
Introduction
The world of wireless connectivity is constantly evolving, and with the introduction of WiFi 7, a new standard promises faster speeds, lower latency, and improved efficiency. But how does it compare to the already impressive WiFi 6? If you’re wondering whether it’s worth upgrading to WiFi 7 or sticking with WiFi 6, his article will explore the key differences, features, and benefits of WiFi 7 vs. WiFi 6 to help you decide which standard best fits your needs.

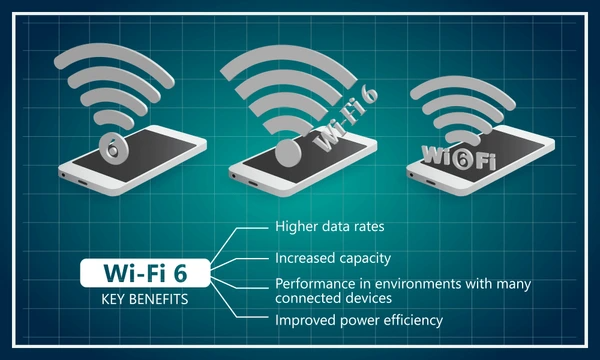
Key Features of WiFi 6
1. Improved Throughput and Speed
WiFi 6 delivers a maximum throughput of up to 9.6 Gbps, significantly faster than previous WiFi generations. This improvement is achieved through several advanced technologies:
- Wider Bandwidth Channels: Channels up to 160 MHz enhance data transmission capacity.
- Higher-Order Modulation: 1024-QAM boosts data rates for more efficient communication.
- OFDMA Technology: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access improves overall efficiency by allowing multiple devices to share channels simultaneously.
2. Better Performance in Dense Environments
WiFi 6 excels in crowded areas with many access points and devices, such as offices, apartments, and stadiums. Key features that enhance performance include:
- MU-MIMO: Multi-User MIMO enables simultaneous communication with multiple devices for faster connections.
- Spatial Reuse and BSS Coloring: These technologies minimize interference, improving overall network performance.
- Target Wake Time (TWT): TWT enhances battery life for IoT devices by scheduling specific times for communication.

3. Lower Latency
WiFi 6 significantly reduces average latency compared to WiFi 5, dropping from around 30ms to 20ms. This improvement supports real-time applications like gaming, video conferencing, and virtual reality, ensuring smoother performance.
4. Extended Range and Outdoor Support
While WiFi 6 primarily targets indoor environments, it also enhances outdoor range and performance. Techniques like Overlapping Basic Service Set (OBSS) management help maintain stable connections in outdoor settings.
5. Convergence with 5G
WiFi 6 is increasingly aligned with 5G technology, creating opportunities for cooperation between the two. This convergence allows WiFi 6 to offload 5G networks in crowded areas, improving connectivity for users and reducing network strain.
Advancements in WiFi 7 Technology
WiFi 7, also known as IEEE 802.11be or Extremely High Throughput (EHT), is the next-generation wireless networking standard that aims to address the growing demand for higher data rates, lower latency, and improved spectrum efficiency.
1. Increased Bandwidth and Channel Width
WiFi 7 introduces a maximum channel width of 320 MHz in the 6 GHz band, doubling the bandwidth available in WiFi 6. This wider channel, combined with advanced modulation schemes, allows data rates of up to 30 Gbps. These improvements make WiFi 7 ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like 8K streaming and large-scale data transfers.
2. Higher-Order Modulation and Spatial Streams
WiFi 7 utilizes 4096-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), enabling significantly higher data throughput compared to WiFi 6’s 1024-QAM. Additionally, it supports up to 16 spatial streams, doubling the capacity of WiFi 6. These advancements enhance multi-user communication and improve overall network efficiency.
3. Multi-Link Operation (MLO)
One of the most innovative features of WiFi 7 is Multi-Link Operation (MLO). This technology allows devices to use multiple frequency bands and channels simultaneously for a single session. MLO improves throughput, boosts reliability, and enhances load balancing across the network.
4. Advanced Interference Management
WiFi 7 incorporates sophisticated interference management techniques to ensure consistent performance in crowded environments. Features like spatial reuse and dynamic frequency selection minimize interference, making WiFi 7 ideal for dense deployments such as offices, stadiums, and urban areas.

Should You Upgrade to WiFi 7?
Deciding whether to upgrade to WiFi 7 depends on your specific needs, current setup, and how you use your network. While WiFi 7 offers impressive advancements, it may not be necessary for everyone right now.
1. Upgrade if You Need Maximum Speed and Capacity
WiFi 7’s increased bandwidth, faster data rates of up to 30 Gbps, and support for 320 MHz channels make it ideal for bandwidth-intensive activities. If you stream 8K videos, use VR applications, or transfer large files regularly, upgrading to WiFi 7 could significantly enhance your experience.
2. Upgrade if You Manage Dense Networks
With features like Multi-Link Operation (MLO) and advanced interference management, WiFi 7 is perfect for handling crowded environments. If you live in an area with many connected devices or manage a business network, WiFi 7 can provide better reliability and efficiency.
3. Wait if You’re Satisfied with WiFi 6
If your current WiFi 6 network meets your needs, upgrading may not offer noticeable benefits right away. WiFi 6 already delivers strong performance for most homes, with fast speeds and lower latency suitable for everyday tasks.
4. Consider Compatibility and Cost
Upgrading to WiFi 7 will require compatible routers and devices, which may come at a higher cost. If your devices are not yet WiFi 7-ready, you may not fully utilize its benefits. Waiting until more affordable options and widespread adoption occur might be a smarter choice.
To get detailed scientific explanations of WiFi 7 vs. WiFi 6, try Patsnap Eureka.

