Counter-pressure filtration of proteins
A protein and filter technology, applied in the direction of peptide/protein components, filtration separation, fixed filter element filter, etc., can solve problems such as damage, reduction of processing yield, and protein destruction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-8
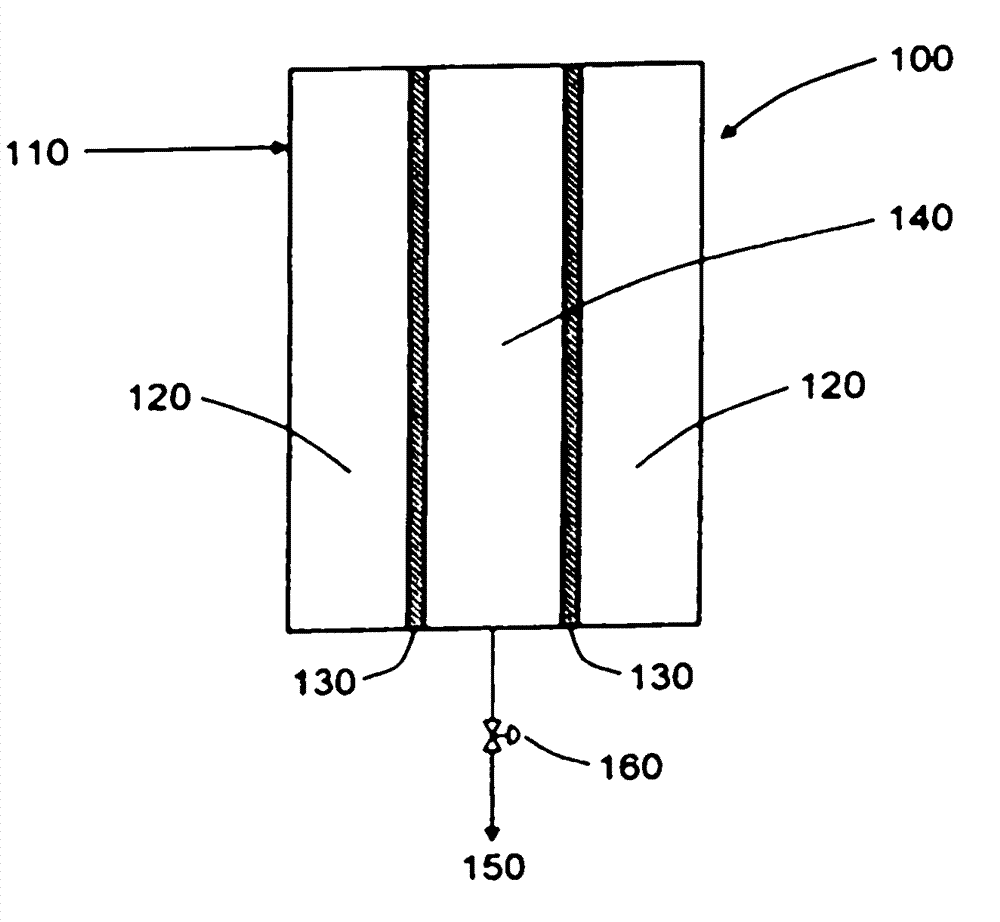
[0033] The aqueous mixture of shear-sensitive, coagulation cascade protein vWF is sterilized and filtered to determine the effect of pressure (and back pressure) and other process variables (such as filter size and type) on the effectiveness of filtration, such as based on the filtrate The activity of vWF being recovered, the average flow rate of the filtrate and the ability to scale up the processing.
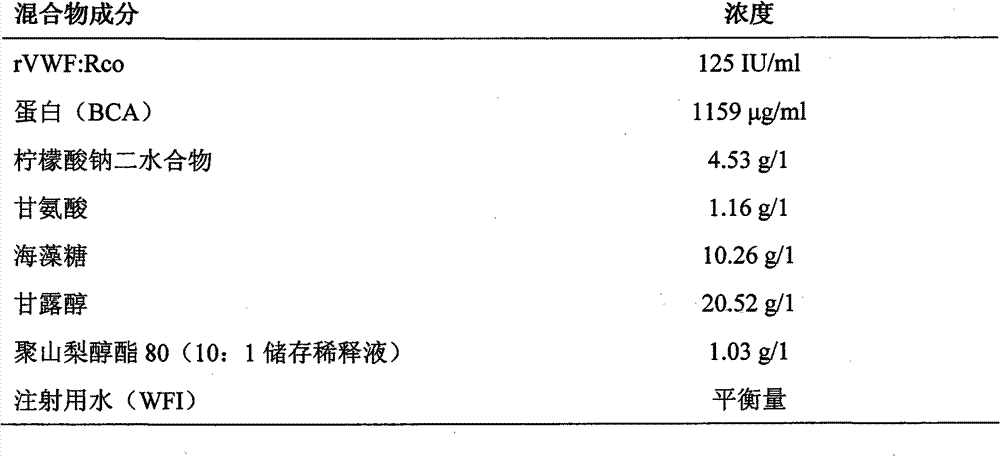
[0034] The aqueous mixture of recombinant vWF ("rVWF:Rco") has an activity of 125IU / ml and the concentration is 1159μg / ml (the bicinchoninic acid ("BCA") experiment). This mixture was prepared for the following Example 1- 8 in each of the examples. A low molecular weight salt is added to adjust the pH of the mixture to 7.3 and the osmolality to a value of about 400 mOsmol / l (milligrams osmolality / liter), respectively. Since Examples 1-8 are used to isolate the hydrodynamic effects (such as shearing) on the protein near the filter, no other dispersed contaminants or materials (...
Embodiment 9-20
[0055] Aqueous solutions containing factor VIII in a SARTOCLEAN pre-filter The filter is tested to determine the effect of back pressure on the effectiveness of the filter, for example based on the required filter surface area. In Examples 9-13, no back pressure filtration was performed; the initial applied pressure was 100 mbar to 500 mbar. In Examples 14-16, the pressure difference was 200 mbar, and in Examples 17-20, the pressure difference was reduced to less than 150 mbar. The surface area of each filter is 1.2m 2 . Table 5 contains the Factor VIII activity before and after filtration in each experiment.
[0056] Table 5. Recovery of FVIII in the filtrate
[0057]
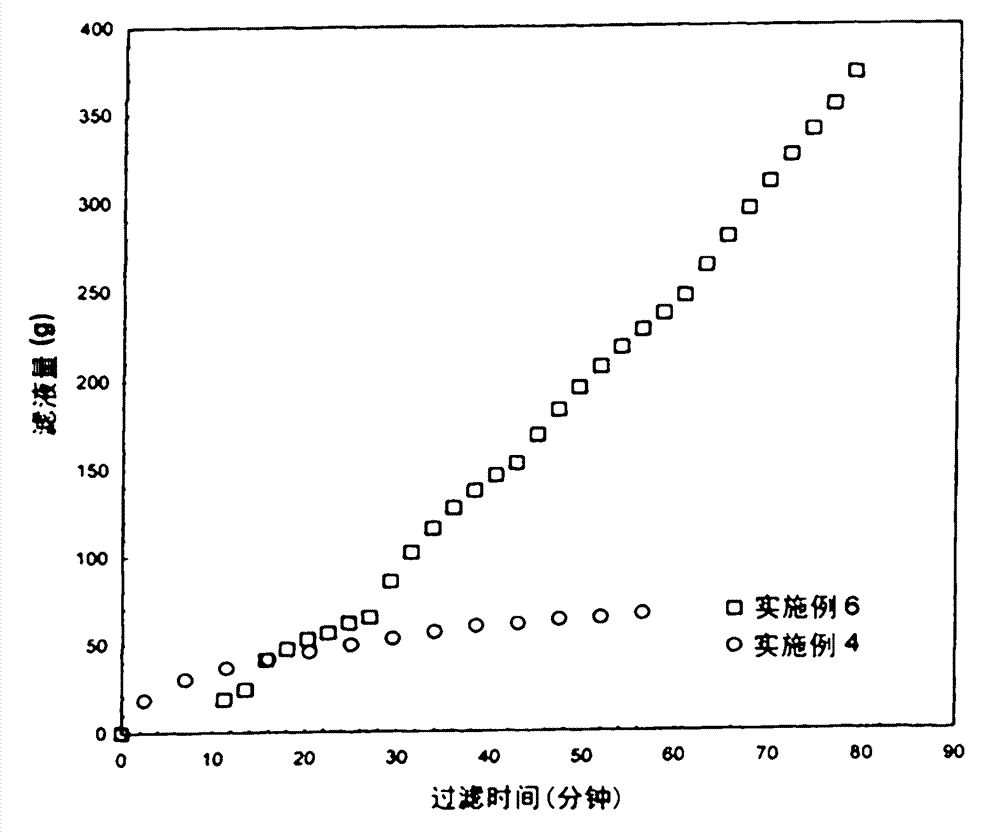
[0058] Previous data proves that when back pressure filtration is used for the same amount of active material, the necessary filtration area is much less. Back pressure filtration stabilizes the filtration, and when the pressure difference is optimized, the average activity yield is improved.
Embodiment 21-25
[0060] The solution containing factor XIII is The N66 polyamide filter was tested to detect the effect of back pressure on the effectiveness of filtration, for example based on the recovered activity and protein concentration of factor XIII in the filtrate. The area of each filter is 0.82m 2 . In Examples 21-23, no back pressure filtration was performed; the applied pressure used in these examples was 600 mbar. In Examples 24-26, the pressure difference is approximately 100 mbar. Table 6 contains the protein concentration, activity and yield before and after filtration for each experiment.
[0061] Table 6. Recovery of FXIII in the filtrate
[0062]
[0063] As shown in Table 6, by using back pressure, the activity yield and protein yield during filtration have been considerably improved.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com