
What is an Anesthesia Machine?
An anesthesia machine is a crucial medical device used to administer anesthetic agents to patients undergoing surgical procedures. It is designed to deliver a precise mixture of medical gases, such as oxygen and nitrous oxide, and anesthetic vapors to maintain anesthesia. The machine also supports patient ventilation and includes a scavenging system to remove excess anesthetic gases, thereby minimizing risks to both patients and healthcare staff.
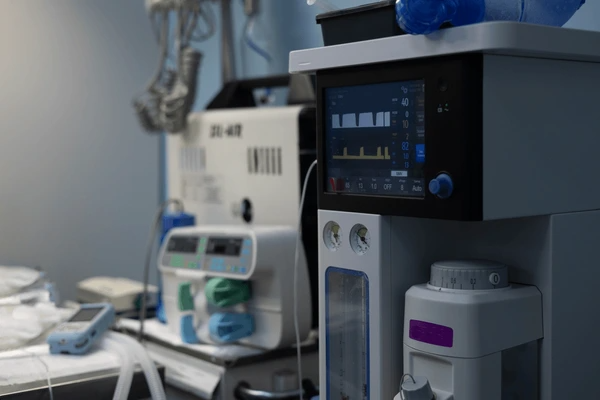
Components of an Anesthesia Machine
- Medical Gas System: The machine receives medical gases from high-pressure cylinders or a central supply line and regulates their flow through individual flowmeters.
- Vaporizers: These devices add anesthetic vapors to the gas mixture based on the user’s settings, ensuring the correct concentration of anesthetics.
- Breathing Circuits: These circuits transport the anesthetic gas mixture to the patient, allowing for spontaneous or controlled ventilation.
- Scavenging System: This system removes expired anesthetic gases from the breathing circuit, preventing rebreathing and reducing environmental contamination.
- Alarms and Monitoring: Modern anesthesia machines are equipped with various alarms and monitoring systems to alert healthcare providers of potential issues and to track patient vital signs.
How Anesthesia Machines Work
- Gas Supply and Mixing: The machine receives medical gases from a pipeline or cylinders. Oxygen is the primary gas, and it flows through the O2 flowmeter. The vaporizer adds anesthetic vapors to the oxygen flow, creating a precise mixture of gases.
- Breathing Circuit: The mixed gas then travels through the breathing circuit, which includes tubing, connectors, and valves. This circuit delivers the gas mixture to the patient’s lungs, either through spontaneous ventilation or mechanical ventilation.
- Scavenging System: After the patient exhales, the used gas is collected by the scavenging system, which removes and recycles the anesthetic gases to prevent environmental contamination.
- Monitoring and Control: Modern anesthesia machines are equipped with monitoring systems that track vital signs, gas concentrations, and other parameters. These systems provide real-time data to anesthesiologists, enabling them to adjust anesthesia levels and ensure patient safety.
Safety Features
- Monitoring and Feedback Control: Modern anesthesia machines feature sophisticated monitoring systems that track physiological parameters and machine functions. This internal feedback control aids in early detection and treatment of patient changes.
- Pressure Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of pipeline and cylinder pressures ensures safety by preventing hypoxia due to gas supply failures.
- Self-Diagnostic Systems: Advanced machines include self-diagnostic panels that identify malfunctions or improper gas flow, helping to prevent anesthesia accidents.
- Alarms and Alerts: Integrated alarms notify anesthesiologists of critical issues, like low gas pressure or incorrect settings, ensuring timely intervention.
- Emergency Oxygen Supply: Anesthesia machines are designed to provide 100% oxygen in emergency situations, ensuring patient safety during critical moments.
Types of Anesthesia Machines
- Traditional anesthesia machines: These machines follow the basic principles of gas delivery and scavenging, with added safety features like fail-safe mechanisms and gas monitoring systems.
- Integrated anesthesia systems: These systems integrate with other medical devices and electronic health records, enhancing workflow efficiency and patient management.
- Modern anesthesia workstations: These machines incorporate advanced monitoring systems, target-controlled infusion pumps, and patient-controlled analgesia devices for personalized anesthesia delivery.
- Portable anesthesia machines: These machines are designed for use in remote locations and are equipped with essential safety features for reliable operation in various settings.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Pre-Use Checks: Before each use, the machine should be checked for proper function of all components, including gas supply, flowmeters, vaporizers, and alarms.
- Daily Maintenance: Regular maintenance should include checking and replacing parts as needed, such as filters and vaporizers.
- Troubleshooting: If a problem is encountered during use, the machine should be checked for malfunctions in the gas supply, breathing circuit, or other components.
- Calibration: The machine should be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate measurement of gas flow and anesthetic concentration.
- Training: Anesthesia providers should be trained in the use and maintenance of the machine, as well as troubleshooting common problems.
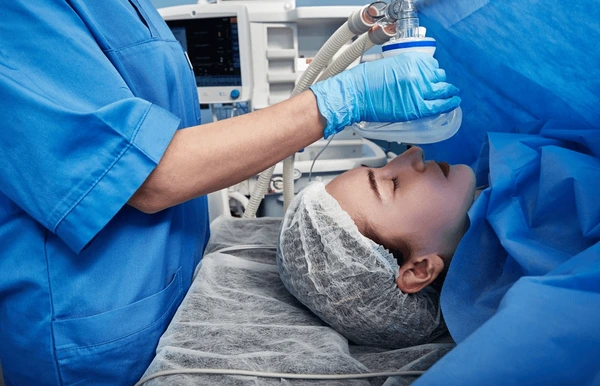
Applications of Anesthesia Machine
- Anesthesia Delivery: Anesthesia machines deliver a mix of medical gases and anesthetic agents to patients. They mix gases from high-pressure cylinders with vapors from vaporizers, providing a precise anesthetic mixture through a breathing circuit.
- Respiratory Support: These machines provide respiratory support by controlling ventilation. They offer modes like manual and mechanical ventilation to assist or fully control a patient’s breathing during surgery.
- Monitoring and Safety: Advanced anesthesia machines include monitoring systems to track vital signs, oxygen levels, and other parameters. This helps anesthesiologists identify complications in real-time, enhancing patient safety.
- Gas Recycling and Scavenging: To conserve anesthetic gases and limit pollution, these machines recycle exhaled gases. They remove carbon dioxide before the gases are re-inhaled, saving costly anesthetic agents.
- Versatility in Procedures: Anesthesia machines adapt to a range of surgical procedures and patient needs. They support general anesthesia, regional anesthesia, and sedation, making them versatile in various medical contexts.
Latest Technical Innovations in Anesthesia Machine
- Automation and Embedded Systems: Modern anesthesia machines use embedded systems to regulate anesthesia delivery automatically, based on real-time physiological data. This increases precision and minimizes human error.
- Integration with EHRs: Advanced anesthesia machines connect with electronic health record systems, facilitating smooth data transfer and real-time documentation, thus improving workflow efficiency and communication among healthcare staff.
- AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and ML supports data analysis, decision-making, and predictive modeling. This helps anesthesiologists optimize anesthesia delivery for better patient outcomes.
To get detailed scientific explanations of anesthesia machines, try Patsnap Eureka.

