
Research design is the roadmap that guides every research journey. Whether you are working on academic research, business innovation, or product R&D, a well-structured research design ensures clarity, direction, and accuracy in solving problems or discovering new knowledge.
However, traditional research design can be slow, fragmented, and often overwhelming. Modern tools like the Eureka AI Agent are reshaping the way research design works — empowering researchers to accelerate problem-solving, optimize processes, and generate better solutions backed by data.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about research design and how integrating Eureka AI can help you create stronger, smarter, and more efficient research.
What is Research Design?
Research design is the overall strategy or plan used to structure and conduct a research project. It acts as a blueprint, outlining how data will be collected, measured, and analyzed to answer a specific research question or solve a particular problem.
Without a research design, any research effort becomes scattered and lacks direction. With a good design, every step — from defining the problem to collecting and analyzing data — happens systematically and logically.
Why is Research Design Important?
A well-planned research design ensures:
- Clear problem definition
- Logical flow of activities
- Efficient data collection
- Reliable and valid results
- Minimized bias and error
- Effective use of time and resources
- Strong foundation for decision-making
Simply put, a research design provides clarity in chaos, helping researchers avoid guesswork and focus on structured discovery.
Key Components of a Research Design
Research Question: This is the central focus of the research, providing a clear and concise statement of what the researcher aims to investigate. It guides the entire research process and helps in defining the scope and objectives of the study.
Theoretical and Conceptual Framework: This provides the underlying principles and concepts that frame the research question. It helps in developing a coherent argument and in understanding the context of the study.
Research Methodology: This refers to the specific methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It includes decisions about the research approach (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods), data collection techniques, and analysis methods.
Sampling Strategy: This involves selecting a representative sample of the population to participate in the study. It includes decisions about sample size, sampling method, and criteria for inclusion or exclusion.
Data Collection Methods: This refers to the techniques and instruments used to gather data from participants or sources. It includes methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments.
Data Analysiis Plan*: This involves the procedures and techniques used to analyze the collected data. It includes decisions about statistical tests, data interpretation methods, and how to draw conclusions from the data.
Research Design Type: This refers to the overall strategy used to integrate the different components of the study. It includes choices between experimental, descriptive, correlational, or other specific research designs.
Ethical Considerations: This involves ensuring that the research is conducted ethically, with considerations for informed consent, confidentiality, and the welfare of participants.
Time Frame: This includes decisions about the duration of the study, the timeline for data collection and analysis, and any follow-up periods.
Resources: This involves planning for the budget, staffing, and other resources needed to conduct the study.
Types of Research Design
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design aims to answer the question “What is?” by systematically describing the characteristics, behaviors, or conditions of a particular group, situation, or phenomenon. It is often used to generate hypotheses, provide a clear picture of the current situation, and establish a baseline for further research.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is a systematic approach used to study scientific problems by manipulating one or more independent variables to observe their effect on dependent variables under controlled conditions. This method is particularly useful for establishing cause-and-effect relationships and is widely used across various fields, including natural sciences, social sciences, and even business and management.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the associations between variables in a natural setting. It helps researchers understand how different variables co-occur and identify potential patterns or trends. The purpose of this design is to explore relationships and not to establish causality, as it cannot determine whether changes in one variable directly cause changes in another variable.
Diagnostic Research Design
Diagnostic research design is a critical aspect of medical research focused on evaluating the accuracy, reliability, and clinical utility of diagnostic tests. This type of research is essential for improving diagnostic procedures and ensuring that they provide accurate and timely information to healthcare providers, ultimately aiding in better patient management and outcomes.
Explanatory Research Design
Explanatory research design is designed to explain and explore the reasons behind certain phenomena. It seeks to answer questions about the causal relationships between variables, making it particularly useful for situations where the “why” of a situation is being investigated . The primary goal is to provide insights into the factors that contribute to a particular outcome, thereby helping to develop a theoretical understanding of the research problem .
How to Create a Strong Research Design: Step-by-Step Guide
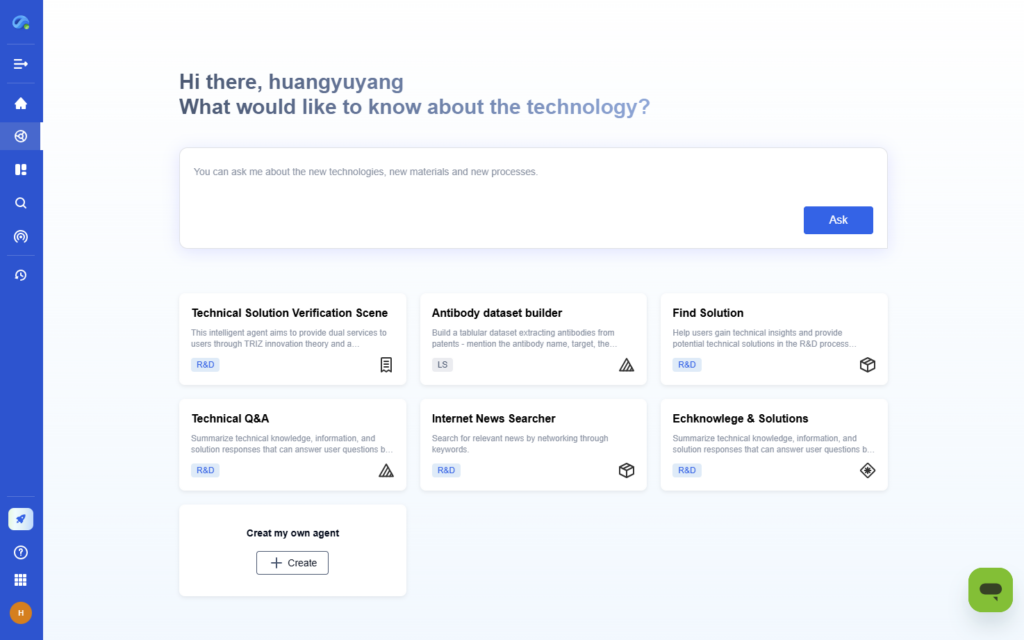
1. Define Your Research Problem and Objectives
Start by clearly defining the research problem or technical challenge you want to address. This forms the foundation of your research design.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka’s Problem Analysis capability helps researchers break down complex challenges, clarify problem statements, and structure research objectives. It guides users to frame questions precisely and avoid vague directions.
Benefits:
- Identify key variables and influencing factors
- Visualize the problem structure
- Generate SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) objectives automatically
2. Choose the Appropriate Research Paradigm
Decide whether your research approach should be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method based on your objectives and research philosophy.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka recommends suitable research paradigms and methods by analyzing best practices and methodologies used in similar global cases.
Benefits:
- Customized research pathway suggestions
- Access to methodological references and frameworks
- Support for positivism, interpretivism, or pragmatism-driven approaches
3. Select the Research Methodology
Choose specific data collection and analysis methods that align with your research problem and ensure reliability and validity.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka’s technical database provides validated methodologies, experimental designs, testing techniques, and real-world case applications from patents, academic papers, and technical standards.
Benefits:
- Suggested tools, materials, testing methods
- Insights from global experts’ practices
- Method reliability and validation checklists
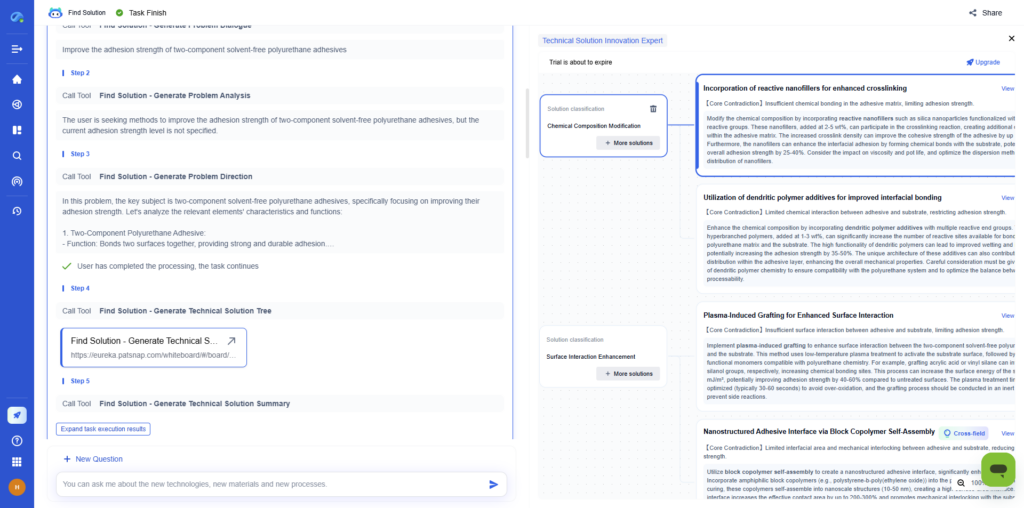
4. Develop a Detailed Research Plan
Outline your full research roadmap, including sampling strategies, data collection processes, and analysis techniques.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka’s Technical Solution Tree visualizes multiple research pathways and options to explore your problem from different angles.
Benefits:
- Visual representation of research strategies
- Prioritization of possible research directions
- Exploration of alternative approaches
5. Ensure Validity and Reliability
Implement strategies that enhance the accuracy and trustworthiness of your research.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka assists in identifying potential risks, suggesting control strategies, and ensuring robustness in experiment design.
Benefits:
- Access to multi-source data validation
- Risk factor identification and mitigation plans
- Suggestions for pilot tests and experiment refinements
6. Address Ethical Issues
Ethics must be embedded in every research process, from data handling to participant privacy.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka provides ethical compliance guidelines relevant to specific industries or research topics, ensuring alignment with global standards.
Benefits:
- Ethical frameworks customized for technical research
- Data privacy and confidentiality checklists
- Automated ethical risk alerts
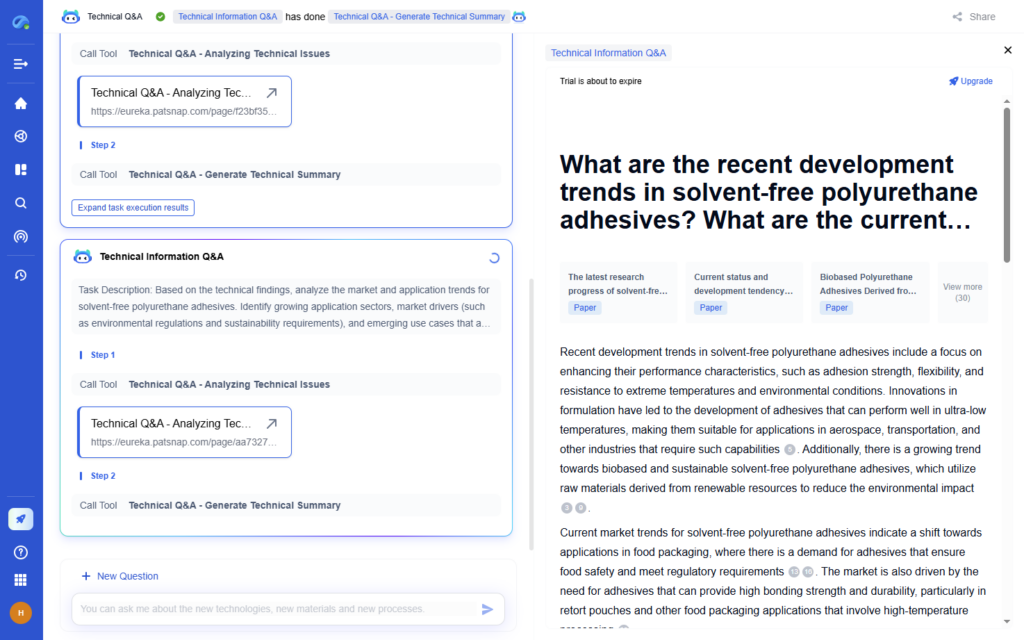
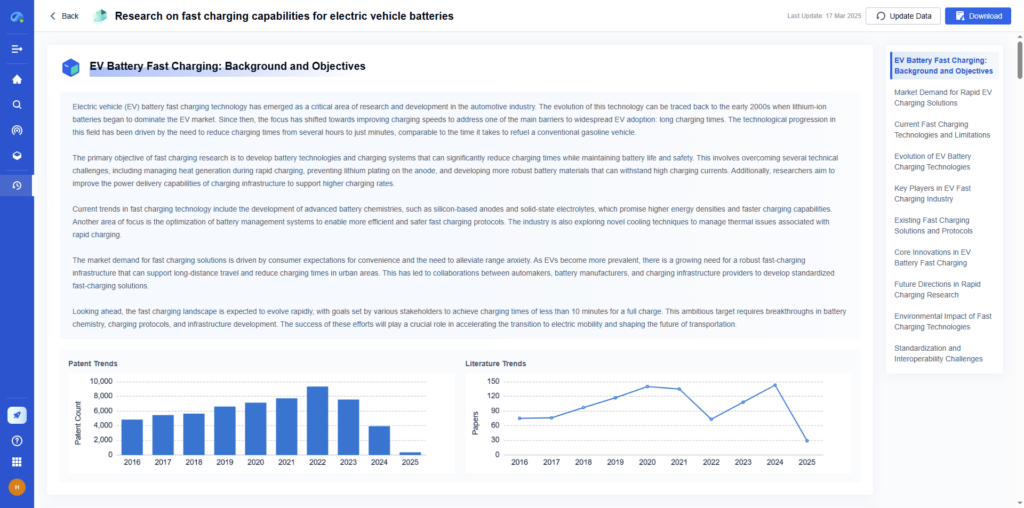
7. Plan for Data Analysis
Ensure your data collection methods align with your research questions and plan your analysis techniques.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka allows smart technical Q&A, automated literature reviews, and real-time data extraction from global knowledge databases.
Benefits:
- Fast access to validated data
- Multi-platform integrated search
- Optimized data collection templates and tools
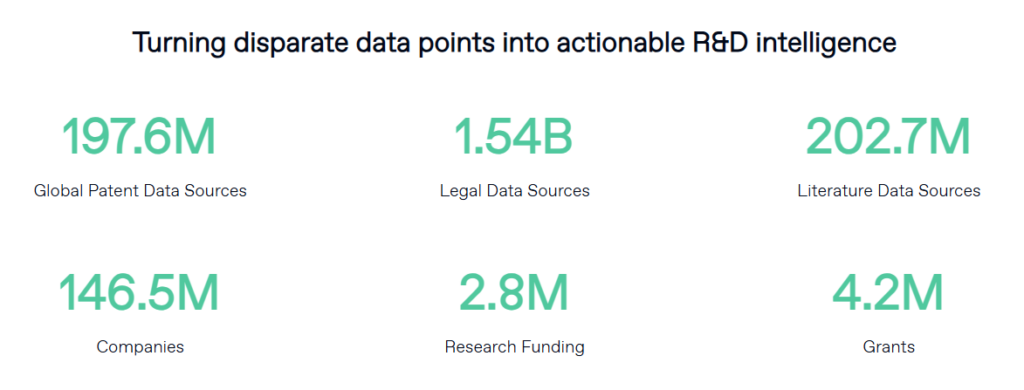
8. Prepare for Reporting and Dissemination
Structure your research report clearly and prepare outputs for both academic and industrial use, including potential intellectual property.
→ How Eureka AI Helps:
Eureka supports structuring research findings into technical documents, visual reports, and patent-ready formats.
Benefits:
- Automatically organized technical knowledge
- Ready-to-use solution blueprints
- IP generation and novelty analysis tools
Benefits of Integrating Eureka AI into Your Research Design
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Faster Research Process | Reduce manual search and analysis time dramatically |
| Better Research Quality | Access validated global knowledge instantly |
| Structured Knowledge Output | Generate clean, organized insights ready for use |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | Build solutions based on real-world data and trends |
| Innovation Acceleration | Move from idea to solution faster with AI guidance |
Final Thoughts
Research design is no longer just about planning a research project — it’s about building an intelligent, structured process that guides you from a problem to a validated solution.
While traditional research design principles remain essential, integrating AI tools like Eureka AI Agent opens up new possibilities for faster discovery, deeper insights, and more innovative results.
In today’s fast-paced research environment, the combination of human creativity and AI-powered tools is not just an advantage — it’s becoming a necessity.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Research Design , try Patsnap Eureka.


