
Isopropylbenzylamine is a chemical compound that has gained attention due to its structural similarity to methamphetamine. While it has legitimate industrial uses, its primary concern arises from its misuse as a methamphetamine cutting agent in illicit drug production. Law enforcement agencies report more cases of mistaking n-isopropylbenzylamine for methamphetamine due to their nearly identical appearance. This article explores the properties, uses, health risks, detection methods, and legal status of isopropylbenzylamine, highlighting why it has become a growing concern for regulatory authorities.
What Is Isopropylbenzylamine
What is Isopropylbenzylamine? Eureka Technical Q&A explores its chemical properties, common uses, and potential concerns, helping you understand its applications and significance in various industries.
Isopropylbenzylamine is a synthetic organic compound with the molecular formula C₁₀H₁₅N. It belongs to the amine class of chemicals, often used in industrial applications such as chemical synthesis and pharmaceutical intermediates.
The compound is colorless or white in crystalline form and is highly soluble in organic solvents. Its structural similarity to methamphetamine raises concerns about its presence in illicit drug markets, where sellers often use it as a methamphetamine substitute or adulterant.
Chemical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C₁₀H₁₅N |
| Molar mass | 149.24 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents |
| Boiling point | 200-220°C |
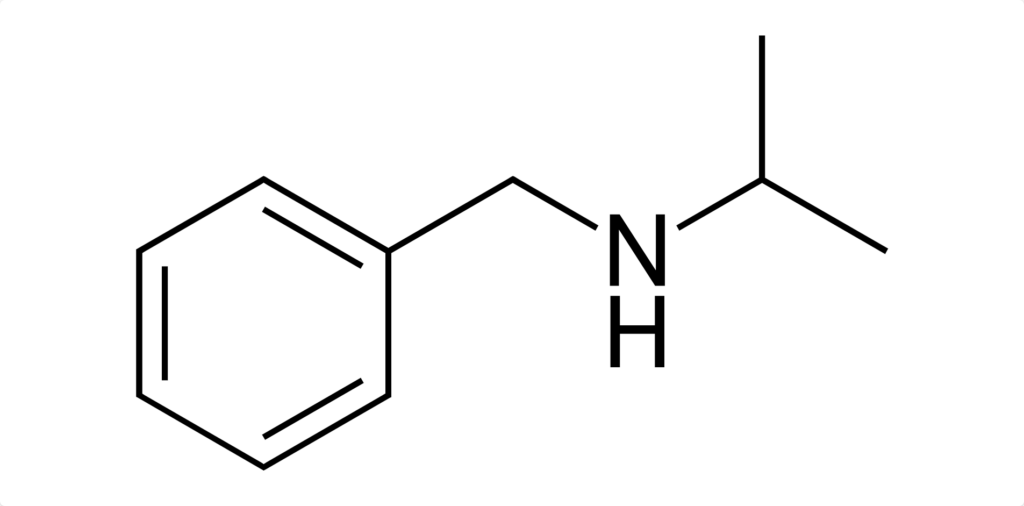
Synthesis of Isopropylbenzylamine
Isopropylbenzylamine can be synthesized using standard organic synthesis techniques involving the reaction of benzylamine with isopropyl halides in the presence of a base. The process is relatively simple and does not require specialized equipment, making it accessible for industrial and illicit production.
Schiff Base Formation
The process begins with benzaldehyde reacting with isopropylamine. This condensation reaction forms a Schiff base, where the aldehyde group of benzaldehyde bonds with the amine group of isopropylamine.
Reduction to Amine
Next, the Schiff base undergoes reduction using specific reducing agents or catalytic hydrogenation. This step converts the imine group into an amine, resulting in the formation of N-isopropylbenzylamine.
Purification for Final Product
To achieve the required purity, the final product goes through crystallization or other purification techniques. This ensures suitability for pharmaceutical applications or further chemical synthesis.
Legitimate Uses of Isopropylbenzylamine
Isopropylbenzylamine has a few industrial applications, including:
- chemical intermediates used in organic synthesis for creating pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals
- solvent and stabilizer acting as a stabilizing agent in certain chemical reactions
- industrial processing used in specialized laboratory research and materials production
However, despite its limited legal applications, the compound has gained notoriety for its misuse in illicit drug production.
Why Is Isopropylbenzylamine Used as a Methamphetamine Adulterant
The physical properties of isopropylbenzylamine closely resemble methamphetamine, making it an attractive cutting agent for drug manufacturers. Some of the key reasons include:
- appearance and texture, forming white or clear crystals, visually similar to methamphetamine
- low cost, making it cheaper to produce and mix with actual methamphetamine
- difficult detection as standard field drug tests often fail to distinguish it from methamphetamine
Since it lacks the stimulant effects of methamphetamine, users who unknowingly consume it experience reduced or no psychoactive effects, leading to health and legal risks.
Health Risks and Toxicity of Isopropylbenzylamine
Although isopropylbenzylamine was initially considered non-toxic, recent studies suggest potential neurotoxicity and health hazards.
Potential Health Risks
- neurological effects, increasing nitric oxide levels in cells, which may lead to neurotoxic effects
- cardiovascular risks, potentially causing increased heart rate and blood pressure when consumed in large quantities
- chemical burns and irritation, leading to skin and respiratory system irritation if improperly handled
Detection and Differentiation from Methamphetamine
The structural similarity between isopropylbenzylamine and methamphetamine makes it difficult to distinguish using standard tests. However, advanced forensic techniques can accurately detect and separate the two substances.
Common Detection Methods
| Detection Technique | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) | highly accurate |
| infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) | effective in differentiating chemical bonds |
| raman spectroscopy | can identify pure substances in mixtures |
| field drug tests | often ineffective, may show false positives |
Law enforcement agencies rely on these advanced laboratory methods to confirm the presence of isopropylbenzylamine in drug seizures.
Legal Status and Regulations
Currently, N-isopropylbenzylamine is not classified as a controlled substance in many countries. However, due to its use as a drug adulterant, authorities in various regions are increasing scrutiny on its import, sale, and possession.
- United States: not classified as illegal, but possession with intent to distribute as methamphetamine is a federal crime
- New Zealand and Australia: reported in illicit drug markets, with potential regulatory actions pending
- China: known to be used in drug manufacturing, facing increased monitoring
As law enforcement agencies become more aware of its misuse, there is a growing likelihood of regulatory changes and stricter legal enforcement.
FAQs
Is isopropylbenzylamine illegal
While it is not a controlled substance in most countries, its possession and distribution for illicit purposes can lead to legal consequences.
Can isopropylbenzylamine be used as a drug
Isopropylbenzylamine does not produce the psychoactive effects of methamphetamine, but it is sometimes sold as fake methamphetamine, misleading users.
How can law enforcement detect isopropylbenzylamine
Advanced laboratory tests such as GC-MS, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopy can accurately identify isopropylbenzylamine and differentiate it from methamphetamine.
What are the risks of consuming isopropylbenzylamine
Although not fully studied, neurological effects, cardiovascular risks, and chemical irritation are potential concerns.
Why is isopropylbenzylamine commonly used as a methamphetamine substitute
Its similar appearance, low cost, and ability to pass basic drug tests make it attractive for drug dealers looking to increase profits.
Conclusion
Isopropylbenzylamine is a chemical compound with limited legal uses but significant illicit applications. While it is not a psychoactive drug, it is often used as a methamphetamine cutting agent, deceiving consumers and raising concerns for public health and law enforcement. As authorities increase awareness and detection efforts, the legal status of isopropylbenzylamine may change to prevent its misuse in illicit drug trade. Continued research into its health effects and regulation will be essential in addressing this emerging issue.
To get detailed scientific explanations of isopropylbenzylamine, try Patsnap Eureka.


