
What is an STP Cable?
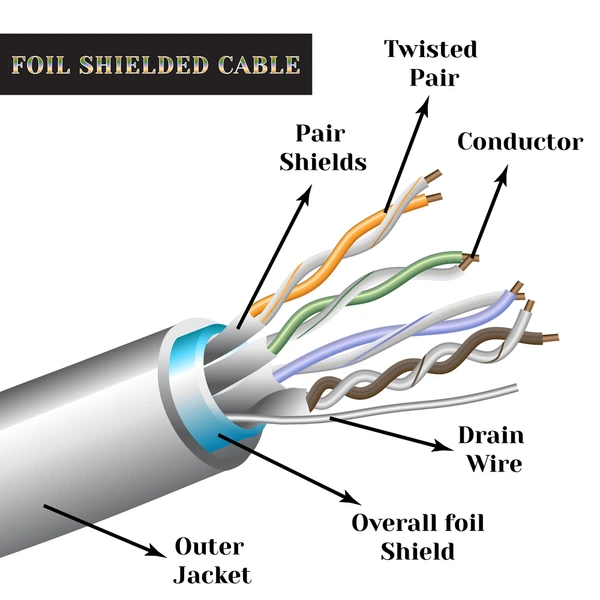
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cables are a type of cable used for data transmission, particularly in Ethernet networks. It consists of pairs of twisted copper wires, with each pair individually shielded and the entire bundle encased in an overall shield.
How STP Cables Work
The shielding in STP cables is designed to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, ensuring signal integrity and reliable data transmission. The shielding works by:
- Reflecting external EMI: The conductive shields reflect external electromagnetic fields, preventing them from interfering with the signal inside the cable.
- Containing Internal EMI: The shielding effectively traps electromagnetic fields generated by internal signals, preventing them from radiating outward. This containment minimizes interference with nearby devices and ensures stable network performance.
- Grounding: Shields are often grounded at one or both cable ends to safely dissipate induced currents. Proper grounding enhances the cable’s ability to handle interference, improving overall reliability and safety.
Advantages of STP Cables
- Improved Signal Integrity: STP cables provide excellent signal quality, reducing data errors and ensuring dependable communication for high-speed transmission. Their sturdy design makes them perfect for demanding applications.
- Electromagnetic Interference Protection: The shielding and twisted pair design effectively block EMI, preserving signal clarity and preventing disruptions from nearby devices or fields.
- Crosstalk Reduction: Individual shielding around each twisted pair minimizes crosstalk, enabling higher data rates and improving signal quality. This feature is crucial for reliable performance in complex networks.
- Versatility: STP cables perform well in various settings, including industrial environments with high EMI and applications requiring fast data transfer. Their adaptability suits diverse networking needs.
Disadvantages of STP Cables
- Higher Cost: STP cables cost more than UTP cables due to shielding materials and complex manufacturing processes. The extra cost improves performance.
- Increased Cable Diameter: The shielding increases cable thickness, making installation in tight spaces more difficult. Proper planning simplifies cable management.
- Grounding Considerations: Effective grounding prevents noise and ensures EMI protection. Follow manufacturer recommendations to avoid ground loops and interference.
- Limited Flexibility: STP cables are less flexible than UTP cables due to shielding. Use proper cable management to reduce installation challenges.
Installation Tips for STP Cables
- Proper Cable Routing: Route STP cables away from power cables or other interference sources to minimize electromagnetic interference effectively.
- Grounding and Bonding: Always ground and bond the cable shielding to the equipment chassis or ground system for optimal shielding performance.
- Cable Management: Use cable ties or trays to organize STP cables, preventing excessive bends or kinks that may damage the shielding.
- Connector selection: Choose high-quality connectors designed specifically for STP cables to maintain the shielding integrity and ensure proper termination.
How to Choose the Right STP Cable for Your Network
- Define Network Requirements:
Identify bandwidth needs, device distances, and EMI levels. Choose cables with suitable shielding and performance for your environment. - Understand Cable Specifications:
Check shielding type, twist rate, and conductor material. Opt for copper for better conductivity and durable jackets like PVC or LSZH. - Compliance and Standards:
Ensure cables meet standards like Cat 5e, 6, or 7 and have certifications verifying performance and quality. - Installation and Compatibility:
Select cables compatible with your network and easy to install, offering flexibility and convenient connectors. - Budget and Vendor Reliability:
Balance cost and performance. Buy from reputable vendors with proven quality and support for reliable products.
STP Cable Categories
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable: STP cables consist of twisted pairs of copper wires enclosed in a conductive shield, usually aluminum foil or braided copper. This shielding reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring better signal quality.
- Screened Shielded Twisted Pair (ScTP) Cable: Also called Foiled Twisted Pair (FTP), ScTP cables include an extra shielding layer over the individually shielded pairs. This additional foil or braided shield provides stronger protection against EMI and crosstalk, making it ideal for challenging environments.
- Shielded Foiled Twisted Pair (SFTP) Cable: SFTP cables combine individual pair shielding with an overall foil or braided shield for maximum EMI and crosstalk protection. This dual-layer design ensures superior signal integrity, especially in high-interference settings.
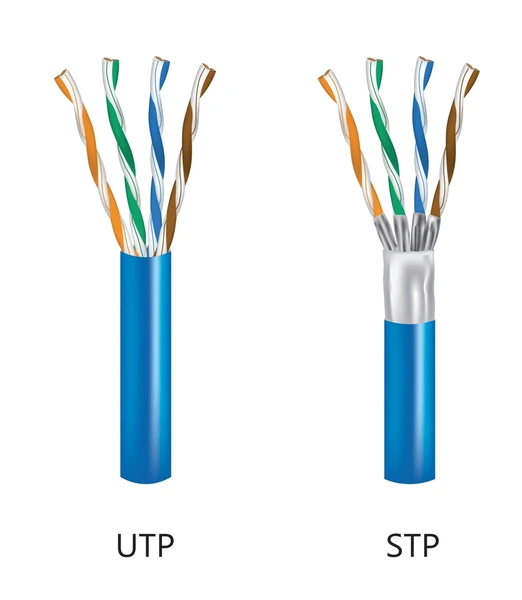
STP vs. UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) Cables
Key Differences between STP and UTP Cables
- Shielding: STP cables feature an additional shielding layer, usually made of aluminum foil or braided mesh, to block interference. This shielding effectively reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring better signal quality. On the other hand, UTP cables lack this shielding, making them more prone to external interference in noisy environments.
- Performance and Data Rates: Thanks to the shielding, STP cables deliver better performance and support higher data rates, even in EMI-heavy environments. UTP cables, however, are more suitable for lower data rates and applications in less demanding settings. While both options are reliable, the choice depends on specific performance needs.
- Application Scenarios: STP cables are ideal for environments with high electromagnetic interference, such as industrial facilities or medical centers. In contrast, UTP cables work well in residential or office spaces where EMI levels are lower. Choosing the right cable depends on the application and surrounding conditions.
Advantages of STP over UTP
- Improved Noise Immunity: The shielding in STP cables effectively blocks external electromagnetic interference, ensuring better signal integrity and reducing data errors caused by crosstalk and noise.
- Higher Bandwidth and Data Rates: STP cables can support higher data rates and bandwidths compared to UTP cables, making them suitable for applications that require faster data transfer speeds, such as high-speed Ethernet networks or video transmission.
- Longer Cable Runs: Due to their superior shielding and reduced crosstalk, STP cables can be run over longer distances without significant signal degradation, allowing for more flexible cable routing and installation.
Considerations for STP vs. UTP
- Cost: STP cables are generally more expensive than UTP cables due to the additional shielding material and manufacturing processes involved.
- Installation and Termination: STP cables require more careful installation and termination procedures to maintain the integrity of the shielding and ensure proper grounding. UTP cables are generally easier to install and terminate.
- Flexibility: UTP cables are typically more flexible and easier to route through tight spaces or around corners due to their smaller diameter and lack of shielding. STP cables can be less flexible, especially those with a solid shielding layer.
Applications of STP Cable
Networking and Telecommunications
- Ethernet Networks: STP cables are widely used in high-speed Ethernet networks, such as Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) and 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps), due to their ability to support high data rates and minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
- Telecommunication Systems: STP cables are employed in telecommunication systems for transmitting voice, data, and video signals over long distances with minimal signal degradation and interference.
Industrial Automation and Control Systems
- Factory Automation: STP cables are used in industrial automation systems, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), computer numerical control (CNC) machines, and robotic systems, where reliable and interference-free data transmission is crucial.
- Process Control: STP cables are utilized in process control systems, including supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, for monitoring and controlling industrial processes in various sectors, such as oil and gas, power generation, and manufacturing.
Building Automation and Security Systems
- Building Management Systems (BMS): STP cables are employed in BMS for integrating and controlling various building systems, such as HVAC, lighting, access control, and fire safety systems, ensuring secure and reliable data transmission.
- Security and Surveillance Systems: STP cables are used in security and surveillance systems, including closed-circuit television (CCTV) and access control systems, to transmit video and data signals with minimal interference and maintain data integrity.
Healthcare and Medical Facilities
- Medical Imaging and Diagnostic Equipment: STP cables are utilized in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment, such as MRI scanners, CT scanners, and ultrasound machines, where high-speed data transfer and shielding from electromagnetic interference are critical.
- Patient Monitoring Systems: STP cables are employed in patient monitoring systems, including vital sign monitors and telemetry systems, to ensure reliable and interference-free data transmission.
Audio/Video and Multimedia Applications
- Professional Audio/Video Systems: STP cables are used in professional audio/video systems, such as recording studios, broadcast facilities, and live event setups, where high-quality signal transmission and noise immunity are essential.
- Home Theater and Multimedia Installations: STP cables are utilized in home theater and multimedia installations to transmit high-definition audio and video signals with minimal interference and signal degradation.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| UTP Cable LG Cable Ltd. | Allows transmission of over 10 Gbps level without align cross talk with an adjacent cable when using 500 to 700 MHz band. | High-speed data transmission in networking and telecommunication systems. |
| Communication Cable with Spacer LG Cable Ltd. | Prevents crosstalk generated when a high frequency signal is transmitted. | Reliable data transmission in industrial automation and control systems. |
| Signal Transmission Cable Assembly Delphi Technology, Inc. | Contains electrically conductive particles that form electrically interconnected networks, providing stable data transmission. | Data transmission in telecommunication and networking environments where electromagnetic interference is a concern. |
Latest Technical Innovations in STP Cable
Cable Structure and Design
- Relocating potentially interfering or highly sensitive lines outside the main shielding to reduce mutual interference and protect signal quality. For example, placing insulated cable cores or twisted pairs between the main shielding and cable jacket or in the corners of a square/oval cross-sectional jacket.
- Optimizing the cross-sectional shape of the cable jacket (e.g. oval or square) to provide additional protection for sensitive cores located in the corners.
Shielding and Interference Reduction
- Enhancing the main shielding design to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between cable cores, improving signal integrity.
- Incorporating advanced shielding materials or techniques, such as double-shielded construction or using specialized EMI-absorbing materials in the shielding layers.
Cable Core Innovations
- Developing new insulation materials or coatings for individual cable cores to improve electrical properties, reduce signal attenuation, and increase durability.
- Optimizing the twisting patterns or lay lengths of twisted pairs to further minimize crosstalk and interference.
- Implementing composite or hybrid cable core designs, combining different materials (e.g. copper and fiber optics) for enhanced performance.
Cable Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Implementing advanced manufacturing techniques, such as precision extrusion or automated quality control, to ensure consistent cable performance and reduce defects.
- Developing new testing and certification standards to validate the performance and compliance of STP cables for emerging applications or higher data rates.
To get detailed scientific explanations of STP Cable, try Patsnap Eureka.

