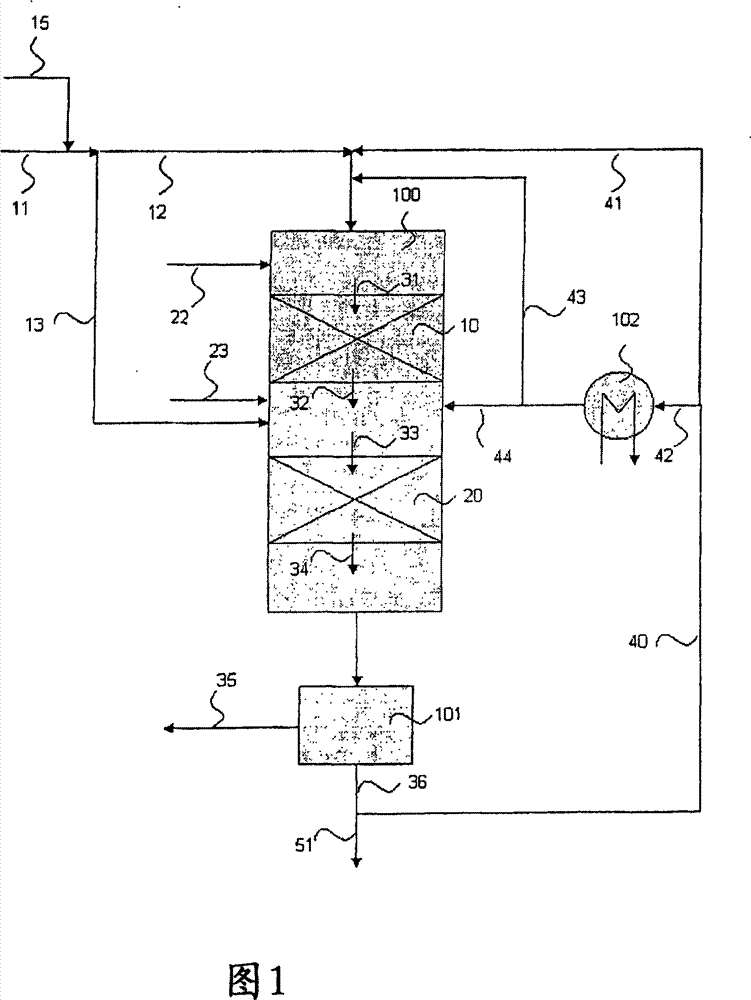
Process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons
A range, diesel technology, applied in the field of preparing diesel range hydrocarbons, can solve the problems of inability to achieve high selectivity for converting n-alkanes, harmful catalysts, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
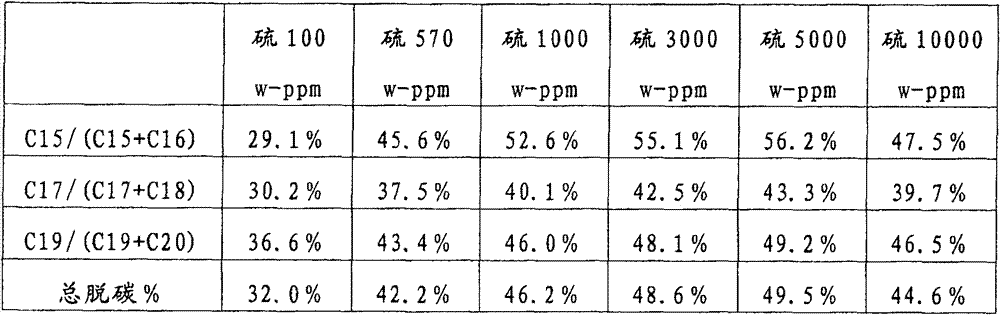
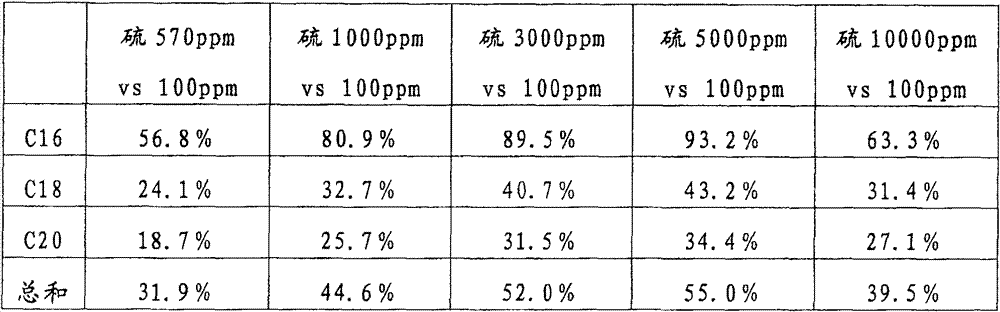
[0091] Example 1 Effect of Sulfur Content of Total Feed
[0092] Palm oil containing 0.3 area-% free fatty acids was used as fresh feed, 5:1 with product recycle, in the presence of hydrogen. C in the fresh feed 12 -C 16 The content of fatty acid triglycerides was 58.3 wt%. The total feed contains less than 10 w-ppm of alkali and alkaline earth metals on an elemental basis. The amount of other metals in the feed is less than 10 w-ppm calculated as elemental metal. The amount of phosphorus is less than 30 w-ppm as elemental phosphorus.
[0093] During the test runs, different amounts of dimethyl disulfide were used in the total feed. The reaction temperature was 305 °C, the reactor pressure was 5 MPa and the space velocity was 0.5 g / g for fresh feed. Higher levels of sulfur in the feed significantly increased the passage of CO and CO 2 The total deoxidation reaction (decarbonization reaction, which produces n-alkanes with one carbon atom less than the original fatty acid...
Embodiment 2
[0100] When embodiment 2 adopts palm oil feed, C 16 Effect of Fatty Acids on Cracking During Isomerization and Diesel Yield at Same Pour Point Levels
[0101] In this fresh feed a C containing 44.8 wt% 12 -C 16 Fatty acid triglycerides of palm oil. Dimethyl disulfide was added to palm oil to obtain a sulfur content in the feed of about 600 w-ppm, calculated as elemental sulfur. The feed purity was the same as in Example 1, but the free fatty acid content was 0.2 area %. No thinner is used. The feed was hydrotreated at 305°C in the presence of hydrogen, the reactor pressure was 5 MPa and the space velocity was 2 g / g for the fresh feed. The product mainly contains n-alkanes. The n-paraffin feed was isomerized at 317°C, 4 MPa and a WHSV of 3 liters / hour in the presence of hydrogen. Catalyst (A) contains Pt, SAPO-11 and alumina support. Product>C 10 The hydrocarbon content was 97% by weight. The cloud point of the liquid product was -22°C. The analytical results of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Example 3 C under the same diesel yield using palm oil feed 16 Effect of Fatty Acid on Pour Point of Isomerized Diesel Oil
[0104] The hydrotreated palm oil obtained in Example 2 was isomerized at 312° C., 4 MPa and a WHSV of 3 liters / hour in the presence of hydrogen, using catalyst A. This gave a liquid product with a cloud point of -14°C. Product>C 10 The hydrocarbon content is now 98% by weight. A small amount of light hydrocarbons can be inferred from the flash point of this product and in the distillation curve, as can be seen in Table 4, which shows the hydrotreatment and isomerization obtained from rapeseed oil and palm oil. Analytical results of products, and HRO=hydrotreated rapeseed oil, HPO=hydrotreated palm oil.
[0105] Table 4 Analytical results of hydrotreated and isomerized products obtained from rapeseed oil and palm oil
[0106]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com