Method for efficiently acquiring grape alga single cells and application thereof
A single-cell, grape algae technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of low production efficiency, large cell damage, and low cell quality, and achieve the effects of low cost, high cell activity, and low light energy utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Separation of botrytis single cell from extracellular tissue
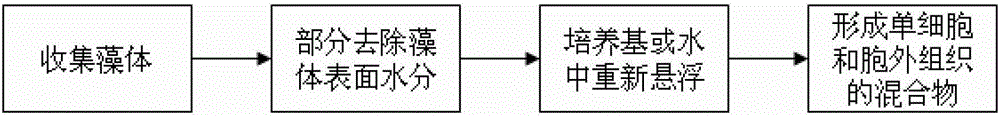
[0042] The technical scheme of this embodiment is as figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are:
[0043] The cultivated algae bodies are collected, and the surface moisture of the algae bodies is removed at 5°C, 10°C, 15°C, 20°C, 25°C, 30°C, 35°C or 40°C respectively. When the amount of algae to be treated is small, clean absorbent paper, desiccant or other water-absorbing materials can be used to remove part of the water on the surface of the algae cells; when dealing with a large number of algae, the collected algae can be placed in a ventilated and dry place Or use low-temperature drying equipment to remove part of the water on the cell surface.
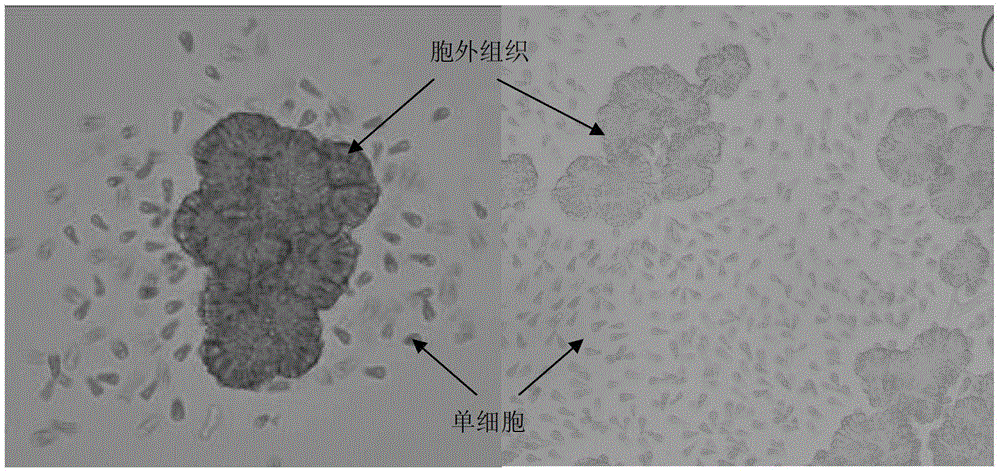
[0044] Put the treated botrytis algae into sterilized medium or distilled water, the single cell of botrytis is naturally separated from the extracellular tissue, and becomes a mixture of single cell and extracellular tissue (see figure 2 ). Among...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2 obtains sterile botrytis single cell
[0047] The technical scheme of this embodiment is as image 3 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048] 1. Collect 100ml of cultured botrytis algae with a 300-mesh sieve, and use sterilized qualitative filter paper at 25°C to remove the water on the surface of the algae cells;
[0049] 2. Take the botrytis algae whose surface has been dried, put it into a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml of BG11 medium, and let it stand for 15 minutes, during which time shake the Erlenmeyer flask more than 3 times. After 15 minutes, most of the algae cells have been separated from the colony. Under aseptic conditions, use a sterile 300-mesh sieve to remove extracellular tissue, collect the filtrate, and obtain a highly active sterile botrytis unicellular algae liquid.
[0050] The composition of BG11 medium is shown in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1BG11 medium formula
[0052]
[0053] *A 5 Composition of trace ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Obtaining Extracellular Tissue and Extracting Oil
[0058] The technical scheme of this embodiment is as Figure 4 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0059] 1. Collect the cultivated botrytis algae, and use clean and sterilized absorbent paper to remove the water on the surface of the algae cells at 20°C;
[0060] 2. Take the botrytis algae whose surface has been dried, put it into the sterilized medium for resuspension; at this time, the single cell of botrytis is separated from the extracellular tissue, and it is a mixture of single cell and extracellular tissue.
[0061] 3. Collect the botrytis extracellular tissue by filtering with a 300-mesh sieve, and freeze-dry the extracellular tissue;
[0062] 4. Take a certain amount of freeze-dried botrytis extracellular tissue and put it in a small glass bottle with a volume of 15-20ml with a Telfnon screw cap, add 5-10ml of n-hexane to ultrasonic for 10-30min, centrifuge at 3500 rpm, and collect n-h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com