
Technology innovation means creating and applying new or improved technologies to solve problems and create value. It often involves developing tools, systems, or methods that enhance products, services, or processes. For instance, innovations in medical devices, communication tools, and clean energy solutions have transformed daily life.
Technology innovation fuels economic growth and creates new industries and jobs. It increases efficiency by automating tasks and streamlining operations. Companies that innovate stay competitive by offering smarter solutions and improving customer experiences.
Engineers and scientists rely on innovation to tackle major global challenges. From climate change to healthcare and space exploration, innovation powers bold ideas and faster discovery. In today’s digital economy, technology innovation isn’t just helpful—it’s essential for progress and long-term success.
Unlock faster, smarter innovation with PatSnap Eureka AI Agent
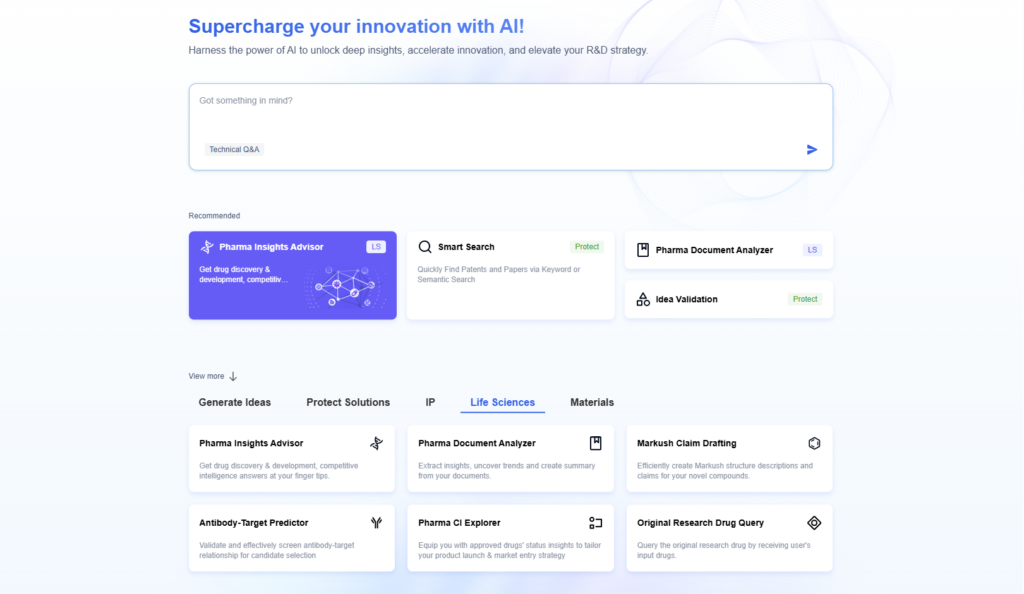
Types of Technology Innovation
Technology innovation takes many forms. Each plays a unique role in driving progress, competitiveness, and long-term growth.
Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves small, steady improvements to existing products, services, or processes. These improvements often focus on usability, performance, or efficiency. For example, each new smartphone model may feature better cameras, longer battery life, or faster processors. This type of innovation strengthens market position without changing the underlying technology. Many companies rely on incremental updates to meet evolving customer expectations and stay relevant in crowded markets.
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation changes how people solve problems or access solutions. It usually begins in niche markets with simpler, lower-cost offerings. These solutions appeal to overlooked customer segments that larger companies ignore. Over time, they improve and enter the mainstream. 3D printing is a good example. It disrupted traditional manufacturing by enabling low-cost, on-demand production of complex parts. Eventually, it reshaped supply chains and created entirely new business models.
Sustaining Innovation
Sustaining innovation helps established companies retain competitive advantage through major product improvements. It adds significant value without changing the overall structure of the market. For instance, automakers may launch a new generation of hybrid engines that offer better performance and fuel efficiency. These upgrades keep existing products competitive and relevant. Sustaining innovation ensures that market leaders can evolve alongside rising customer expectations and technological standards.
Radical Innovation
Radical innovation introduces entirely new technologies, often based on scientific breakthroughs. These innovations redefine industries and create new markets. The invention of the internet is a classic example. It changed how businesses operate and people communicate worldwide. Another example is CRISPR gene editing, which introduced a new era in biotechnology. Radical innovation carries higher risk, but it offers unmatched potential for growth and long-term value creation.
Each type of innovation plays a strategic role in building a robust innovation portfolio. Successful companies often combine different innovation types to stay agile, resilient, and future-ready.
The Innovation Process: From Ideation to Deployment
Innovation follows a multi-stage process, much like product development. Although models vary, a common framework includes:
- Ideation and Research: Generating and selecting new ideas. Teams study market needs, customer pain points, and technology trends. In this stage they define project goals and research the problem space and potential solutions.
- Concept and Prototyping: Turning ideas into tangible concepts. The team specifies requirements and builds prototypes or proof-of-concepts to test core functionality. Early prototypes help validate feasibility and gather feedback.
- Development and Testing: Refining the solution. Engineers or scientists iterate on the prototype, conducting experiments or pilot studies. They test and improve the design to meet performance, cost, and safety goals.
- Deployment and Commercialization: Launching the innovation. After validation, the new technology is scaled up, integrated into products or processes, and rolled out to customers or end-users. This phase includes marketing, user training, and measuring performance in the real world.
Each phase is essential. For instance, one R&D framework emphasizes defining clear objectives first, then creating a detailed development plan and prototype. By following a structured process, teams avoid wasting resources and ensure innovations are practical and aligned with needs. Iteration often continues even after deployment, as innovators learn from real-world use and improve the solution further.
Strategic Value of Technology Innovation
Technology innovation is a powerful engine of business success and national growth. It delivers lasting benefits across key areas.
Growth and Competitiveness
Innovations fuel growth by creating new products, services, and entire industries. These breakthroughs open up fresh revenue opportunities. Companies that innovate attract more investment, talent, and customer attention. Leading economies also benefit by becoming global hubs for tech and business activity. Organizations that invest in innovation build long-term competitive advantage and strengthen their economic position.
Efficiency and Productivity
Technology often simplifies complex processes and reduces human workload. Automation tools improve accuracy and speed across operations. For example, robotics and AI can handle repetitive tasks with minimal errors. Software platforms can streamline communications and supply chains. These changes free employees to focus on creative, high-value tasks. The result is better productivity and improved cost efficiency.
Social and Sustainability Impact
Innovation can solve major global challenges. Clean energy systems reduce pollution and protect natural resources. Telemedicine platforms bring healthcare to remote communities. Smart farming tools help feed growing populations more sustainably. These innovations improve lives while helping companies meet their social and environmental goals. By solving real-world problems, businesses also build stronger brands and customer trust.
Innovation Strategy
A strong innovation strategy links every effort to the company’s mission. Top firms align R&D with business goals like entering new markets or improving service. They encourage teamwork between departments to spark fresh ideas. They support experimentation to test and refine new technologies quickly. This strategy ensures innovation leads to measurable results and long-term growth.
In short, technology innovation drives progress. It helps companies grow faster, work smarter, and make a bigger impact on the world.
Innovation in Corporate R&D
Research and development (R&D) teams drive innovation within established companies. They explore ideas from small improvements to bold breakthroughs. A strong R&D department keeps a company agile, competitive, and ready to adapt. Without consistent innovation, even dominant firms can fall behind. Blackberry’s failure to match the iPhone is a classic example of missed technological shifts.
Corporate R&D projects often focus on improving current products or chasing transformative ideas. Some projects aim for radical outcomes, where new technologies or solutions create entirely new markets. For example, some R&D projects in the technology space focus on improving functionality or exploring new applications for existing products.
Modern R&D teams no longer rely solely on manual research. They use advanced tools to work faster and smarter. PatSnap’s Eureka AI Agent is a vital resource for R&D teams looking to streamline their workflows. It serves as an intelligent research assistant, capable of rapidly searching millions of patents, academic papers, and databases to answer complex questions.
Life sciences and engineering teams rely on Eureka to search for patents, drug mechanisms, regulatory information, and technical diagrams. The tool helps teams gather critical insights quickly, eliminating the need for redundant work. Eureka boosts R&D productivity by up to 75%, while also cutting research costs by about 25%. Large biotech companies use Eureka to accelerate innovation and maintain confidentiality in their projects.
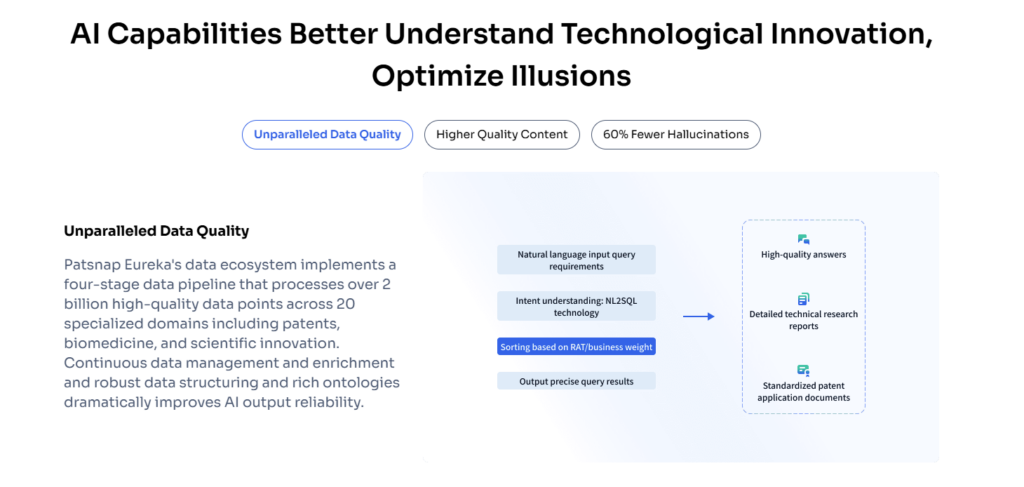
In short, PatSnap Eureka AI Agent helps R&D teams focus on solving problems rather than spending time on data gathering. This capability unlocks faster innovation and more effective solutions.
Innovation in Startups
Startups thrive on innovation. Without legacy systems to protect, they often pursue bold, disruptive ideas. According to one analysis, “many startups start with research or even scientific projects.” They conduct market and technical feasibility studies, build prototypes, and test them aggressively. This focus on R&D helps validate the business model and attract investors. A working prototype can prove viability and enhance investment appeal.
Startups typically follow lean methodologies, quickly launching a minimum viable product (MVP) to gather customer feedback. This rapid build–measure–learn cycle allows them to iterate and pivot at a low cost. Agile innovation processes help startups respond to customer needs and outpace larger competitors. Disruptive innovations often come from startups targeting niches that incumbents overlook. For instance, iconic tech companies, from early search engines to ride-sharing apps, began as lean startups experimenting with novel tech.
In short, startups harness technology innovation by embracing risk, speed, and customer-driven iteration. Their success shows how deep R&D, even in small teams, can yield breakthrough products and create entirely new markets.
Intellectual Property and Innovation
Protecting and managing intellectual property (IP) is essential for technology innovation. Many innovations are patentable, and patents grant inventors exclusive rights to commercialize their inventions. Specifically, patents protect inventors by allowing them to prevent others from making, selling, or importing their new technology. This legal protection enables companies to recoup R&D investments and even license their innovations for additional revenue.
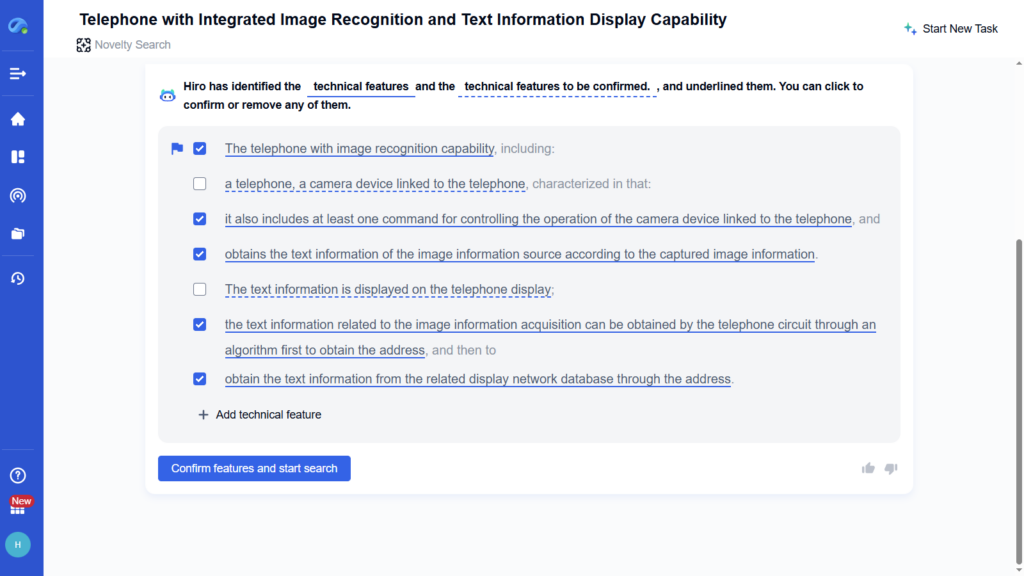
As a result, smart innovators incorporate IP strategy into their R&D planning. Before launching new technology, companies conduct patent landscaping and freedom-to-operate searches to check for potential conflicts. Modern AI tools accelerate this process significantly. For instance, PatSnap’s Eureka can automate “prior art” analysis with specialized modules for life science sequences, engineering concepts, and more. If a biotech firm engineers a new protein, Eureka can quickly compare hundreds of DNA or amino-acid sequences against global patent databases to identify existing claims. This automated sequence analysis can flag novelty issues in minutes – a task that used to take months. By verifying whether an innovation is novel and patentable quickly, AI tools like Eureka help innovators secure IP rights confidently and focus on creative work.
In essence, intellectual property planning ensures that innovation is sustainable. As WIPO explains, patents contribute technological knowledge to the public domain while rewarding inventors. This strikes a balance between disclosure and exclusivity. By combining AI-driven IP research with innovation planning, companies can better align their innovation roadmap with patent strategy. This approach helps protect breakthroughs and guide future R&D directions.
AI Tools Accelerating Innovation
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing innovation across industries, providing powerful tools that accelerate research and development (R&D). Generative AI models and intelligent agents are speeding up tasks from idea generation to concept validation. According to industry analysts, generative AI “could trigger a new era of human innovation” by streamlining processes that once took significant time and effort.
In practice, AI tools can quickly draft design concepts, simulate outcomes, and even suggest creative solutions that humans might miss. For example, AI systems can propose new product features, optimize engineering designs, and predict market trends, all in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.
Real-world examples highlight AI’s impact. In software engineering, AI-powered coding assistants are now essential. Google reports that over 25% of its new code is generated by AI, while Amazon credits AI tools with saving thousands of developer-years. In the life sciences, models like AlphaFold have solved protein structures in hours, something that once took scientists decades. AI is also transforming materials science. In 2024, Microsoft and Pacific Northwest National Lab used AI to screen 32 million virtual materials for a new solid-state battery electrolyte. This would have taken years through traditional lab work. The AI-identified material was then synthesized and validated in the lab, showing how AI speeds up innovation by finding “needles in the haystack.”
Among AI tools, PatSnap’s Eureka AI Agent stands out. Eureka acts as an AI research assistant, answering natural-language questions about everything from drug mechanisms to material properties. It provides evidence-backed answers almost instantly, allowing scientists to focus on creativity and decision-making. PatSnap reports that Eureka has reduced AI errors by 60% and greatly increased confidence in R&D results. In short, AI tools are transforming the innovation process, from ideation to deployment. They help individuals and teams explore more ideas, test hypotheses quickly, and bring new technologies to market faster.
Conclusion
Technology innovation – whether incremental or disruptive – is the lifeblood of progress. By introducing new technologies and constantly improving existing ones, organizations and societies solve problems, open new markets, and drive efficiency. The process typically moves from creative ideation through R&D and prototyping, to deployment and scaling. Strategically aligning these innovation efforts with business goals pays dividends in growth and competitive advantage. In today’s world, modern R&D teams and startups alike use advanced tools – especially AI-driven platforms – to accelerate every stage of innovation, from literature review to patent analysis. Tools like PatSnap’s Eureka exemplify this trend, enabling faster insights and smarter decision-making in research and IP planning. Ultimately, embedding a strong innovation strategy (backed by technology and IP planning) empowers organizations to turn creative ideas into real impact.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Technology Innovation, try Patsnap Eureka.

