
When conducting research, ensuring that measurements truly capture distinct concepts is crucial. Discriminant validity is a key aspect of construct validity that helps researchers determine whether a measurement is unique and not simply overlapping with another. Without discriminant validity, research findings may be misleading, as they might measure the wrong constructs or blend concepts that should remain separate.
This guide explores:
- What discriminant validity is and why it matters
- How to test for it using statistical methods
- Common challenges in establishing validity
- How AI-powered tools like Eureka enhance research accuracy
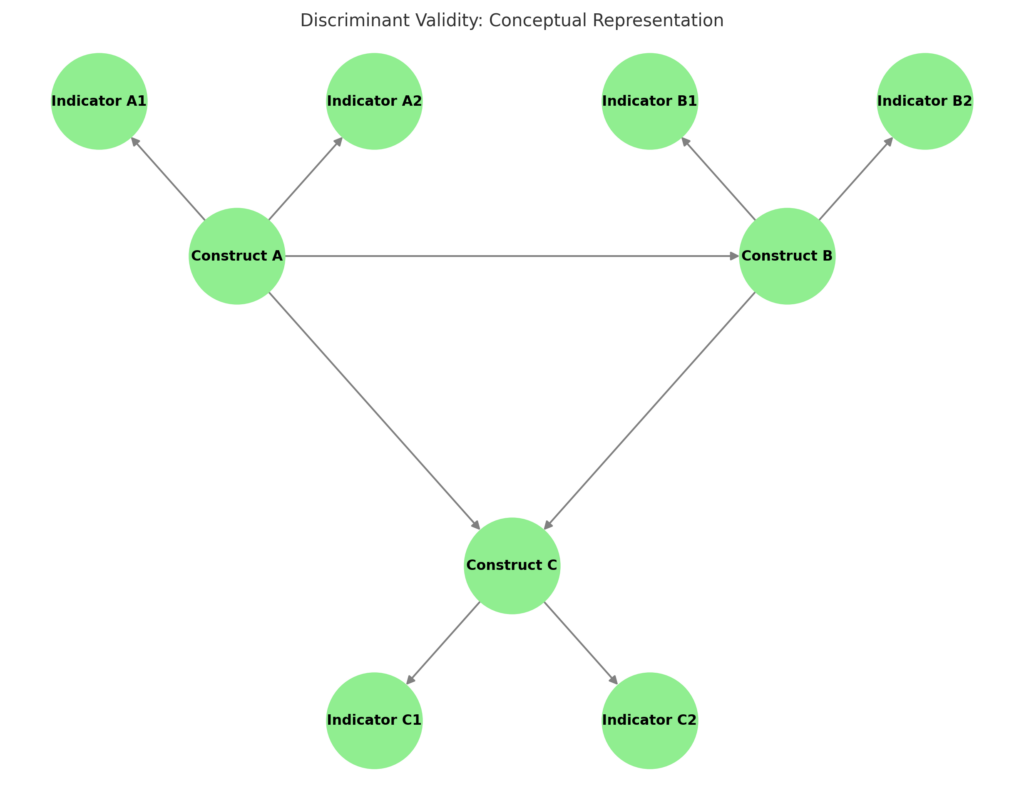
What is Discriminant Validity?
🔹 Definition
Discriminant validity is a statistical test that ensures that two or more measures that should be theoretically unrelated are actually distinct in practice.
For example, if a researcher is measuring job satisfaction and work stress, discriminant validity ensures that the two variables do not overlap in meaning.
🔹 Why is Discriminant Validity Important?
- Ensures clear separation between variables
- Prevents conceptual overlap in research
- Improves measurement accuracy
- Enhances theoretical development
Want to understand discriminant validity? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its importance in research, helping you evaluate whether constructs are truly distinct and ensuring the reliability of your measurement models.
How to Test for Discriminant Validity
Several statistical methods are used to test discriminant validity:
1️⃣ Fornell-Larcker Criterion
✅ Compares the square root of average variance extracted (AVE) with the correlation between constructs.
✅ If the AVE square root is higher than the correlations, discriminant validity is confirmed.
📌 Example:
A study on customer loyalty and brand trust should show that customer loyalty’s AVE square root is greater than its correlation with brand trust.
🔍 How Eureka Helps:
AI-powered statistical testing in Eureka quickly calculates AVE and highlights violations of discriminant validity.
2️⃣ Cross-Loadings Method
✅ Measures how strongly each variable loads onto its intended factor compared to other factors.
✅ If a variable loads higher on a different construct than its own, discriminant validity is compromised.
📌 Example:
If a customer engagement variable loads more strongly onto brand perception than engagement, the measurement may be flawed.
🔍 How Eureka Helps:
Eureka’s machine learning algorithms detect unexpected cross-loadings and suggest adjustments.
3️⃣ Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT)
✅ Measures the correlation between constructs in relation to their internal consistency.
✅ HTMT values below 0.85 indicate strong discriminant validity.
📌 Example:
If HTMT between social media influence and consumer trust is 0.92, they may be measuring similar constructs instead of distinct ones.
Test Steps
- Conduct a Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA): Start by estimating a measurement model where all indicators are related to their respective constructs.
- Calculate AVE: Compute the Average Variance Extracted for each construct to assess convergent validity.
- Apply the Fornell-Larcker Criterion: Compare the square root of the AVE for each construct to the correlations between the constructs. If the square root of the AVE is greater than the correlation between any two constructs, discriminant validity is established.
- Examine Cross-Loadings: Ensure that the loading of an indicator on its intended construct is higher than its loading on any other construct.
- Use HTMT Ratio: Calculate the HTMT ratio to assess discriminant validity. A value below 0.85 or 0.90 indicates discriminant validity.
- Consider Alternative Methods: Depending on your data and model, you may also consider using the Chi-Square Difference Test or discriminant analysis.
Common Challenges in Establishing Discriminant Validity
❌ Overlapping Constructs
Some concepts naturally share elements, making it hard to ensure full distinction.
📌 Example:
“Job satisfaction” and “employee engagement” are related but must remain distinct.
🔍 Eureka’s Solution: AI-powered construct mapping identifies overlap and recommends variable adjustments.
❌ Poorly Designed Surveys
Ambiguous questions may cause variables to correlate more than they should.
📌 Example:
A questionnaire using similar wording for motivation and performance may inflate correlations.
🔍 Eureka’s Solution: AI-driven survey validation detects and revises problematic survey items.
❌ Sample Bias
If sample characteristics influence both variables, correlations may be artificially high.
📌 Example:
If a study on leadership styles and employee satisfaction only includes managers, results may not generalize.
🔍 Eureka’s Solution: AI-powered sample optimization ensures diverse representation.
Steps to Ensure Discriminant Validity
🔹 Step 1: Define Constructs Clearly
Ensure that each variable has a unique conceptual meaning.
📌 Example:
Differentiate “brand trust” from “brand loyalty” with precise definitions.
🔹 Step 2: Choose an Appropriate Testing Method
Use Fornell-Larcker, HTMT, or cross-loadings based on research needs.
📌 Example:
If variables have high correlations, HTMT is the most sensitive test.
🔹 Step 3: Use Advanced Statistical Tools
Ensure accurate calculations using AI-powered software like Eureka.
📌 Example:
Eureka automates validity testing and provides real-time feedback.
🔹 Step 4: Adjust Survey Items if Needed
Modify or remove problematic survey questions to improve construct separation.
📌 Example:
If work stress and burnout correlate too highly, revise item wording.
🔹 Step 5: Validate with External Data
Compare results with previous studies to confirm consistency.
📌 Example:
Check if brand perception and customer engagement maintain distinct meanings across studies.
How Eureka Enhances Discriminant Validity Testing
🔍 What is Eureka?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered research intelligence tool that helps researchers:
- Identify potential measurement issues early in study design
- Analyze global trends in construct validity
- Improve statistical accuracy with AI-driven testing
🔍 How Eureka Helps Researchers
- Detects validity violations—AI flags problematic correlations.
- Automates statistical calculations and reduces errors in Fornell-Larcker, HTMT, and cross-loadings analysis.
- Optimizes survey design—identifies overlapping questions before data collection.
- Improves sample representation—Ensures diverse, unbiased sampling.
📌 Example of Eureka in Action:
A psychology research team investigating self-esteem and anxiety can:
- Use AI to detect concept overlap before finalizing survey items.
- Compare historical research trends to validate construct distinctions.
- Automatically test discriminative validity across multiple datasets.
Conclusion
Discriminant validity ensures that research measures distinct concepts rather than overlapping constructs. By applying statistical tests like Fornell-Larcker, HTMT, and cross-loadings, researchers can confirm the uniqueness of their variables.
🚀 Eureka enhances discriminative validity testing by:
- Detecting construct overlap before data collection
- Automating advanced statistical tests
- Improving survey item wording and sample diversity
🔍 Want to ensure accuracy in your research? Explore Eureka today and take your study design to the next level with AI-powered insights!
FAQs
1️⃣ What is the difference between discriminant and convergent validity?
✅ Discriminative validity ensures that constructs are distinct, while convergent validity checks that measures of the same construct correlate well.
2️⃣ How do I know if my study has poor discriminant validity?
✅ High correlations between unrelated constructs or low Fornell-Larcker values suggest poor discriminative validity.
3️⃣ Why is discriminant validity important in survey research?
✅ It prevents measurement errors and ensures each survey item measures only one construct.
4️⃣ How does AI improve validity testing?
✅ AI-powered tools like Eureka analyze global datasets, detect biases, and optimize survey designs to enhance research accuracy.
5️⃣ Can discriminant validity be tested in qualitative research?
✅ While primarily used in quantitative studies, qualitative research can ensure concept separation through rigorous thematic analysis.
To get detailed scientific explanations of discriminant validity, try Patsnap Eureka.


