
Perbromic acid is a strong oxidizing agent and a powerful acid. Bromic acid belongs to the family of oxoacids, specifically bromine oxoacids, and derives from bromine. It plays a role in various chemical processes and remains highly reactive. Due to its strong oxidizing nature, you must handle it with care.
What is Perbromic Acid?
Perbromic acid has the chemical formula HBrO₄. It consists of a bromine atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, with one of these oxygens bonded to a hydrogen atom, forming the acid. The oxidation of bromine compounds, particularly bromates, in acidic solutions produces this acid.
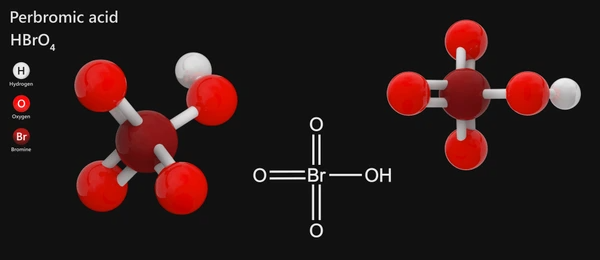
Chemical Structure of Perbromic Acid
The structure of HBrO₄ features a central bromine atom (Br) bonded to four oxygen atoms. The hydrogen ion (H) bonds with one oxygen, while the other three oxygen atoms form the oxo group (O–Br). The acid can be written as:
H–BrO₄
This structure resembles other perhalogen acids, such as perchloric acid (HClO₄) and periodic acid (HIO₄), where the central halogen atom bonds with four oxygen atoms.
Properties of Perbromic Acid
- Molecular Formula: HBrO₄
- Appearance: HBrO₄ is typically a colorless or pale yellow liquid or gas.
- Density: HBrO₄ is dense, though it is highly soluble in water.
- Boiling Point: It has a relatively high boiling point compared to other similar acids, due to its high oxidation potential.
- Reactivity: As a strong oxidizer, HBrO₄ reacts violently with reducing agents and flammable substances. It can also attack many metals and organic compounds.
Preparation of Perbromic Acid
Producers typically create HBrO₄ by reacting bromates (BrO₃⁻) in an acidic environment. They usually achieve this by reacting bromine with a strong oxidizing agent like nitric acid or by reacting bromine with water under specific conditions. The reaction proceeds as follows:
2 KBrO₃ + 2 H₂SO₄ → 2 HBrO₄ + K₂SO₄ + H₂O
Uses of Perbromic Acid
- Oxidizing Agent
Perbromic acid is used as a powerful oxidizing agent in a variety of chemical reactions. It can oxidize a range of materials, including metals, nonmetals, and organic compounds, making it valuable in industrial and laboratory processes. - Synthesis of Bromine Compounds
Producers employ it in synthesizing various bromine-containing compounds, which are often used in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. - Electrochemical Applications
Due to its strong oxidizing ability, industries use HBrO₄ in certain electrochemical applications, such as fuel cells and batteries, where oxidation is necessary for energy release. - Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemists use HBrO₄ to break down other compounds and test for the presence of various elements and compounds.
💡 Wondering about the uses of perbromic acid? Eureka Technical Q&A provides detailed insights into its applications in chemical synthesis and industrial processes, helping you grasp its role, handling precautions, and industrial importance.
Hazards and Safety Measures
Perbromic acid is a highly reactive and corrosive substance. It poses several hazards:
- Toxicity: Inhalation or ingestion of HBrO₄ can cause severe health issues, including damage to the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems.
- Corrosivity: It can cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Protective clothing, gloves, and eyewear should be worn when handling it.
- Reactivity: Due to its strong oxidizing properties, HBrO₄ can react explosively with reducing agents and flammable materials. It is important to store it away from such substances and handle it in well-ventilated areas.
Safety Measures:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Handle HBrO₄ in a fume hood or under controlled environments.
- Store HBrO₄ in cool, dry places, away from reducing agents and combustible materials.
Storage and Handling
Perbromic acid should be stored in tightly sealed containers made of materials that can withstand its corrosive nature, such as glass or certain plastics. Storage should be in a cool, dry area, and the containers should be kept away from any incompatible materials.
When working with perbromic acid, it’s important to use equipment that is resistant to strong acids and oxidation. Containment procedures must be in place in case of a spill, and neutralizing agents for acids should be available on-site.
Environmental Impact
Perbromic acid, like other strong acids, has the potential to harm the environment if released improperly. It can contribute to pollution, particularly in aquatic ecosystems, where its highly reactive nature can disrupt biological processes. Proper disposal methods must be followed to avoid environmental contamination.
Comparison to Other Perhalogen Acids
| Property | Perbromic Acid | Perchloric Acid | Periodic Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | HBrO₄ | HClO₄ | HIO₄ |
| Oxidizing Power | Strong | Very Strong | Moderate |
| Boiling Point | High | High | High |
| Solubility | Soluble in water | Soluble in water | Soluble in water |
| Corrosivity | Highly Corrosive | Highly Corrosive | Corrosive |
Conclusion
Perbromic acid is a highly reactive and powerful oxidizing acid, valuable for various chemical processes, including synthesis and analytical applications. However, due to its toxicity, corrosiveness, and reactivity, it must be handled with care, using appropriate safety precautions and storage methods. When compared to other perhalogen acids like perchloric acid and periodic acid, perbromic acid offers similar properties but with a distinct chemical profile.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Perbromic Acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


