In the realm of modern biosciences, gel electrophoresis stands as one of the most powerful and accessible techniques for molecular separation. Whether researchers are decoding genetic material, verifying recombinant proteins, or conducting forensic analysis, gel electrophoresis provides a visual and analytical platform to separate, identify, and quantify biomolecules.
With the integration of PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, this time-tested method gains new relevance—researchers, product teams, and biotech strategists can now access real-time IP landscapes, technical benchmarks, and competitor insights related to electrophoresis tools, reagents, and workflows.
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
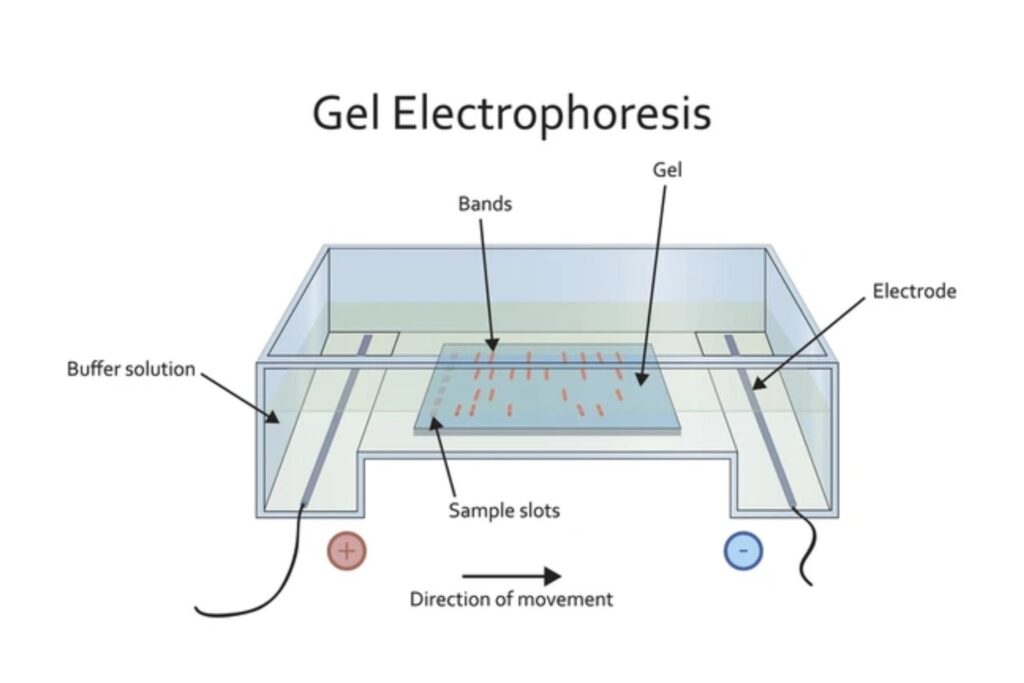
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to molecular size. The process involves applying an electric current to a gel matrix, typically made of agarose or polyacrylamide. Molecules move through the gel at different rates based on size and charge, allowing for separation and analysis. This technique is crucial in research, diagnostics, and forensic science for tasks such as DNA fingerprinting, assessing genetic mutations, and analyzing protein expression. Components of gel electrophoresis systems include gels, buffers, sample wells, and electrodes to facilitate the electrophoretic process.
How It Works:
- Sample Preparation: Molecules are mixed with a loading buffer and sometimes dyes for visualization.
- Gel Loading: Samples are pipetted into wells of the gel.
- Electrophoretic Run: An electric field is applied, with negatively charged molecules migrating toward the positive electrode.
- Separation: Smaller molecules migrate faster through the gel pores; larger ones move more slowly.
- Visualization: Stains or dyes (e.g., ethidium bromide, SYBR Green) are used to observe the results under UV or blue light.
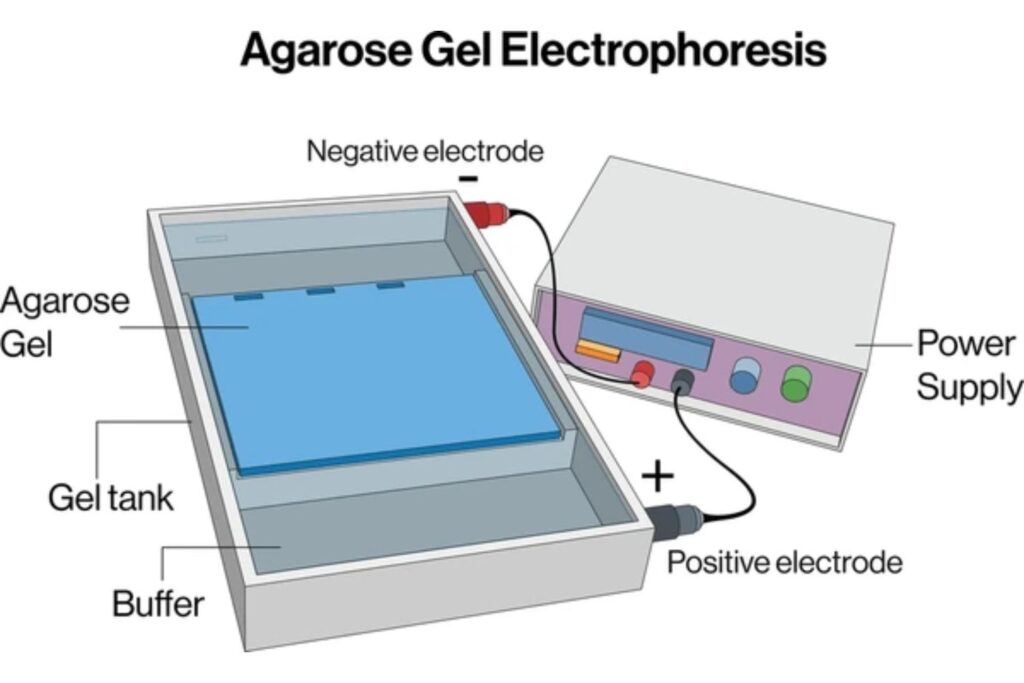
Types of Gel Electrophoresis
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis – Ideal for large DNA/RNA fragments (100 bp to 25 kb).
- Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) – Offers higher resolution, ideal for proteins and small DNA (<1000 bp).
- SDS-PAGE – A denaturing form of PAGE for proteins; separates by size regardless of charge.
- 2D Gel Electrophoresis – Separates proteins in two dimensions: isoelectric point and size.
With PatSnap Eureka AI Agent‘s technical database, users can query any of these variants, track improvements in gel chemistry, or discover new designs in gel chamber architecture.
Key Specifications and Operational Parameters
| Parameter | Details & Technical Notes |
|---|---|
| Gel Material | Agarose (0.5–3% for DNA/RNA), Acrylamide (4–20% for proteins); varies by resolution needs |
| Buffer Systems | TAE (Tris-Acetate-EDTA), TBE (Tris-Borate-EDTA), SDS-PAGE buffer (for denatured proteins) |
| Voltage Range | 50–150V for standard gels; up to 300V for high-speed runs (short gels only) |
| Resolution Capacity | DNA: ~5 bp difference, Proteins: ~1–2 kDa, RNA: ~50–100 nt |
| Stains & Visualization | Ethidium bromide (classic, mutagenic), SYBR Safe, Coomassie, Silver Stain, GelRed |
| Equipment Compatibility | Horizontal (agarose) vs vertical (PAGE) chambers; imaging systems like Bio-Rad, GelDoc, etc. |
Real-World Applications & Use Scenarios
1. Genetic Research & Diagnostics
- Verify the presence and size of PCR-amplified DNA.
- Detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or insertions/deletions.
- Analyze gene editing outcomes (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9).
2. Proteomics and Drug Development
- Characterize recombinant protein products.
- Detect protein degradation or aggregation.
- Support QC in biosimilar pipelines and antibody production.
3. Forensics
- DNA fingerprinting in criminal investigations.
- Kinship analysis and identification of human remains.
- Archival sample validation and re-testing.
4. Agriculture & GMOs
- Validate transgenic organisms.
- Authenticate plant or livestock genotypes for IP protection.
5. Education & Laboratory Training
- A staple of undergraduate and graduate biology education.
- Hands-on demonstration of electrophoretic theory and molecular separation.
Market Relevance & Competitive Positioning
Global Market Snapshot
- Market Size: Estimated at USD 1.5–1.8 billion (2024) with CAGR of 5–6%.
- Segments: Instruments (power supplies, chambers), reagents (gels, stains), and services (custom kits, CROs).
- Growth Drivers: Personalized medicine, forensic testing expansion, growing biotech investments.
Key Players & Ecosystem
| Company | Positioning |
|---|---|
| Bio-Rad Laboratories | Comprehensive systems and reagents; leading in education and proteomics |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | High-throughput and automation-focused electrophoresis platforms |
| Merck KGaA | Strong in buffer systems and life science integration |
| Agilent Technologies | Microfluidics and digital gel analysis integration |
| Cleaver Scientific | Affordable academic & research tools |
Innovation & Technology
Miniaturization & Automation
- Microfluidic gel electrophoresis offers low-volume, chip-based separation for rapid diagnostics.
- Pre-cast gel cassettes eliminate preparation errors and increase reproducibility.
Imaging and AI Analysis
- High-res gel scanners paired with AI-powered band detection are automating interpretation and quantification.
- Some platforms now offer cloud storage and remote viewing of gel results.
Enhanced Safety and Sensitivity
- Safer dyes like GelGreen and SYBR Safe are replacing ethidium bromide.
- Improved post-stain detection sensitivity for faint bands and low-abundance proteins.
Hybrid Techniques
- Isoelectric focusing + SDS-PAGE for 2D protein separation.
- Gel electrophoresis combined with mass spectrometry for high-confidence proteomic profiling.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities in Electrophoresis R&D
| Functionality | Electrophoresis-Specific Benefits |
|---|---|
| Patent Landscaping | Identify dominant IP holders in gel matrix formulation, imaging systems, and microfluidic innovation |
| Competitive Benchmarking | Compare Bio-Rad vs Thermo Fisher patent trends, product updates, and regional presence |
| Keyword-Based Tech Discovery | Track mentions of “SDS-PAGE automation” or “microfluidic chip electrophoresis” across global filings |
| Licensing Intelligence | Find out who’s licensing key components in gel systems and kits |
| R&D Collaboration Finder | Uncover high-publishing universities or inventors in gel diagnostics and protein isolation |
Conclusion
Gel electrophoresis remains a cornerstone of molecular science. From undergraduate classrooms to advanced proteomic workflows, its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and reliability continue to make it an irreplaceable technology.
Yet the future is equally exciting: automation, AI, and micro-scale integration are rapidly evolving the landscape. With PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, innovators can move beyond the bench—into strategic decision-making backed by patent data, competitive foresight, and deep technical analysis.
FAQs
Lab method to separate biomolecules (DNA/RNA/proteins) by size/charge. Used for DNA analysis, protein checks, and diagnostics.
Biomolecules move through gel matrix under electric field. Smaller molecules travel farther/faster.
Tighter matrix for high – resolution separation of small DNA fragments (100–2000 bp), good for PCR products.
Yes. Using high-resolution gels and proper conditions, even single-nucleotide differences can sometimes be resolved.
DNA gels run between 20–60 minutes depending on size and voltage. Protein gels may take 1–2 hours.
To get detailed scientific explanations of the gel electrophoresis, try Patsnap Eureka.