Black nightshade pest-resistant gene and uses thereof
An insect-resistant gene, Solanum nigrum technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problem of protease inactivation, etc., and achieve the effect of improving insect resistance and plant insect resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
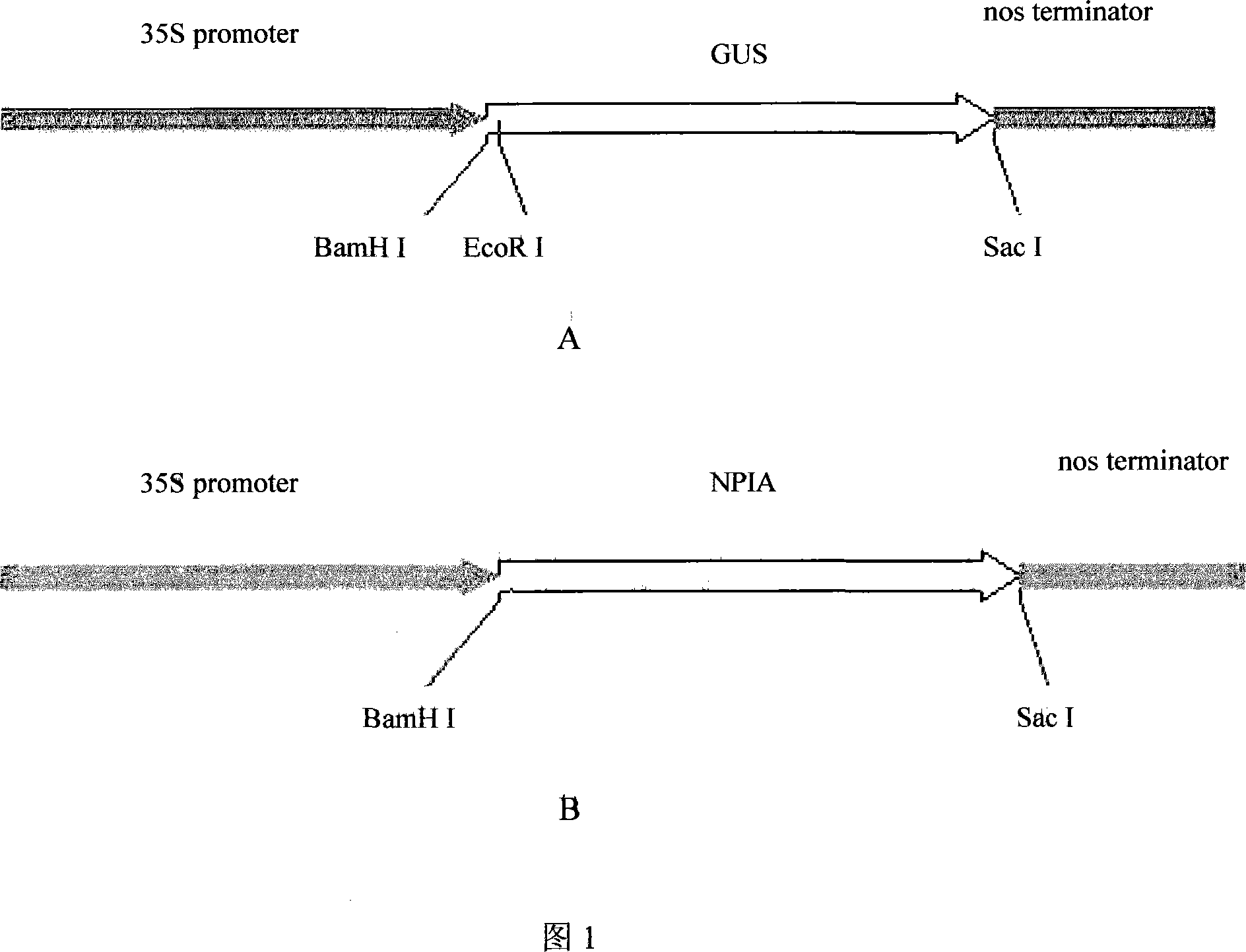
[0034] Embodiment 1: the acquisition of solanum protease inhibitor gene A and the construction of plant expression vector
[0035]According to the sequence of solanum protease inhibitor gene IIa (SaPIN2a), gene-specific primers were designed, and the 5' untranslated region (UTR) was obtained by rapid amplification of cDNA ends. Use GeneRacer 5'primer and GeneRacer 5'nested primer and reverse gene-specific primer 2A-KDELSAC1 to amplify cDNA as a template, and clone the RT-PCR product into the pMD-18T vector to obtain the vector p5'RACE- TV. A pair of primers 2a-full-1 and 2a-full-2 were synthesized to amplify the solanum protease inhibitor IIa gene cDNA from the transcription start point to the UAA stop codon from p5'RACE-TV-1. The product was also cloned into pMD-18T to obtain pF-TV. The pF-TV was digested with BamH I+Sac I to obtain the NPIA gene, which is 496 bp long (see SEQ ID NO: 1).
[0036] The obtained NPIA gene replaced the GUS gene on pBI121, and the plasmid was n...
Example Embodiment
[0049] Example 2: Agrobacterium-mediated tobacco transformation and kanamycin resistance selection
[0050] Inoculate the corresponding Agrobacterium strain from the plate in 5ml YEB liquid medium (kanamycin 50mg / ml, rifampicin 50mg / L), and culture at 28°C 180 rpm for two days; then dilute the Agrobacterium solution to OD with liquid TRM medium 600 About 0.2-0.3. The sterile leaves were cut into leaf discs and placed in diluted Agrobacterium solution for 5 minutes. Get a small amount of cut leaves and put them into the liquid TRM medium without Agrobacterium, and move them to plates without or with Kan (50mg / L) respectively as positive and negative controls for transformation. Incubate in the dark at 28°C for two days; rinse the explants at least 5 times with liquid TRM medium. Blot the liquid on sterile filter paper. The explants were transferred to TRM solid plates (containing 100 μg / ml kanamycin and 250 μg / ml carbenicillin) and cultured at 28°C. Change the medium every ...
Example Embodiment
[0053] Example 3: PCR detection of kanamycin-resistant transgenic plants
[0054] Primers used to identify pF-121 (F series)
[0055] 5' primer sequence: ZF56 5'-TCCCACTATCCTTCGCAAGACCC-3'
[0056] 3' end primer sequence:
[0057] ZF103 5'GCGGATCCTTAGAAATAAGCAGTGGTCT-3'
[0058] Primers used to identify pBI-121 (B series)
[0059] 5' primer sequence: ZF56 5'-TCCCACTATCCTTCGCAAGACCC-3'
[0060] 3' end primer sequence: ZF47 5'-TCACCGAAGTTCATGCCAGT-3'
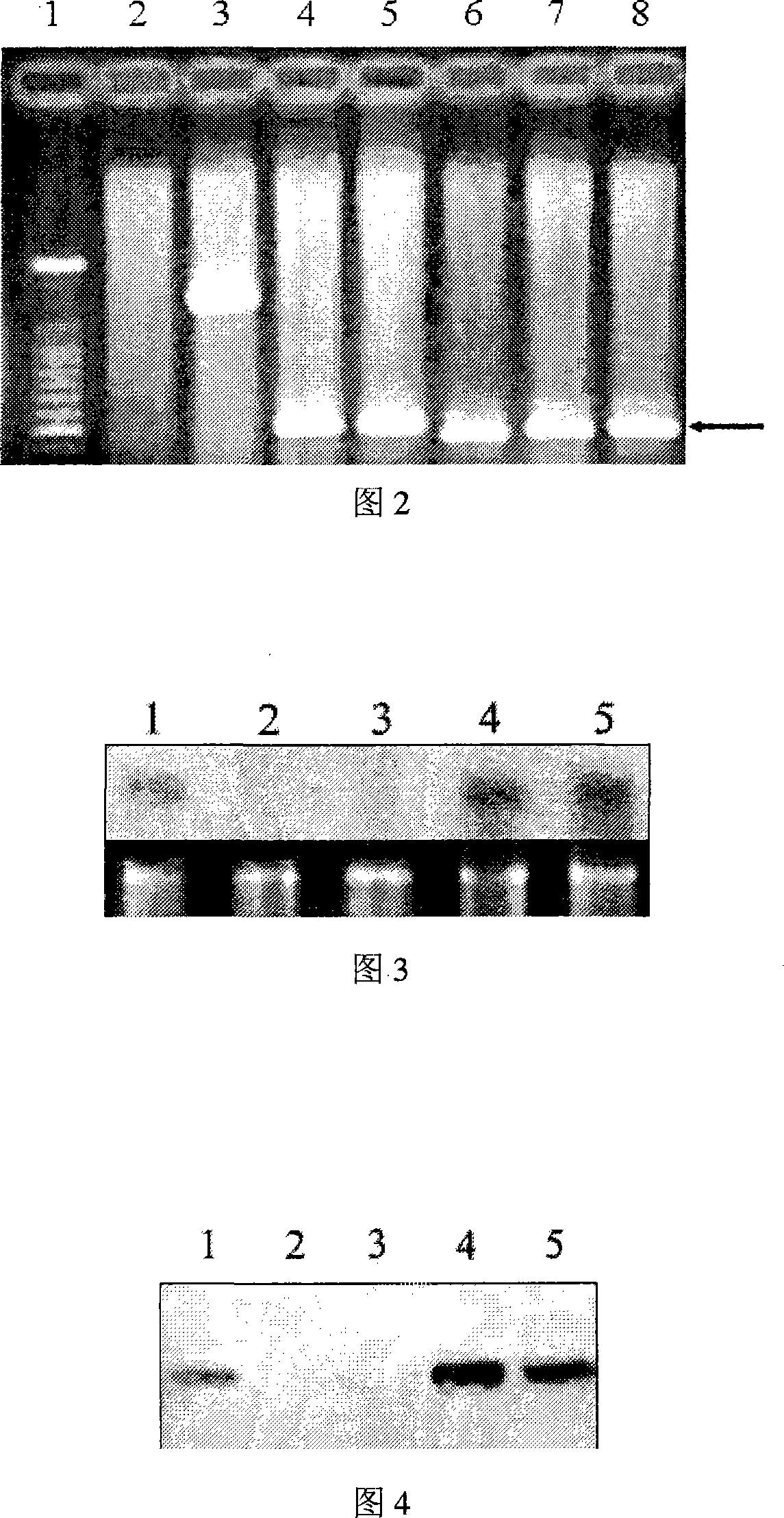
[0061] The PCR reaction conditions were: 95°C, 5 minutes for 1 cycle, followed by 95°C for 50 seconds, 58°C for 40 seconds, 72°C for 40 seconds, 35 cycles, and then 72°C for 10 minutes. Materials identified as positive by PCR were selected. The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2.
[0062] Table 2
[0063] positive
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap