Method, device and system for assigning IP (Internet Protocol) address in wireless LAN (Local Area Network)
A wireless local area network, IP address technology, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve the problems of DHCP flooding attacks, legitimate terminals cannot obtain IP addresses normally, and legitimate terminals cannot access the Internet, etc., so as to reduce malicious consumption and avoid flooding attacks. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
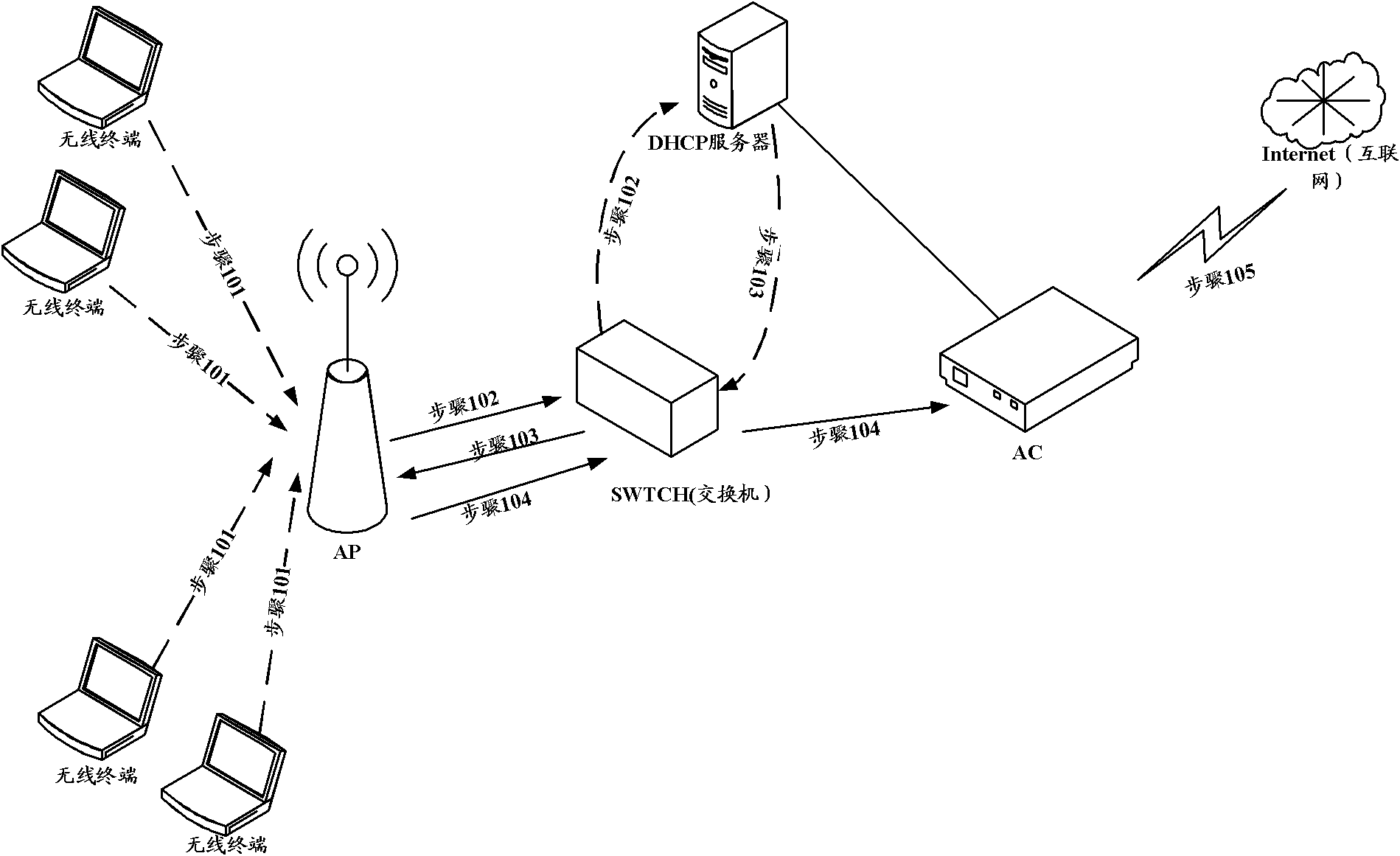
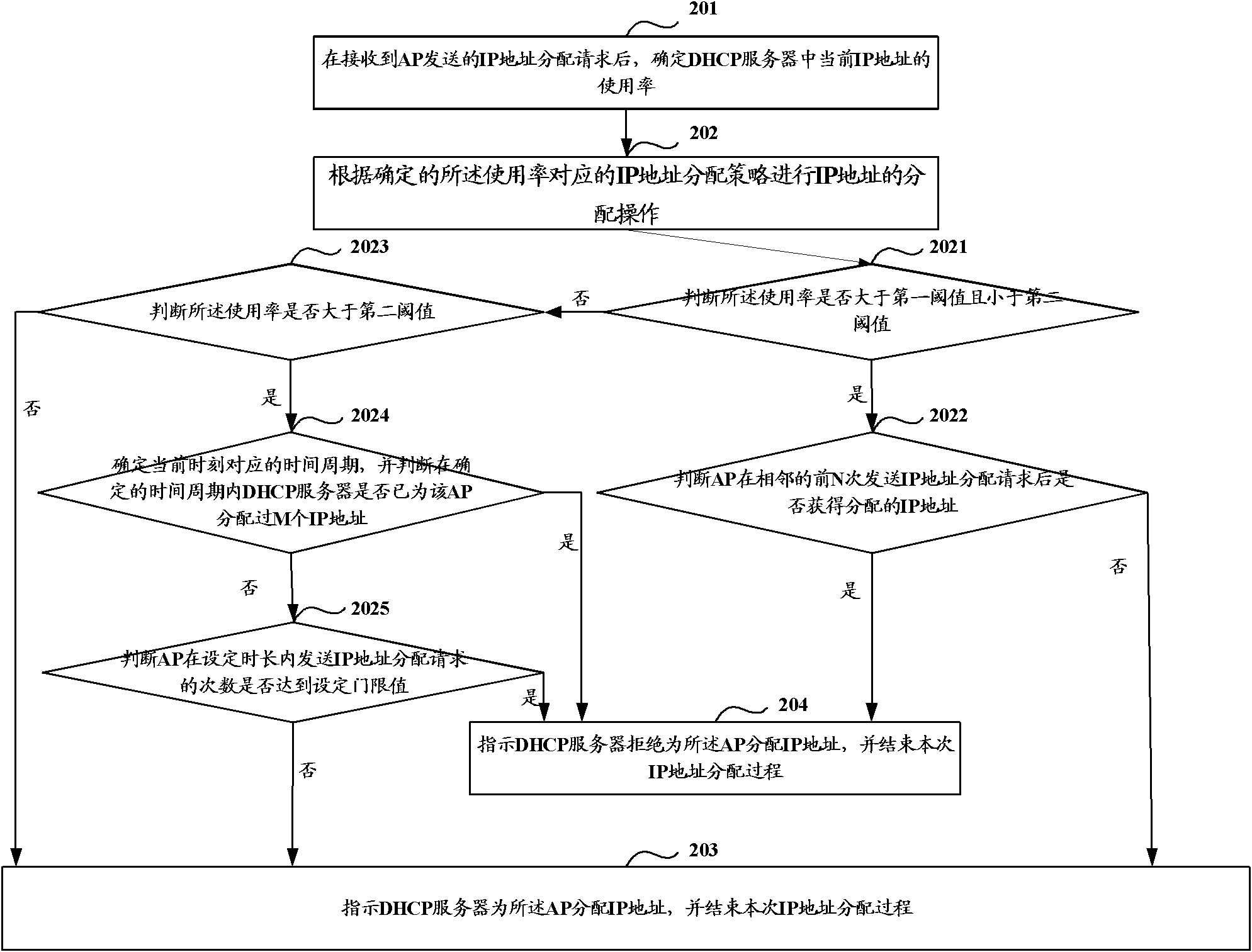
[0034] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for assigning an IP address in a wireless local area network in Embodiment 1, and the method includes:
[0035] Step 201: After receiving the IP address allocation request sent by the AP, determine the usage rate of the current IP address in the DHCP server.
[0036] In order to ensure that the available IP addresses in the IP resource pool of the DHCP server are not consumed by malicious terminals, when receiving the IP address allocation request sent by the AP, the usage rate of the current IP address in the DHCP server (that is, the number of IP addresses already allocated to the AP) is judged. The ratio of the total number of IP addresses in the IP resource pool of the DHCP server) to indicate the number of remaining available IP addresses in the current DHCP server, and provide a basis for whether to adopt a strict IP address allocation strategy.
[0037] In this step 201, there are many ways to determine ...
Embodiment 2
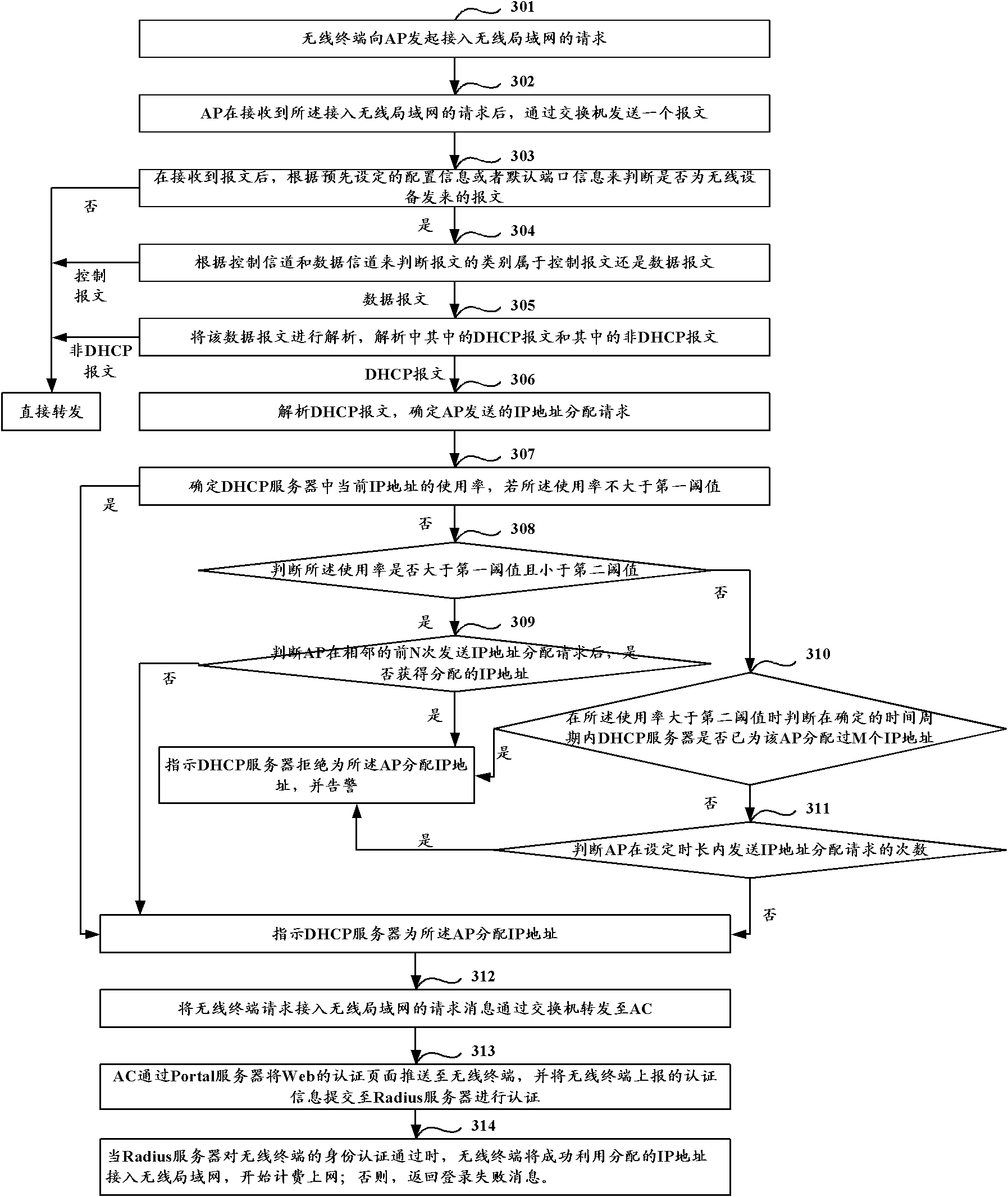
[0065] The second embodiment describes the solution of the first embodiment in detail with specific examples, as image 3 Shown is the schematic flow chart of the method of this embodiment two, and the method comprises:
[0066] Step 301: the wireless terminal initiates a request for accessing the wireless local area network to the AP.
[0067] Step 302: After receiving the request for accessing the wireless local area network, the AP sends a message through the switch, which includes an IP address assignment request.
[0068] Step 303: After receiving the message, judge whether it is a message sent by the wireless device according to the preset configuration information or default port information, and if so, perform step 304; otherwise, forward it directly.
[0069] Step 304: According to the control channel and the data channel, it is judged whether the type of the message belongs to a control message or a data message, and if it belongs to a control message, it is directl...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Such as Figure 4 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of a device for allocating IP addresses in a wireless local area network according to the third embodiment. The device includes: a receiving module 41 , a determining module 42 and an IP address allocating module 43 . in,
[0083] The receiving module 41 is used to receive the IP address allocation request sent by the AP; the determination module 42 is used to determine the utilization rate of the current IP address in the DHCP server; the IP address allocation module 43 is used to determine the corresponding IP address according to the determined utilization rate. The address allocation policy allocates IP addresses.
[0084]Specifically, the IP address assignment module 43 includes: a usage ratio judging submodule 44 , a first time number judging submodule 45 and an IP address assignment submodule 46 .
[0085] Utilization rate judging submodule 44, for judging whether the utilization rate of the curre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com