
What Is BX Cable?
BX cable, also called armored cable (AC cable), is a durable and reliable type of electrical wiring used in residential and commercial settings. It features insulated conductors protected by a flexible metal casing or armor, typically made from aluminum or galvanized steel. This design provides added protection for the wiring, making BX cable a popular choice for applications where enhanced safety and durability are required. In this article, we’ll explore the features, benefits, and common uses of BX cable, as well as tips for proper installation.
Key Components of BX Cable
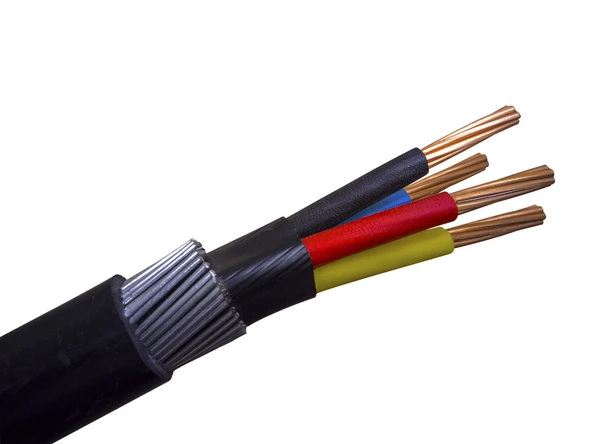
1. Metallic Shielding or Armor
The outer layer, made of interlocked aluminum or steel strips, protects the cable from physical damage and adds mechanical durability. This armor also offers additional safety in challenging environments.
2. Insulated Conductors
Inside the metallic armor are copper conductors, each covered with insulation to safely carry electrical current. The number of conductors can vary based on the cable’s intended application, offering flexibility for different wiring needs.
3. Filler Material
Between the conductors and the metallic armor, filler material like paper or plastic provides extra insulation and support. This filler helps maintain the cable’s structure and enhances overall durability.
Benefits of Using BX Cable
- Flexibility: The interlocked metallic armor allows easy bending and routing, ideal for areas where rigid conduits are unsuitable.
- Time-Saving Installation: BX cable eliminates the need for separate conduits, reducing both installation time and labor costs.
- Physical Protection: The durable metallic shielding safeguards the inner conductors from damage during installation or regular use.
- Grounding Capability: The metallic armor can act as a grounding path, improving electrical safety and system reliability.
Applications of BX Cable in Electrical Wiring
- Fire-Resistant Wiring: BX cables are ideal for fire-fighting equipment, emergency lighting, and alarm systems. Their mineral-insulated construction ensures heat and flame resistance, maintaining electrical supply during fires.
- Residential and Commercial Use: BX cables are widely used for branch circuits, appliance connections, and general wiring. Their flexibility allows easy routing in confined spaces, while the metal sheath provides mechanical protection.
- Industrial and Hazardous Environments: BX cables excel in industrial settings, handling exposure to moisture, chemicals, and physical stress. They are reliable for manufacturing plants, processing facilities, and other demanding environments.
- Temporary and Portable Wiring: Their flexibility and toughness make BX cables perfect for temporary installations like construction sites, outdoor events, and mobile equipment, ensuring durability under harsh conditions.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral Insulated (MI) Cables | Excellent heat and flame resistance, ensuring continuity of electrical supply in fire conditions. | Fire-resistant wiring for critical systems like fire-fighting equipment, fire alarm systems, emergency lighting, and other life-safety applications. |
| BX Cables (Armored Cables) | Robust construction with flexible metal sheath providing mechanical protection against physical damage. | Residential and commercial building wiring, branch circuit wiring, appliance connections, and general-purpose electrical installations. |
| BX Cables (Armored Cables) | Rugged construction suitable for harsh environments, with metal sheath protecting against moisture, chemicals, and physical impacts. | Industrial and hazardous environment wiring, such as in manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, and outdoor installations. |
Installation Tips for BX Cable
Cutting the Cable
Cutting BX cable requires precision to avoid damaging the insulation on the inner wires, which could lead to short circuits. Newer cables with reduced clearance between the shielding and wires make this process more challenging. Rotary cable cutters with adjustable depth controls help manage cut length for different cable sizes, but larger cable diameters can increase the risk of insulation damage due to deeper cuts.
Using Specialized Cable Cutter Tools
Specialized cable cutters are essential for safely cutting larger BX cables. These tools allow for increased cut length without increasing cut depth. Many include removable adapters that center smaller cables, ensuring precise cuts and preventing damage to the inner wires.

Installation Process
Before installation, remove the device’s terminal cover to access the wiring compartment. Secure a BX cable coupler into the device’s cable entry point. In tight spaces, such as under sinks, connect the wiring before mounting the device to ensure proper alignment with the fixed cable length.
Safety Considerations for BX Cable
Cutting Challenges
Cutting BX cable poses safety risks, especially with newer designs that have reduced clearance between the metallic shielding and inner wires. Damaging the wire insulation during cutting can lead to electrical shorts or hazards.
Cutting Depth Control
Rotary cable cutters with adjustable depth are common for cutting BX cable. However, larger cable diameters often require increased cut depth, raising the risk of damaging insulation. Specialized cutters designed for larger cables can remove shielding without excessive depth, ensuring safety.
Grounding and Bonding
Proper grounding and bonding are critical for BX cable safety. The metallic shielding must be securely connected to the grounding system to prevent shock hazards and provide a reliable ground fault path.
Code Compliance
BX cable installations must adhere to electrical codes like the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States. These regulations outline requirements for support, bending radii, and terminations to ensure safe and compliant installations.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Electricians working with BX cable should wear safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. These precautions help avoid injuries from sharp edges or accidental contact with live wires.
To get detailed scientific explanations of methyl calcium nitride, try Patsnap Eureka.

