Method for controlling focus rotation by utilizing orthogonal polarized beam
A technology of beam control and orthogonal lines, applied in the field of applied optics, can solve problems such as large size, unfavorable super-resolution microscopic imaging, elliptical spot rotation angle error, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing applicability and usability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
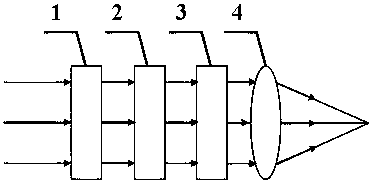
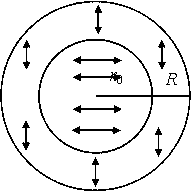
[0018] Based on a single objective lens focusing optical system, when linearly polarized light is focused by a high numerical aperture objective lens, the larger the numerical aperture of the objective lens, the greater the influence of the vector characteristics of the light wave on the light intensity distribution in the focal area, so the focused spot becomes an ellipse In the past, the rotation of the elliptical spot can only be achieved by artificially rotating the half-wave plate. The present invention adopts an orthogonal linearly polarized beam as the incident light, wherein the beam is divided into two parts, one part is the inner ring beam, and the other part is the outer ring beam. Beams, the inner and outer ring beams are concentrically distributed, and the polarization direction of the inner ring linearly polarized light is perpendicular to the polarization direction of the outer ring linearly polarized light. Ring radius, the elliptical focal point rotates around ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap