, allowing greater optimization and faster adaptation to complex driving environments.
- Is Waymo ahead of Zoox in autonomous mobility?
Zoox, owned by Amazon, is building a fully custom autonomous vehicle for urban shared transport. Although innovative, Zoox is still in earlier commercial stages. Waymo’s broader regulatory relationships and multi-city operational presence give it a clear lead in real-world deployment and safety validation.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
Using PatSnap Eureka’s Company Search AI Agent, analysts can:
- Explore Waymo’s key IP filings in LIDAR, sensor occlusion, behavior prediction, and real-time routing
- Track technology convergence in computer vision, edge AI, and cloud-based vehicle coordination
- Visualize patent overlaps between Waymo and rivals like Cruise, Tesla, or Aurora
- Identify emerging innovation themes such as emergency vehicle detection, multi-passenger routing, or long-range LIDAR reflectivity compensation
Eureka’s AI mapping helps identify strategic white space, potential licensing opportunities, and R&D risks.
Conclusion
Waymo stands at the forefront of autonomous mobility, blending world-class AI, robust sensor systems, and cloud integration to redefine how people and goods move. As robotaxis and self-driving freight shift from concept to reality, Waymo’s commitment to safety, simulation, and technical excellence positions it as an industry benchmark.
With PatSnap Eureka’s Company Search AI Agent, innovators and strategists can decode the intellectual and strategic fabric driving Waymo forward—and leverage those insights to shape the next wave of intelligent transportation.
FAQs
About $0.90 per mile plus $0.30 per minute, similar to Uber/Lyft rates. Prices vary by city.
To develop and deploy autonomous driving technology for safer, more accessible transportation.
Yes, but with fully driverless vehicles. Waymo offers app-based rides without a human driver.
Concerns include safety incidents, public resistance, regulatory delays, and limited real-world deployment.
In some cases, yes—especially for shared or off-peak rides—but generally priced similarly.
For more detailed information of Waymo, try PatSnap Eureka’s Company Search AI Agent.