
What is Negative Pressure Wound Therapy?
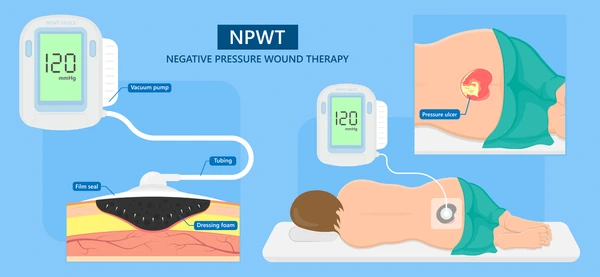
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), also called vacuum-assisted closure (VAC), is an advanced treatment designed to promote faster wound healing. This method applies sub-atmospheric pressure to the wound site using a specialized device, creating an environment that supports tissue repair and reduces complications. NPWT is widely used for a range of wounds, including burns, diabetic foot ulcers, traumatic injuries, and surgical incisions. This article will explain how NPWT works, its benefits, and its applications, helping you understand why it’s a trusted option in modern wound care.
How Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Works
Fluid Removal
Negative pressure actively removes excess fluid from the wound, reducing swelling and creating a drier environment. This helps inhibit bacterial growth and supports faster healing.
Wound Contraction
By applying consistent pressure, the therapy pulls wound edges closer together. This natural contraction process accelerates closure and reduces healing time.
Microdeformational Healing
The continuous negative pressure causes small deformations in the wound tissue, stimulating cellular activity and promoting tissue repair at a deeper level.
Granulation Tissue Formation
This therapy encourages the growth of granulation tissue, which plays a key role in wound closure and overall recovery. Enhanced tissue formation helps wounds heal more efficiently.
Moist Wound Healing
Negative pressure maintains a balanced moist environment, preventing the wound from drying out. This promotes optimal conditions for cellular regeneration and faster healing.
Microbial Management
The therapy reduces bacterial levels within the wound, significantly lowering the risk of infection. This added protection ensures a cleaner, healthier healing process.
Benefits of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Enhanced Wound Healing
Negative pressure therapy accelerates healing by promoting granulation tissue growth, improving blood flow, and enhancing epithelialization and wound contraction. These combined effects support faster recovery.
Improved Blood Flow and Oxygenation
The therapy boosts circulation and oxygen delivery to the wound site, creating optimal conditions for tissue repair and regeneration.
Effective Fluid Management
By evacuating excess fluid, this method reduces swelling and creates a healthier wound environment. This promotes quicker healing and minimizes complications.
Infection Control
Negative pressure therapy helps lower bacterial levels in the wound, making it especially effective for managing infections and reducing the risk of complications.
Reduced Surgical Site Infections
When applied to closed surgical incisions, it lowers the risk of infections and wound dehiscence by up to 50% in high-risk patients.
Improved Scar Appearance
By supporting effective healing, the therapy can result in better scar quality and improved wound maturity over time.
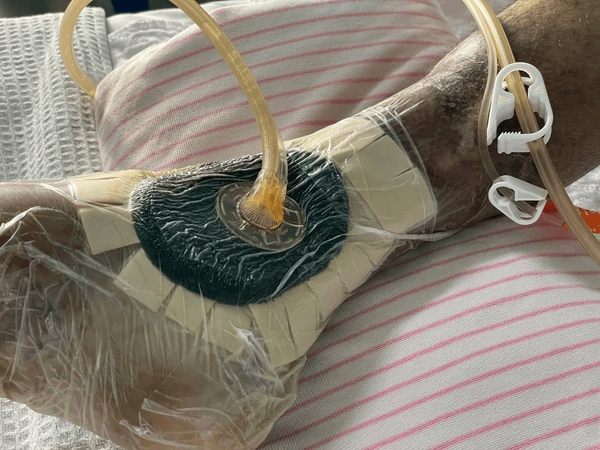

Versatility Across Wound Types
This therapy is suitable for a wide range of wounds, including chronic, acute, surgical, traumatic, and burn injuries. Its flexibility makes it a valuable tool in wound care.
Fewer Dressing Changes
The reduced need for frequent dressing changes lightens the workload for healthcare providers and enhances patient comfort.
Assistance with Hemostasis
In cases of soft tissue wounds with refractory bleeding, the therapy aids in achieving hemostasis, adding another layer of therapeutic benefit.
Cost-Effective Wound Care
Though initial costs may vary, shorter healing times and fewer complications often lead to significant long-term cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems.
Limitations and Risks of NPWT
Limitations of NPWT
- Mechanical Challenges
Traditional systems can be bulky and complex, limiting their use outside clinical settings. Portable, single-use options address these issues but still require proper training and careful system transfers. - High Costs
While NPWT reduces long-term treatment costs by minimizing surgeries and hospital stays, its initial setup and maintenance can be expensive, limiting accessibility in some cases. - Variable Effectiveness
The success of NPWT depends on wound type, severity, and patient health. Wounds with poor circulation or significant infection may not respond as well to this therapy.
Risks of NPWT
- Infection Risk
Although effective, NPWT can introduce infection risks. Bacterial contamination with Staphylococci or Pseudomonas may lead to complications, making regular evaluation and antibiotic use essential. - Bleeding Concerns
Bleeding risks exist, particularly in patients with malignancies or clotting disorders. Though traditionally a contraindication, newer studies show benefits in carefully monitored cases. - Compartment Syndrome
NPWT can lower the risk of compartment syndrome, but close monitoring is critical for patients with poor peripheral circulation to prevent complications. - Other Complications
Additional risks include petechial bleeding, intestinal fistulas, and contact dermatitis from adhesive tape. Addressing these issues ensures safer and more effective treatment.

Applications of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Types of Wounds Treated by NPWT
Chronic and Acute Open Wounds
Negative pressure therapy effectively treats wounds like diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and traumatic injuries. It promotes faster healing by stimulating granulation tissue growth and removing excess fluid, creating a healthier wound environment.
Postsurgical Wounds
This therapy reduces the risk of surgical site infections and wound dehiscence, especially in high-risk patients. It enhances local blood flow, minimizes swelling, and accelerates wound contraction, resulting in quicker recovery and improved scar appearance.
Burns
NPWT is widely used in burn surgery for wound repair, skin grafting, and cosmetic procedures. It improves tissue integrity, promotes angiogenesis, and supports better overall healing outcomes.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| PICO Single Use NPWT System T.J. Smith & Nephew Ltd. | Portable and convenient NPWT device suitable for outpatient use, promoting healing while allowing patient mobility. | Management of surgical site infections and wound dehiscence in short-stay surgical units and community care settings. |
| RENASYS Negative Pressure Wound Therapy System Smith & Nephew plc | Advanced wound dressings with liquid/gas permeable layers and conformable suction adapters for effective exudate management. | Treatment of complex wounds with exposed bone, implants, or high risk of infection across various acute and chronic wound types. |
| Avance Negative Pressure Wound Therapy System Mölnlycke Health Care, AB. | User-friendly design with audible/tactile signals for easy operation, providing controlled negative pressure delivery. | Inpatient and outpatient wound care, particularly for patients requiring frequent dressing changes or remote monitoring. |
| NPWT Dressing with One-Way Valve Avery Dennison Corp. | Innovative one-way valve design allows fluid evacuation while preventing backflow, maintaining consistent negative pressure. | Wound treatment in situations where consistent negative pressure is critical, such as highly exudating wounds or infected wounds. |
| PICO Single Use NPWT System Barts Health NHS Trust | Portable and convenient NPWT device suitable for outpatient use, promoting healing while allowing patient mobility. | Management of surgical site infections and wound dehiscence in short-stay surgical units and community care settings. |
Latest Technical Innovations in Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Targeted Drug Delivery and Stem Cell Therapy
Emerging advancements combine negative pressure therapy with targeted drug delivery and stem cell treatments. This synergy enhances healing by addressing both cellular regeneration and localized medication delivery.
Filtration Devices and Smart Dressings
The integration of filtration devices and smart dressings has revolutionized wound care. These innovations allow real-time monitoring and precise pressure adjustments, offering personalized and efficient treatment options.
Orthopedic and Vascular Implant Infections
Negative pressure therapy plays a crucial role in managing infections around orthopedic and vascular implants. It promotes healing, reduces infection levels, and supports better outcomes in complex cases.
To get detailed scientific explanations of negative pressure wound therapy, try Patsnap Eureka.

