High-efficiency calculus-removing expansion sheath of percutaneous nephroscope
A nephroscopic and high-efficiency technology, applied in the field of expanding sheath for efficient removal of stones, can solve the problems of unreasonable structural design, increase the pressure in the renal pelvis, and reduce the space for stone removal, so as to improve the efficiency of stone removal, reduce the incidence and prevent blocking effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The present invention is described in detail in conjunction with accompanying drawing now.
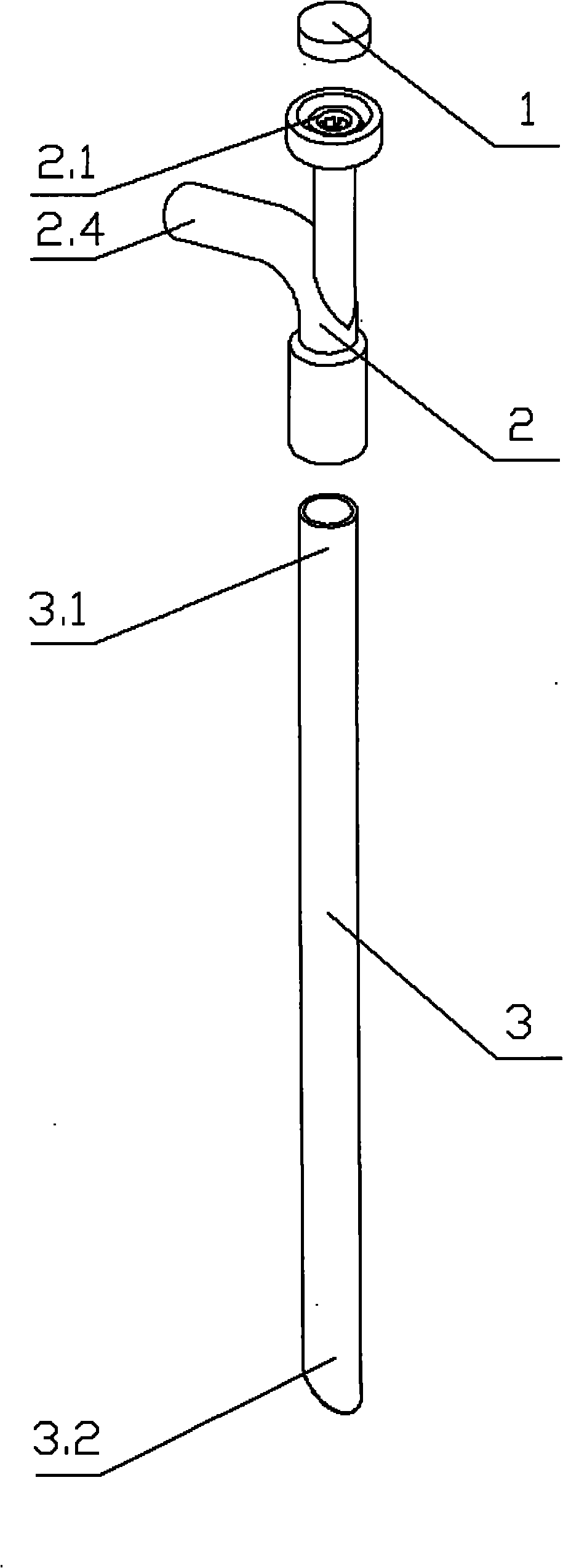
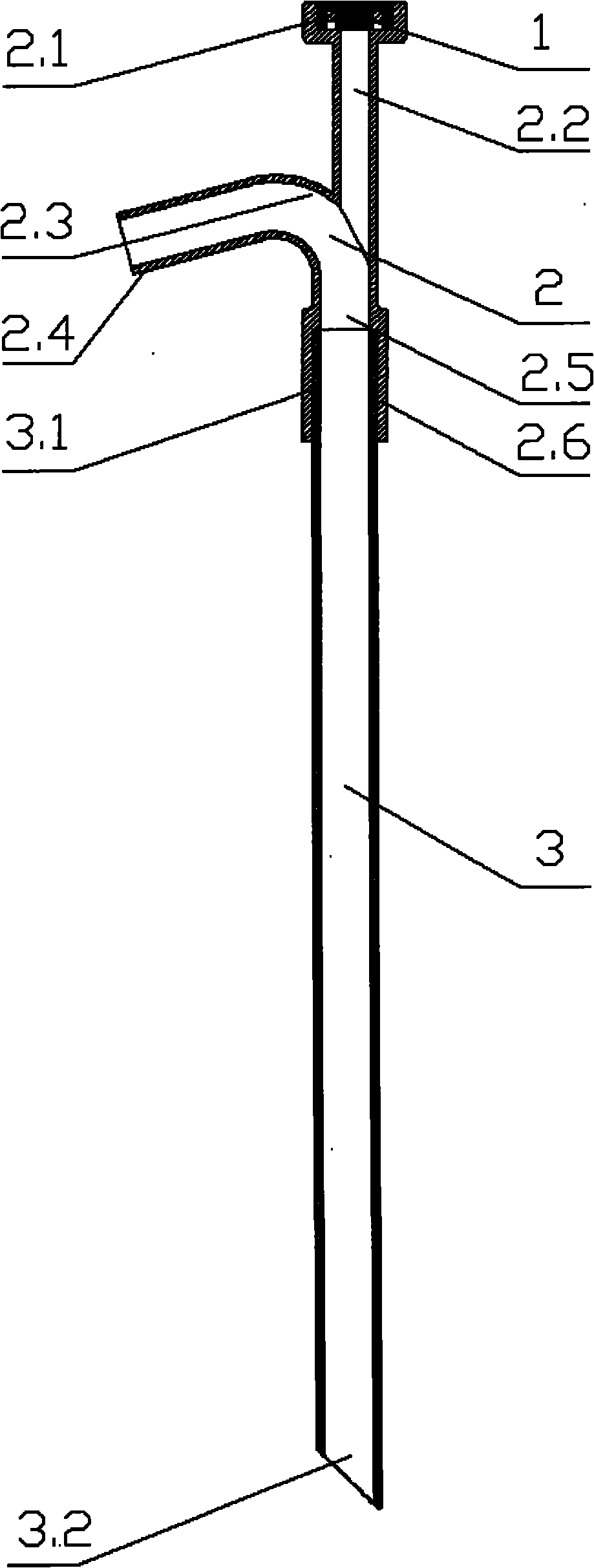
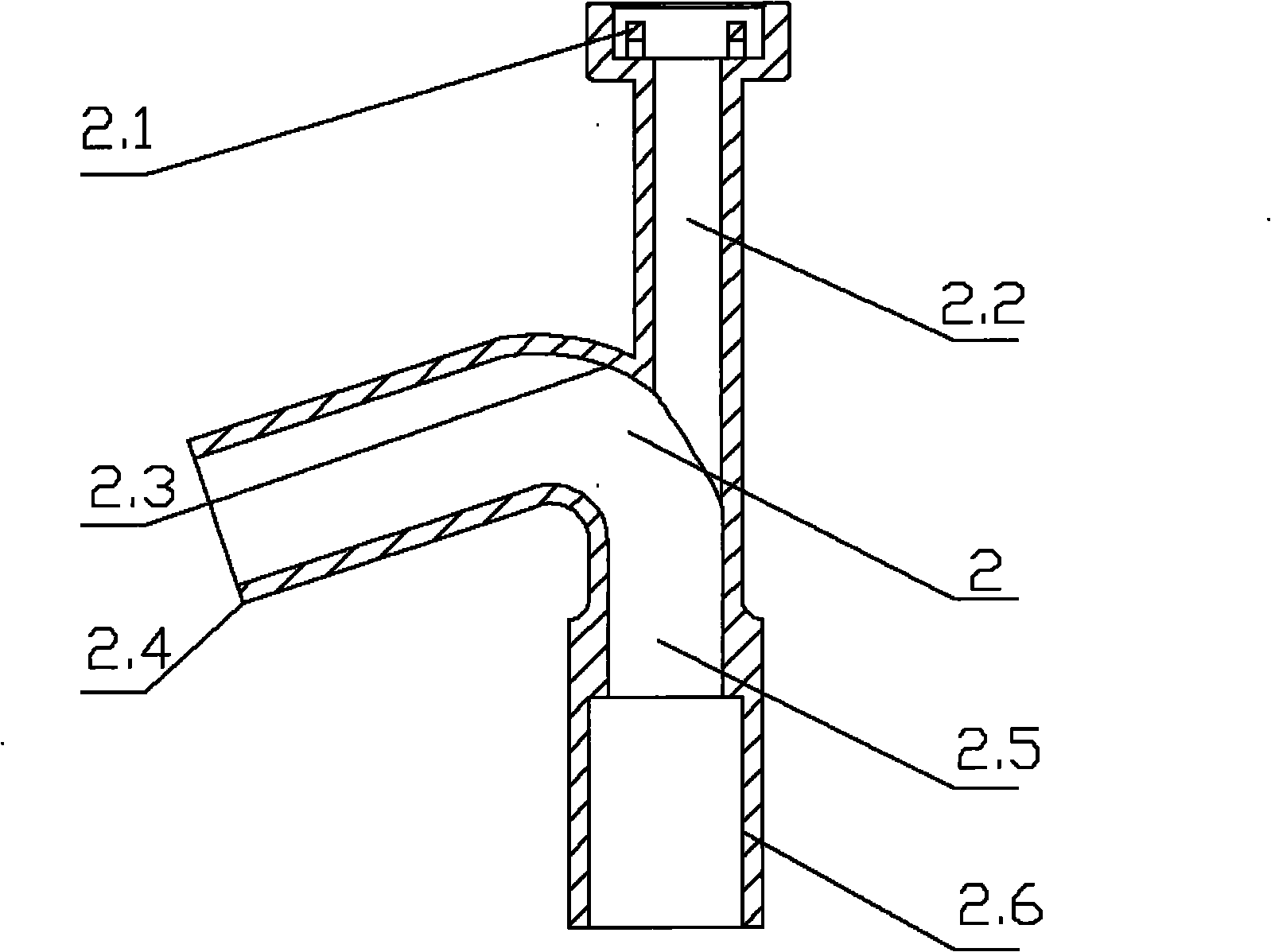
[0014] The present invention is composed of a sealing cap 1, an eccentric solenoid 2, an expansion sheath 3 and an expansion sheath inner core 4. The sealing cap 1 is made of a thermoplastic elastomer with excellent elasticity and tightness, and the sealing cap 1 is fixed on the eccentric solenoid 2 on the sealing cap bracket 2.1, the endoscope is inserted into the endoscope channel 2.2 through the sealing cap, and the inner diameter of the endoscope channel 2.2 matches the selected endoscope outer diameter, because the endoscope channel 2.2 and the eccentric The solenoid water inlet 2.5 is internally tangent (that is, when the expansion sheath and the eccentric solenoid are installed, the endoscope channel and the expansion sheath are also internally tangent), and the length of the endoscope channel 2.2 is much greater than its inner diameter. When the endoscope is inserted int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com