Preparation method of (methyl) acrylic polymer
A technology of methyl methacrylate and methacrylic acid, which is applied in the field of continuous bulk polymerization to prepare acrylate polymers, which can solve the problems of polymer transparency, heat resistance degradation, and influence on polymer color, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
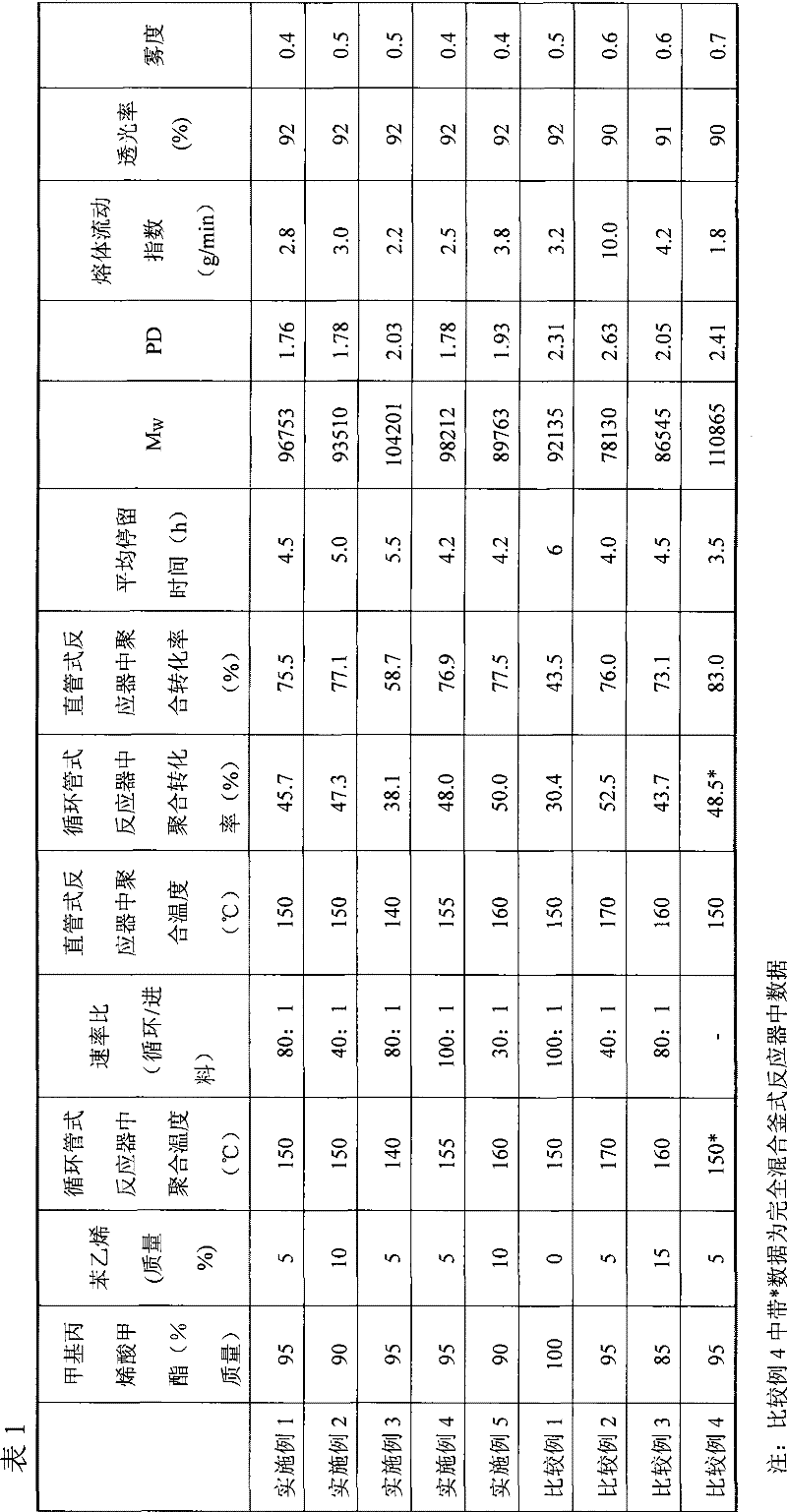
[0027] In the batching tank with a jacket, the raw materials such as methyl methacrylate, styrene and tert-dodecyl mercaptan are initially mixed, and then sent to the intermediate tank for temporary storage to ensure a fixed feed amount. The polymerized monomer mixed solution was kept at 10°C. The composition of the mixed solution is: 95 parts of methyl methacrylate, 5 parts of styrene and 0.05 part of tert-dodecyl mercaptan (corresponding to the total amount of polymerized monomers). Fill the batching tank and the intermediate tank with nitrogen (by nitrogen system), remove the oxygen mixed in the monomer mixed solution, and control the oxygen content therein at 2ppm. The reactor is also replaced with nitrogen to exhaust oxygen before feeding monomer. The monomer is fed into the circulation tube reactor at a rate of 1.2kg / h through the metering pump, and the material circulates in the reactor through the circulation pump, and the ratio of the material circulation rate to the...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The same procedure as in Example 1 was used except that the ratio of polymerized monomers and the ratio of recycle to feed rate were adjusted. The composition of the mixed solution was: 90 parts of methyl methacrylate, 10 parts of styrene and 0.05 part of t-dodecyl mercaptan. In the circulating tubular reactor, the ratio of the material circulation rate to the feed rate is controlled to be 40:1, and the polymerization temperature is 150°C. The polymerization conversions in the circulation tube reactor and the straight tube reactor were 47.3% and 77.1%, respectively. After the reaction is complete, the polymer mixture is sent to a vented extruder for devolatilization. Polymerization conditions and test results are listed in Table 1. Under this condition, the continuous polymerization process and devolatilization process of the system can be stably controlled, and a colorless and transparent polymer with excellent performance is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The same method as in Example 1 was used, except that the polymerization temperature of the system was lowered. 95 parts of methyl methacrylate, 5 parts of styrene and 0.05 parts of tert-dodecyl mercaptan are passed through nitrogen to remove dissolved oxygen in the monomer, and then sent to a circulating tubular reactor. The polymerization temperature is 140°C. In the circulating tubular reactor, the ratio of material circulation rate to feed rate is controlled to be 80:1. The polymerization conversions in the circulating tube reactor and the straight tube reactor were 38.1% and 58.7%, respectively. After the reaction is complete, the polymer mixture is sent to a vented extruder for devolatilization. Polymerization conditions and test results are listed in Table 1. Under this condition, the continuous polymerization process and devolatilization process of the system can be stably controlled, and a colorless and transparent polymer with excellent performance is obtain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com