
In today’s data-saturated environment, gaining a competitive edge often depends not on how much data you collect—but how effectively you use what already exists. Secondary research, also known as desk research, is a method of analyzing pre-existing information to extract insights that support smarter decision-making. It’s fast, efficient, and a key component of academic studies, business strategy, policy development, and innovation planning.
This article explores how to conduct high-impact secondary research, the challenges it solves, and how PatSnap Eureka—an AI-powered innovation intelligence platform—supercharges every step of the process.
What Is Secondary Research?
Conducting secondary research? Patsnap Eureka helps you find credible sources, synthesize existing data, and uncover key insights—streamlining your research and boosting its relevance.
Secondary research involves collecting data that has already been compiled, published, or archived by others. This data can come from sources such as academic journals, patents, market reports, government records, or news outlets. It is used to analyze trends, validate ideas, shape strategy, or inform primary research design.
Key Characteristics of Secondary Research
- Efficiency: Utilizes existing materials, making it quicker and more cost-effective than primary data collection.
- Breadth of Scope: Enables cross-comparison across multiple sectors, timelines, and geographies.
- Foundational Insight: Often used to support initial stages of research or validate decisions.
Common Sources Used in Secondary Research
- Academic Journals and Textbooks: Foundational knowledge and peer-reviewed insights.
- Government Data: Official statistics, population data, regulatory updates.
- Industry Reports and Market Research: Sales figures, forecasts, and competitor overviews.
- News Media and Publications: Up-to-date events, interviews, expert commentary.
- Patent and Innovation Databases: Technical advancements, inventor networks, R&D trajectories.
Advantages of Secondary Research
- Speed and Accessibility: Reduces the time needed to gather critical data.
- Strategic Depth: Helps identify trends, gaps, or emerging opportunities.
- Cost-Efficient: Ideal for early-stage exploration or resource-constrained teams.
Limitations of Secondary Research
- Limited Specificity: Data may not align exactly with your research goals.
- Outdated Sources: Some materials may not reflect the current market or science.
- Quality Concerns: Not all data is peer-reviewed or validated.
Common Applications of Secondary Research
- Competitive Benchmarking: Comparing industry players through published metrics.
- Innovation Strategy: Identifying technology gaps, funding trends, and IP activity.
- Policy and Public Research: Evaluating social programs or legislative impact.
- Academic Work: Supporting literature reviews and citation-rich analysis.
How to Conduct Effective Secondary Research: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Define Research Goals
Clarify the objective. Are you exploring market potential, tracking innovation, or preparing a literature review? The more specific your focus, the more targeted your data sources will be.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Instantly explore related publications, patents, and competitor activity to validate your research scope.
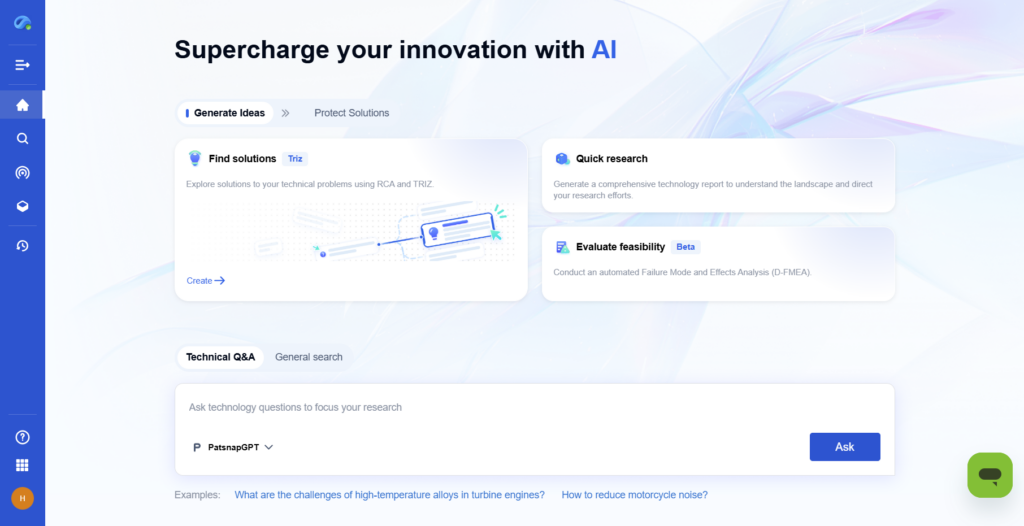
Step 2: Identify and Prioritize Data Sources
Determine which sources are most relevant—such as journals for scientific theory, patents for technological innovation, or funding databases for emerging markets.
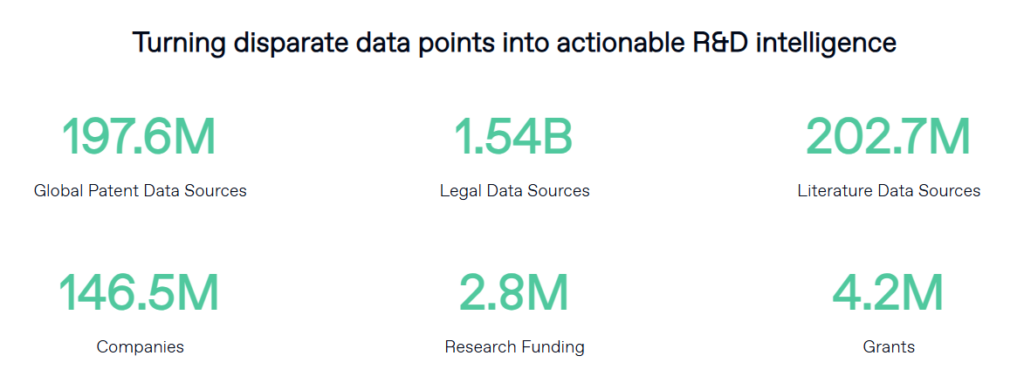
- With PatSnap Eureka: Access millions of global records from patents, literature, grants, and legal databases—all searchable in one place.
Step 3: Use Smart Search and Filters
Extract data using focused criteria. This includes filtering by date, sector, geography, assignee, or citation relevance.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Leverage semantic AI to search naturally—no complex Boolean needed. Filter results using industry-specific taxonomies and AI-generated tags.
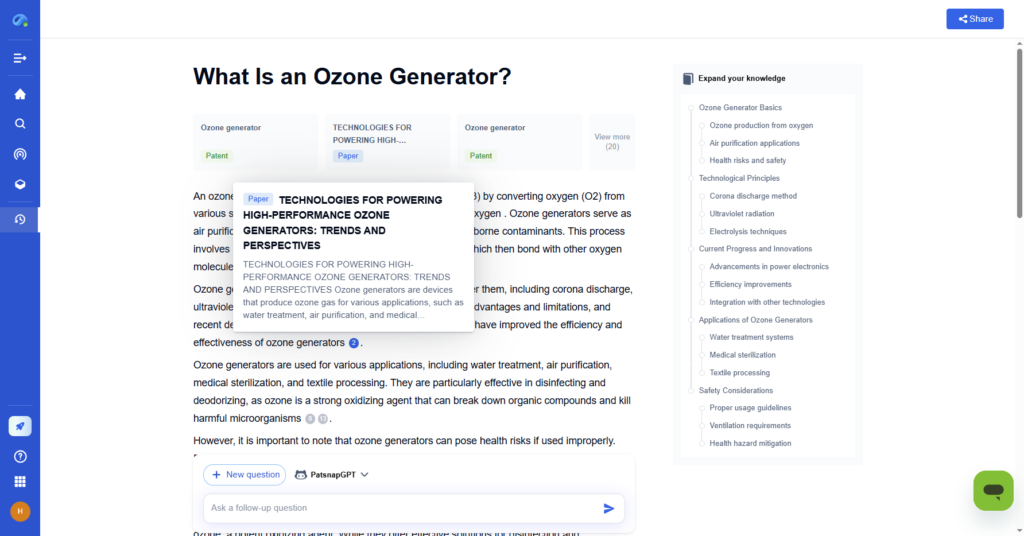
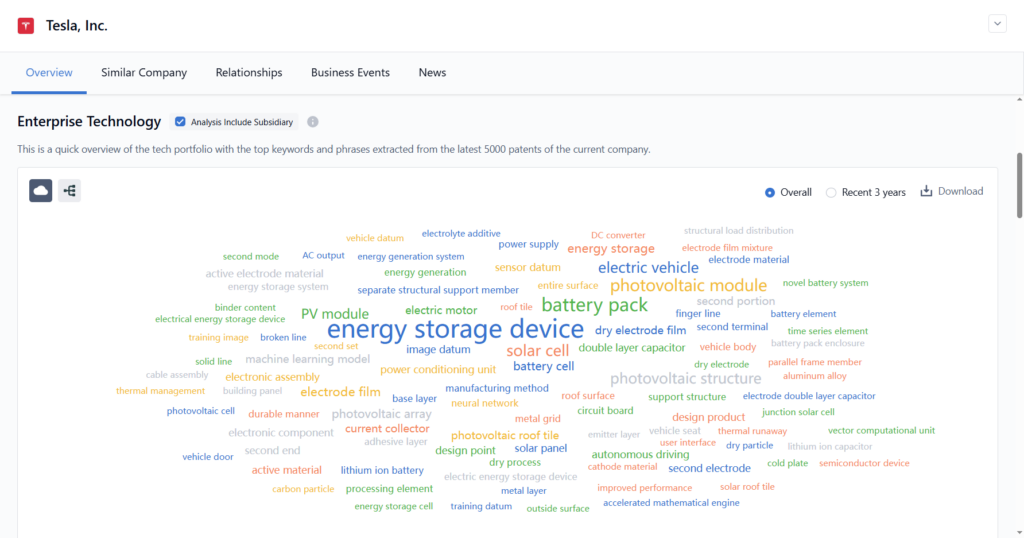
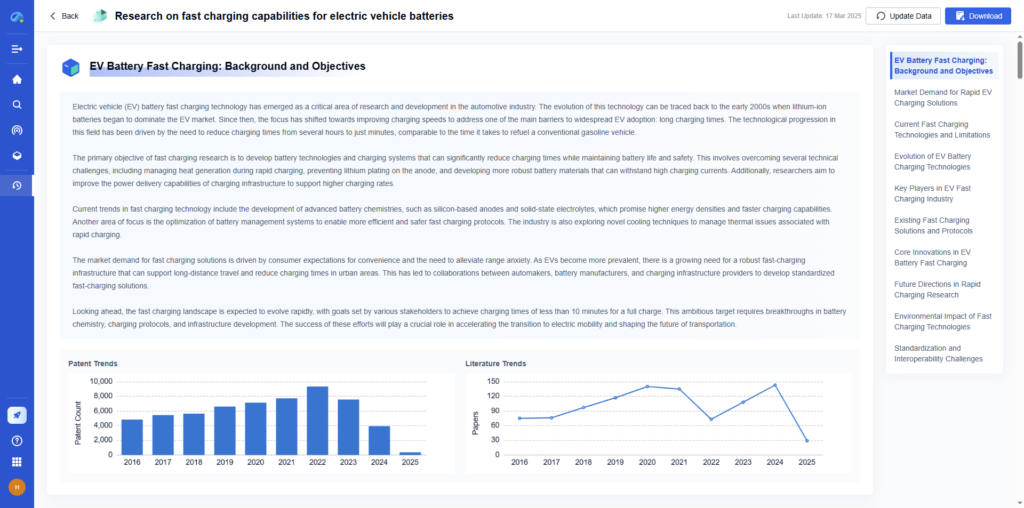
Step 4: Analyze Trends and Synthesize Insights
Review findings for patterns, correlations, and knowledge gaps. Compare across industries, timeframes, or technologies.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Utilize dashboards and visual maps to identify whitespace opportunities, innovation clusters, and funding trajectories.
Step 5: Validate and Cross-Reference
Ensure the accuracy of your findings by comparing data from multiple independent sources.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Overlay patent filings with literature mentions, market reports, or legal events to build layered, verified insights.
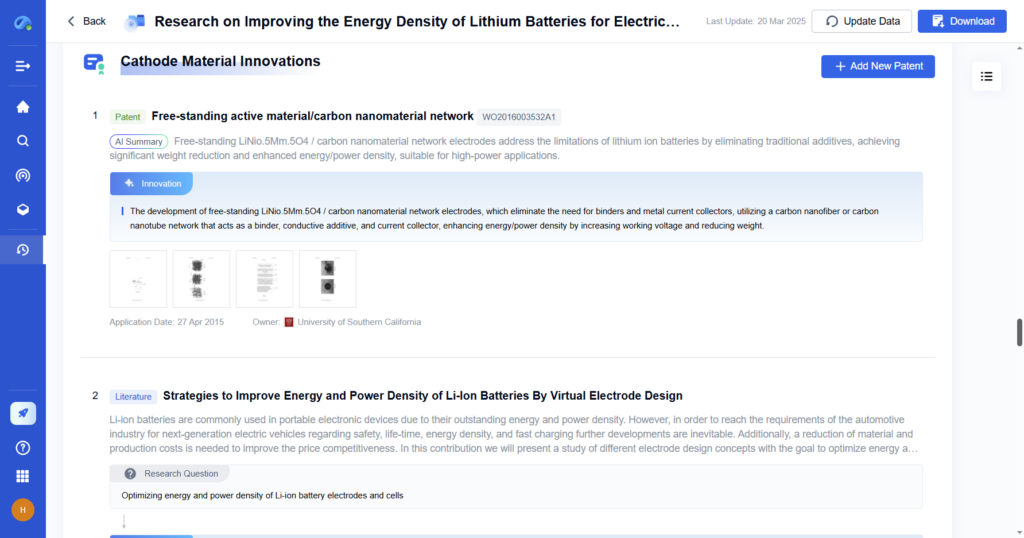
Step 6: Compile and Present Results
Organize insights into structured summaries or visual reports for internal decision-makers or external stakeholders.
- With PatSnap Eureka: Generate exportable reports with charts, timelines, and competitor landscapes—all formatted for immediate presentation.
Conclusion
Secondary research is no longer just a preliminary exercise—it’s a strategic tool for surfacing valuable insights in a time- and cost-efficient way. Whether your goal is to innovate, compete, or publish, leveraging existing data effectively can save months of effort and unlock smarter outcomes.
With PatSnap Eureka, researchers and analysts gain more than just access to information—they gain the ability to explore, visualize, and act on insights in real time. From scoping your project to producing final reports, Eureka transforms secondary research into a high-impact intelligence engine. In an era of information overload, smart tools make the difference between noise and knowledge.
To get detailed scientific explanations of secondary research, try Patsnap Eureka.


